Summary
Low temperature ashing by excited gas (LTA) causes crystallographic and paramagnetic alterations of the human bone and tooth enamel mineral.
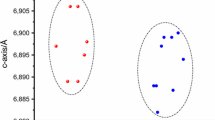
On the one hand, LTA induces variations of thea lattice parameter. These variations depend upon the nature of the gas used, but are little affected by its degree of excitation. Trapping of gas molecules in the crystal structure is demonstrated. On the other hand, LTA produces two preponderant paramagnetic centers in bone and enamel samples at 20°C. Their inorganic origin is clearly indicated. One of the two radicals has been identified as O3 − (g1=2.002, g2=2.010, g3=2.016) and the other as CO 3−3 (g‖=1.996, g⊥=2.003).
Variations of thea lattice parameter and trapping of paramagnetic gas species do not seem to be directly related.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berkley, C., Chung, J., Selikoff, I.J., Smith, W.E.: The detection and localization of mineral fibers in tissue. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci.132, 48–63 (1965)
Boivin, G., Tochon-Danguy, H.J.: Etude chez le rat d'une calcinose cutanée induite par calciphylaxie locale. II—Aspects biophysiques de la substance minérale. Ann. Biol. anim. Biochim. Biophys.16, 755–764 (1976)
Bonel, G.: Contribution à l'étude de la carbonatation des apatites. I. Synthèse et étude des propriétés physico-chimiques des apatites carbonatées de type A. Ann. de Chimie7, 65–88 (1972a)
Bonel, G.: Contribution à l'étude de la carbonatation des apatites. II. Synthèse et étude des propriétés physico-chimiques des apatites carbonatées de type B. III. Synthèse et étude des propriétés physico-chimiques d'apatites carbonatées dans deux types de sites. Evolution des spectres infrarouge en fonction de la composition des apatites. Ann. de Chimie7, 127–144 (1972b)
Cevc, P., Schara, M., Ravnik, C.: Electron paramagnetic resonance study of irradiated tooth enamel. Radiat. Res.51, 581–589 (1972)
De Siebenthal, J.M.: Etude expérimentale des centres paramagnétiques dus à la présence d'oxygène, de soufre et d'azote dans les monocristaux de chlorure de strontium. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Geneva, 1977
Doberenz, A.R., Wyckoff, R.W.G.: The microstructure of fossil teeth. J. Ultrastruct. Res.18, 166–175 (1967)
Dupré La Tour, F., Boudjicanian, K.: Procédé simplifié de minéralisation des tissus à basse température. Ann. Biol. clin.28, 303–307 (1970)
Eanes, E.D., Gillessen, I.H., Posner, A.S.: Intermediate states in the precipitation of hydroxyapatite. Nature208, 365–367 (1965)
Frazier, P.D., Brown, F.J., Rose, L.S., Fowler, B.O.: Radio frequency oxygen excitation apparatus for low-temperature ashing. J. Dent. Res.46, 1098–1101 (1967)
Gleit, C.E.: Electronic apparatus for ashing biologic specimens. Am. J. med. Electronics2, 112–118 (1963)
Gleit, C.E., Holland, W.D.: Use of electrically excited oxygen for the low temperature decomposition of organic substances. Anal. Chem.34, 1454–1457 (1962)
Kato, Y., Ogura, H.: Low-temperature ashing of bovine dentine. Calcif. Tiss. Res.18, 141–148 (1975)
Mikheikin, I.D., Zhidomirov, G.M., Chuvylkin, N.D., Kazanskii, V.B.: Parameters of the ESR spectra and structure of O3 − radicals. J. Structural Chem.15, 678–681 (1974)
Miller, A.L., Schraer, H.: Ultrastructural observations of amorphous bone mineral in avian bone. Calcif. Tiss. Res.18, 311–324 (1975)
Montel, G.: Conceptions actuelles sur la structure et la constitution des apatites synthétiques comparables aux apatites biologiques. Colloques internationaux C.N.R.S. No 230, Paris (1973)
Rey, C.: Etude physico-chimique, et en particulier par R.P.E., des apatites oxygénées. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Toulouse, 1972
Sanui, H.: Activated oxygen ashing of biological specimens for the microdetermination of Na, K, Mg, and Ca by atomic absorption spectrophotometry. Anal. Biochem.42, 21–28 (1971)
Schlick, S.: Identification of the O3 − radical ion in X-irradiated KClO3. Chem. Phys. Let.4, 421–422 (1969)
Serway, R.A., Marshall, S.A.: Electron spin resonance absorption spectra of CO3 − and CO 3−3 molecule-ions in irradiated singlecrystal calcite. J. Chem. Phys.46, 1949–1952 (1967)
Termine, J.D., Eanes, E.D., Greenfield, D.J., Nylen, M.U., Harper, R.A.: Hydrazine-deproteinated bone mineral. Calcif. Tiss. Res.12, 73–90 (1973)
Thomas, R.S.: Ultrastructural localization of mineral matter in bacterial spores by microincineration. J. Cell Biol.23, 113–133 (1964)
Thomas, R.S., Greenawalt, J.W.: Microincineration, electron microscopy, and electron diffraction of calcium phosphate loaded mitochondria. J. Cell Biol.39, 55–76 (1968)
Trombe, J.C.: Contribution à l'étude de la décomposition et de la réactivité de certaines apatites hydroxylées et carbonatées. Ann. de Chimie8, 251–269 (1973a)
Trombe, J.C.: Mise en évidence d'oxygène à différents degrés d'oxydation dans le réseau des apatites phosphocalciques et phosphostrontiques. Ann. de Chimie8, 335–347 (1973b)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tochon-Danguy, H.J., Very, J.M., Geoffroy, M. et al. Paramagnetic and crystallographic effects of low temperature ashing on human bone and tooth enamel. Calc. Tis Res. 25, 99–104 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02010757
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02010757