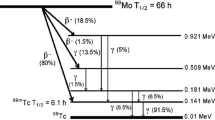
Summary
During a number of years at Vilnius the sounding of clouds has been carried out from airplanes in order to study the contents of radioactive materials accumulated in cumuli. Two methods for taking samples have been used: 1) the collection on cooled surfaces and 2) using the method of filter paper covered with erythrosin and kept in a special collector within the Venturi tube. In the first case radioactivity has been measured with the help of Geiger-Müller counter and in the second by means of nuclear photo emulsion (sensitive to α-particles) which was brought into contact with the filter paper moistened in the cloud. This method has made it possible: 1) to measure radioactivity in local zones of a cloud, 2) to measure radioactivity of separate big drops and 3) to study the composition of α-radioactivity contained in cloud particles.
The magnitude of specific radioactivity of cloud elements appears to be of the same order with the rain drops and at times even greater than that of the rain samples.
There exist two types of the distribution of radioactivity in a cumulus according to the height: 1) an increase of radioactivity from the bottom to maximum at the height of 0.6 part of the cloud's thickness and 2) two maxima of radioactivity at the bottom and in the centre. The latter phenomenon is characteristic of thick cumuli where big radioactive drops apparently fall out from the centre. The distribution of radioactivity at different heights correlates well with cloud's liquid-water.
In a cumulus there takes a place a process of accumulation of radioactive aerosol with the accumulation coefficient of 1000. This circumstance points to a very important part played by clouds as accumulators of radioactive materials from the air which continuously filters itself through them. And just by this is expressed one of the properties of clouds as purifiers of the atmosphere from radioactive aerosol, for, as theoretical calculations indicate, the ability of drops to absorbe radioactive aerosol diminishes with the process of cloud droplets growing to the size of rain drops.
The composition of radioactive materials in cloud elements is very complex. In drogs there appear nearly all the natural radioactive elements (emitting α-particles) which exist in the earth's crust.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Styra B. J.:Fragen der Kernmeteorologie. Vilnius, 1–418, 1959.
Styra B. J.:Zur Theorie der Radioaktivitätsgewinnung der Niederschlagsteilchen in der Luft. Moksliniai praneŝimai, Lietuvos TSR Mokslu Akademija, Geol. ir geogr. inst., Bd 3, 31–44 (1956).
Styra B. J. &Garbaliauskas C. A.:Zur Frage der Aktivitätsmessung einzelnen Regentropfen, Lietuvos TSR Mokslu Akademijos darbai, serija B, 2, 21 (1955).
Pocius W. J.:Methodik zur Messung der Radioaktivität der Wolkenelemente durch α-radiographische Methode. Moksliniai pranešimai, Lietuvos TSR Mokslu Akademija, Geol. ir geogr. inst., B. 10 Hf. 1, 63–79 (1959).
Pocius W. J.:Die Quantitative Messung der Radioaktivität der Wolkenelemente. Moksliniai pranesimai, Lietuvos TSR Mokslu Akademija, Geol. ir geogr. inst., B. 11, 48–72, (1960).
Pocius W. J.:Über die Verteilung der Radioaktivität in Wolkenelementen der Höhe nach. Moksliniai pranešimai, Lietuvos TSR Mokslu Akademija, Geol. ir geogr. inst., B. 11, 73–82 (1960).
Pocius W. J. &Nedveckaite T. N.:Über die Entfernung der Ablagerungen in den zur Erforschung der Radioaktivität der Atmosphäre angewandten Kernemulsionen. Moksliniai pranešimai, Lietuvos TSR Mokslu Akademija, Geol. ir geogr. inst., B. 11, 42–48, (1960).
Baranov W. J.:Radiometrie. Akademija Nauk SSSR, 1–343, 1955.
Styra B. J. & Garbaliauskas C. A.:Zur Frage der quantitativen radioagraphischen Analyse der Radioaktivität der atmosphärischen Luft. Lietuvos TSR Mokslu Akademijos darbai, ser. B, 3–55 (1958).
Styra B. J.:Über die Aktivierung negativ beladenen Tropfen in der Wolken. Lietuvos TSR Mokslu Akademijos darbai, ser. B, 2, 21 (1956).
Styra B. J.:Über die Aktivierung der unbeladenen Tropfen. Lietuvos TSR Mokslu Akademijos darbai, ser B, 3, 11, (1956).
Styra B. J.:Über die Radioaktivierung der Tropfen unter dem Einfluss der nicht elektrischen Kräfte. Lietuvos TSR Mokslu Akademijos darbai, ser. B, 2, 39 (1958).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Styra, B.J. Die Erforschung der Natürlichen Radioaktivität von Wolkenelementen und einige damit verbundene Probleme. Geofisica Pura e Applicata 50, 249–259 (1961). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02000652
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02000652