Abstract
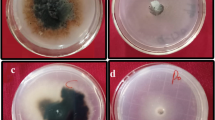
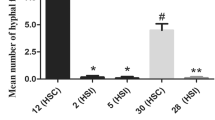
The pathogenicity and vegetative compatibility of mainly Dutch isolates ofFusarium oxysporum collected from diseased gladioli and other Iridaceae were investigated. Based on their pathogenicity to two differential gladiolus cultivars, the isolates could tentatively be divided into two races. All self-compatible isolates ofFusarium oxysporum f.sp.gladioli belonged to one of three distinct vegetative compatibility groups, VCG 0340, 0341 or 0342, and were incompatible with isolates that were not pathogenic to gladiolus. Isolates of one of the two races were restricted to one VCG while isolates of the other race were present in all three VCGs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armstrong, G.M. & Armstrong J.K., 1966. Races ofFusarium oxysporum f.conglutinans; race 4, new race; and a new host for race 1,Lychnis chalcedonica. Phytopathology 56:525–530.
Armstrong, G.M. & Armstrong, J.K., 1981. Formae speciales and races ofFusarium oxysporum causing wilt diseases. In: P.E. Nelson, T.A. Toussoun & R.J. Cook (Eds),Fusarium: diseases, biology, and taxonomy. Pennsylvania State University Press, pp. 391–399.
Baayen, R.P. & Kleijn, J., 1989. The Elegans fusaria causing wilt of carnation. II. Distinction of vegetative compatibility groups. Netherlands Journal of Plant Pathology 95:185–194.
Bald, J.G., Suzuki, T. & Doyle, A., 1971. Pathogenicity ofFusarium oxysporum to Easter lily,Narcissus andGladiolus. Annals of Applied Biology 67:331–342.
Boerema, G.H. & Hamers, M.E.C., 1989. Check-list for scientific names of common parasitic fungi. Series 3b: Fungi on bulbs: Amaryllidaceae and Iridaceae. Netherlands Journal of Plant Pathology 95, Suppl. 3: 1–32.
Bosland, P.W. & Williams, P.H., 1987. An evaluation ofFusarium oxysporum from crucifers based on pathogenicity, isozyme polymorphism, vegetative compatibility, and geographic origin. Canadian Journal of Botany 65:2067–2073.
Buxton, E.W., 1954, Heterokaryosis and variability inFusarium oxysporum f.gladioli (Snyder & Hansen). Journal of General Microbiology 10:71–84.
Buxton, E.W., 1956. Heterokaryosis and parasexual recombination in pathogenic strains ofFusarium oxysporum. Journal of General Microbiology 15:133–139.
Correll, J.C., Klittich, C.J.R. & Leslie J.F., 1987 Nitrate non utilizing mutants ofFusarium oxysporum and their use in vegetative compatibility tests. Phytopathology 77:1640–1645.
Correll, J.C., Puhalla, J.E. & Schneider, R.W., 1986. Identification ofFusarium oxysporum f. sp.apii on the basis of colony size, virulence and vegetative compatibility. Phytopathology 76:396–400.
Elias, K.S. & Schneider, R.W., 1991. Vegetative compatibility groups inFusarium oxysporum f. sp.lycopersici. Phytopathology 81:159–162.
Elmer, W.H. & Stephens C.T., 1989. Classification ofFusarium oxysporum f. sp.asparagi into vegetative compatible groups. Phytopathology 79:88–93.
Garibaldi, A., 1977. Race differentiation inFusarium oxysporum f. sp.dianthi and varietal susceptibility. Acta Horticulturae 71:97–101.
Jacobson, D.J. & Gordon, T.R., 1988. Vegetative compatibility and self-incompatibility withinFusarium oxysporum f.sp.melonis. Phytopathology 78:668–672.
Jacobson, D.J. & Gordon, T.R., 1990a. Further investigations of vegetative compatibility withinFusarium oxysporum f.sp. melonis. Canadian Journal of Botany 68:1245–1248.
Jacobson, D.J. & Gordon T.R., 1990b. Variability of mitochondrial DNA as an indicator of relationships between populations ofFusarium oxysporum f.sp.melonis. Mycological Research 94:734–744.
Larkin, R.P., Hopkins, D.L. & Martin, F.N., 1990. Vegetative compatibility withinFusarium oxysporum f.sp.niveum and its relation to virulence, aggressiveness, and race. Canadian Journal of Microbiology 36:352–358.
Lewis, G.J., Obermeyer, A.A. & Barnard, T.T., 1972. Gladiolus: a revision of the South African species. Edited by H.B. Rycroft. Journal of South African Botany 10: (supplement) pp. 316. Cape Town: Purnell & Sons Ltd.
Löffler, H.J.M. & Rumine, P. 1991. Virulence and vegetative compatibility of Dutch and Italian isolates ofFusarium oxysporum f.sp.lilii. Journal Phytopathology 132:12–20.
Manicom, B.Q., Bar-Joseph, M., Kotze, J.M. & Becker, M.M., 1990. A restriction fragment length polymorphism probe relating vegetative compatibility groups and pathogenicity inFusarium oxysporum f.sp.dianthi. Phytopathology 80:336–339.
Massey, L.M., 1926. Fusarium rot of gladiolus corms. Phytopathology 16:509–510.
McClellan, W.D., 1945. Pathogenicity of the vascularFusarium of gladiolus to some additional iridaceous plants. Phytopathology 35:921–930.
Nelson, P.E., Horst, R.K. & Woltz, S.S., 1981.Fusarium disease of ornamental plants. In: P.E. Nelson, T.A. Toussoun & R.J. Cook (Eds),Fusarium: disease, biology and taxonomy. Pennsylvania State University Press, pp. 121–128.
Ohri, D. & Khoshoo, T.N., 1983. Cytogenetics of garden gladiolus. IV. Origin and evolution of ornamental taxa. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of India B49 3:279–294.
Ploetz, R.C., 1990. Variability inFusarium oxysporum f.sp.Cubense. Canadian Journal of Botany 68:1357–1363.
Ploetz, R.C. & Correll, J.C., 1988. Vegetative compatibility among races ofFusarium oxysporum f.sp.cubense. Plant Disease 72:325–328.
Puhalla, J.E., 1984. A visual indicator of heterokaryosis inFusarium oxysporum from celery. Canadian Journal of Botany 62:540–545.
Puhalla, J.E., 1985. Classification of strains ofFusarium oxysporum on the basis of vegetative compatibility. Canadian Journal of Botany 63:179–183.
Puhalla, J.E. & Spieth, P.T., 1985. A comparison of heterokaryosis and vegetative incompatibility among varieties ofGibberella fujikuroi (Fusarium moniliforme). Experimental Mycology 9:39–47.
Snyder, W.C. & Hansen, H.N., 1940. The species concept inFusarium. American Journal of Botany 27:64–67.
Woltz, S.S., Magie, R.O., Switkin, C., Nelson, P.E. & Toussoun, T.A., 1978. Gladiolus disease response to prestorage corm inoculation withFusarium species. Plant Disease Reporter 62:134–137.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roebroeck, E.J.A., Mes, J.J. Physiological races and vegetative compatibility groups within Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. gladioli. Netherlands Journal of Plant Pathology 98, 57–64 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01998078
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01998078