Summary
Investigations have shown that in groundwater- and oil-bearing strata there are preferential directions of flow that are often maintained over wide areas.Johnson & Hughes (1948, see Ref.) analysed a series of oil well cores by cutting them into small horizontal plugs and they obtained directional permeabilities which they plotted in the form of polar graphs. They were not able to give a physical explanation of this phenomenon. On the other hand, there exists a theory of permeability in which the latter is represented as a symmetric tensor. This theory has been developed byFerrandon (1948, see Ref.), but no experimental substantiation of it seems ever to have been attempted.
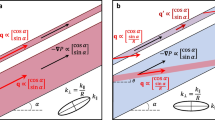
In the present paper, the author undertakes to compare the two sets of findings. FromFerrandon's theory, the directional permeabilities (denoted byk) corresponding to the experiments ofJohnson & Hughes are calculated and it is shown thatk −1/2 if plotted as polar graph, should form an ellipse. The data ofJohnson & Hughes are then are drawn. In this manner, a substantiation of the tensor theory ofFerrandon is obtained.
Zusammenfassung
Untersuchungen der Permeabilität von Grundwasser und Erdöl führenden Gesteinsschichten haben gezeigt, dass dieselbe in vielen Fällen richtungsabhängig ist. Hierbei bleibt die Richtung extremaler Permeabilität oft über weite Gebiete konstant.Johnson & Hughes untersuchten eine Reihe von Bohrkernen von Oelquellen auf Richtungsabhängigkeit der Permeabilität. Hierzu schnitten sie aus denselben kleine, waagrechte Stücke, bestimmten deren Permeabilität und stellten das Ergebnis ihrer Messungen in der Form von Permeabilitätspolardiagrammen dar. Sie waren nicht im Stande, eine theoretische Erklärung der erhaltenen Kurven zu geben. Auf der anderen Seite existiert eine Theorie der Permeabilität, wobei die letztere als symmetrischer Tensor behandelt wird. Diese Theorie wurde vonFerrandon vorgeschlagen; es scheint aber, dass keine experimentelle Bestätigung davon je versucht worden ist.
In der vorliegenden Arbeit vergleicht der Verfasser die zwei Typen von Untersuchungen. Nach derFerrandon'schen Theorie wird die «gerichtete» Permeabilität (mitk bezeichnet), die den Experimenten vonJohnson & Hughes entspricht, berechnet. Es wird gezeigt, dassk −1/2, als Polardiagramm dargestellt, die Gestalt einer Ellipse haben sollte. Die Resultate vonJohnson & Hughes werden dann in die Form vonk −1/2 umgerechnet und als entsprechende Polardiagramme dargestellt. In dieser Weise wird eine experimentelle Bestätigung der Tensortheorie vonFerrandon erhalten.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferrandon, J.:Les lois de l'écoulement de filtration, Génie civil, 125, No. 2, 24–28 (1948).
Johnson, W. E. &Breston, J. N.:Directional permeability measurements on oil sandstones from various states. Producers Monthly, 14, No. 4, 10–19 (1951).
Johnson, W. E. &Hughes, R. V.:Directional permeability measurements and their significance. Producers Monthly 13, No. 1, 17–25 (1948).
Irmay, S.:Darcy-law for non-isotropic soils. Assoc. Int. Hydrol. Sci. U.G.G.A., Assemblée Gén. Bruxelles, 2, 179–183 (1951).
Litwiniszyn, J.:Stationary flows in heterogeneously anisotropic media. Ann. Soc. Pol. Math., 22, 185–99 (1950).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Published by Permission of Imperial Oil Limited, Calgary, Alberta (Canada).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scheidegger, A.E. Directional permeability of porous media to homogeneous fluids. Geofisica Pura e Applicata 28, 75–90 (1954). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01992394
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01992394