Abstract
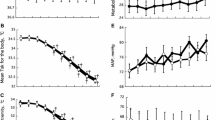
Using a non-invasive laser Doppler velocimetry technique to measure skin blood flow in the rat skin, we have shown that chronic treatment with capsaicin inhibited the vasodilator response to a non-pathological, local heat (44°C, 20 min duration) stimulus. However, sympathectomy, accomplished with chronic treatment of guanethidine, had no effect on this heat-induced vasodilation. Topical steroids have also been shown to inhibit this response thus, since the heat-dilator response appears from these results to be brought about by the release of sensory neuropeptides, the sensory neuron may be a target for topical steroid action.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. W. Mckenzie and R. B. Stoughton,Method for comparing percutaneous absorption of steroids. J. Invest. Dermatol.86, 608–610 (1962).
B. W. Barry and R. Woodford,Vasoconstrictor activities and bioavailabilities of seven proprietary corticosteroid creams assessed using a non-occluded multiple dosage regimen: Clinical implications, Br. J. Dermatol97, 555–560 (1977).
A. Ahluwalia and R. J. Flower,Betamethasone inhibits heat-induced vasodilation in the rat skin. Fund. Clin. Pharmacol.5, 419 (1991).
A. Ahluwalia and R. J. Flower,Steroid inhibition of oedema formation in the rat skin. Br. J. Pharmac.106, 628–631 (1992).
A. Saria,Substance P in sensory nerve fibres contributes to the development of oedema in the rat hind paw after thermal injury. Br. J. Pharmac.82, 217–222 (1984).
T. J. Coderre, A. I. Basbaum and J. D. Levine,Neural control of vascular permeability: Interactions between primary afferents, mast cells and sympathetic efferents. J. Neurophysiol.62, 48–58 (1989).
A. Raychaudhuri, C. Colombo, G. Pastor, M. Wong and A. Y. Jeng,Effect of capsaicin on carrageenan-induced inflammation in rat pleurisy and exudate substance P level. Agents and Actions34, 251–253 (1991).
J. Donnerer, R. Amann and F. Lembeck,Neurogenic and non-neurogenic inflammation in the rat paw following chemical sympathectomy. Neurosci.45, 761–765 (1991).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahluwalia, A., Flower, R.J. Effect of chronic capsaicin and guanethidine treatment on skin blood flow of the rat. Agents and Actions 38 (Suppl 2), C16–C18 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01991123
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01991123