Abstract
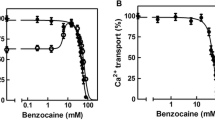
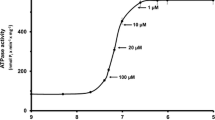
The excitation-contraction (E-C) coupling process in single twitch fibres from frog toe muscle was inhibited selectively by phenylglyoxal (PGO), a specific guanidyl modifying reagent. A new protein (31.5 kDa), which has PGO-binding ability and seems to play a key role in the E-C coupling process, was solubilized from transverse tubule membrane-junctional sarcoplasmic reticulum complexes (TTM-JSR) of frog skeletal muscles, using14C-PGO. The monoclonal antibody against this protein applied extracellularly inhibited the E-C coupling process of the single fibres. This protein appears to constitute the very first step of input for E-C coupling. It is considered to behave as an indispensable part of an ‘electrometer’ to measure membrane potentials. Therefore, the name ‘electrometrin’ is suggested for the new protein.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature
Fujino, M., Sato, Y., Arima, T., and Takai, H., J. physiol. Soc. Japan45 (1983) 507.
Fujino, M., Sato, Y., Arima, T., and Takai, H., J. physiol. Soc. Japan46 (1984) 469.
Takahashi, K., J. biol. Chem.243 (1968) 6171.
Fujino, S., and Fujino, M., Can. J. Physiol. Pharmac.60 (1982) 542.
Fujino, S., Satoh, K., Bando, T., Kurokawa, T., Nakai, T., Takashima, K., and Fujino, M., Experientia45 (1989) 466.
Brunschwic, J. P., Brandt, N., Caswell, A. H., and Lukeman, D. S., J. Cell Biol.93 (1982) 533.
Laemmli, U. K., Nature227 (1970) 680.
Wood, J. G., and Sarinana, F. O., Analyt. Biochem.69 (1975) 320.
Mayol, R. F., and Thayer, S. A., Biochemistry9 (1970) 2484.
Köhler, G., and Milstein, C., Eur. J. Immun.6 (1976) 511.
Tijssen, P., Practice and Theory of Enzyme Immunoassays. Elsevier Science Publishers, Amsterdam 1985.
Fujino, M., Arima, T., Yamada, C., Harano, K., Takahashi, M., Goto, M., and Seno-o, M., Proc. Int. Union Physiol. Sci.XVII (1989) 186.
Fujino, M., Arima, T., Sato, Y., Shinohara, K., Harano, K., and Tokunaga, K., J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil.8 (1987) 282.
Fujino, M., Arima, T., Harano, K., Goto, M., Seno-o, M., and Shimada, N., J. physiol. Soc. Japan50 (1988) 525.
Fujino, M., Satellite Symposium (Hakone) for muscle contraction at the XXIII Int. Congress of Physiol. Sci., Tokyo 1965.
Leung, A. T., Imagawa, T., and Campbell, K. P., J. biol. Chem.262 (1987) 7943.
Catterall, W. A., Science242 (1988) 50.
Jay, S. D., Ellis, S. B., McCue, A. F., Williams, M. E., Vedvick, T. S., Harpold, M. M., and Campbell, K. P., Science248 (1990) 490.
Tanabe, T., Takeshima, H., Mikami, A., Flockerzi, V., Takahashi, H., Kangawa, K., Kojima, M., Matsuo, H., Hirose, T., and Numa, S., Nature328 (1987) 313.
Rios, E., and Brum, G., Nature325 (1987) 717.
Leung, A. T., Imagawa, T., Block, B. A., Franzini-Armstrong, C., and Campbell, K. P., J. biol. Chem.263 (1988) 994.
Block, B. A., Imagawa, T., Campbell, K. P., and Franzini-Armstrong, C., J. Cell Biol.107 (1988) 2587.
Borsotto, M., Barhanin, J., Fosset, M., and Lazdunski, M., J. biol. Chem.260 (1985) 14255.
Kawamoto, R. M., Brunschwig, J.-P., Kim, K. C., and Caswell, A. H., J. Cell Biol.103 (1986) 1405.
Lai, F. A., Erickson, H. P., Rousseau, E., Liu, Q. Y., and Meissner, G., Nature331 (1988) 315.
Fujino, S., Fujino, M., Satoh, K., Nakai, T., et al, 3rd Int. Symp. on Excitation-Contraction Coupling in Skeletal, Cardiac and Smooth Muscle. Banff, Alberta, Canada, June 26–30, 1991. Abstract P9.
Fujino, S., Fujino, M., Satoh, K., and Nakai, T., Jap. J. Pharmac.55 Suppl. 2 (1991) 154P.
Arima, T., Hasegawa, C., Harano, K., and Fujino, M., Jap. J. Physiol.41 Suppl. (1991) S 286.
Schneider, M. F., and Chandler, W. K., Nature270 (1973) 746.
Etter, E. F., J. Physiol., Lond.421 (1990) 441.
Cullen, M. J., Hollingworth, S., Marshall, M. W., and Robson, E., J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil.11 (1990) 167.
Towbin, H., Staehelin, T., and Gordon, J., Proc. natl Acad. Sci. USA76 (1979) 4350.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fujino, S., Satoh, K., Nakai, T. et al. Studies of a key protein in the mechanism of the excitation-contraction coupling process of frog skeletal muscle, using phenylglyoxal. Experientia 49, 138–144 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01989418
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01989418