Abstract
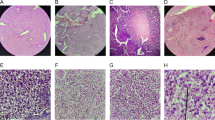
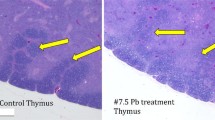
The effect of exposing White Leghorn hens for six weeks to 50 ppm of Aroclor 1254 in water was investigated. While egg production decreased temporarily, no significant effects were noted on egg weights or fertility. Incubation of eggs from exposed hens indicated that this polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB) did not interfere with gametogenesis and fertilization. As Aroclor 1254 accumulated in the yolk, however, embryonic development was arrested at progressively earlier developmental stages. When PCB was removed from the water there was an initial rapid decline in the PCB content of the yolk and a slow return of the normal developmental pattern of the embryo. Leg, toe, and neck deformities were present in many of the chicks hatched from eggs in which yolk PCB level was 10–15 ppm or more. The gross appearance of the liver and the presence of hemorrhages suggest that the liver and the vascular elements may be targets for PCB action.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, D. W., J. J. Hickey, R. W. Risebrough, D. F. Hughes, and R. E. Christensen: Significance of chlorinated hydrocarbon residues to breeding pelicans and cormorants. Can. Field-Naturalist83, 91 (1969).
Bagley, G. E., W. L. Reichel, and E. Cromartie: Identification of polychlorinated biphenyls in two bald eagles by combined gas-liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Assoc. Offic. Anal. Chem.53, 251 (1970).
Bailey, S., and P. J. Bunyan: Interpretation of persistence and effects of polychlorinated biphenyls in birds. Nature236, 34 (1972).
Berlin, M.: PCB effects on mammals. National Swedish Environ. Protection Board 43-50 PCB Conf., Sept. 29, 1970, Solna, Sweden.
Bush, B., and R. Dell'Acqua: Personal communication (1972).
Bush, B., and F. C. Lo: Thin-layer chromatography for quantitative polychlorinated biphenyl analysis. J. Chromatog.7, 377 (1973).
Cecil, H. C., J. Bitman, G. F. Fries, L. W. Smith, and R. J. Lillie: PCBs in laying hens. Personal communication (1972).
Dahlgren, R. B., Y. A. Greichus, and R. L. Linder: Storage and excretion of polychlorinated biphenyls in the pheasant. J. Wildlife Management35, 823 (1971).
Dahlgren, R. B., and R. L. Linder: Effects of polychlorinated biphenyls on pheasant reproduction, behavior, and survival. J. Wildlife Management35, 315 (1971).
Fishbein, L.: Chromatographic and biological aspects of polychlorinated biphenyls. J. Chromatog.68, 345 (1972).
Flick, D. F., R. G. O'Dell, and V. A. Childs: Studies of the chick edema disease. 3. Similarity of symptoms produced by feeding chlorinated biphenyls. Poultry Sci.44, 1460 (1965).
Grant, D. L., D. C. Villeneuve, K. Khera, D. J. Clegg, and W. E. J. Phillips: Studies on the embryotoxicity and placental transfer of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs). Proc. Can. Fed. Biol. Soc.14, 52 (1971).
Hays, H., and R. W. Risebrough: Pollutant concentrations in abnormal young terns from Long Island Sound. The Auk89, 19 (1972).
Koeman, J. H., M. C. Ten Noever de Braun, and R. H. De Vos: Chlorinated biphenyls in fish, mussels, and birds from the River Rhine and the Netherlands coastal area. Nature221, 1126 (1969).
Kuratsune, M., T. Yoshimura, J. Matsuzaka, and Y. Yamaguchi: Yusho, a poisoning caused by rice oil contaminated with polychlorinated biphenyls. HSMHA (Health Serv. Ment. Health Admin.) Health Rept.86, 1083 (1971).
McCune, E. L., J. E. Savage, and B. L. O'Dell: Hydropericardium and ascites in chicks fed a chlorinated hydrocarbon. Poulty Sci.41, 295 (1962).
McLaughlin, J., Jr., J. P. Marliac, M. J. Verrett, M. K. Mutchler, and O. G. Fitzhugh: The injection of chemicals into the yolk sac of fertile eggs prior to incubation as a toxicology test. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol.5, 760 (1963).
Pardini, R. S.: Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCB): Effect on mitochondrial enzyme system. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol.6, 539 (1971).
Peakall, D. B.: Effect of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) on the eggshells of ringdoves. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol.6, 100 (1971).
Peakall, D. B., and J. L. Lincer: Polychlorinated biphenyls. Another long-life, widespread chemical in the environment. Bioscience20, 958 (1970).
Peakall, D. B., J. L. Lincer, and S. E. Bloom: Embryonic mortality and chromosomal alterations caused by Aroclor 1254 in ringdoves. (1972) in press.
Platonow, N. S., and H. S. Funnell: Anti-androgenic-like effect of polychlorinated biphenyls in cockerels. Vet. Record88, 109 (1971).
Platonow, N. S., and H. S. Funnell: The distribution and some effects of polychlorinated biphenyls (Aroclor 1254) in cockerels during prolonged feeding trial. Can. J. Comp. Med.36, 89 (1972).
Rehfeld, B. M., R. L. Bradley, Jr., and M. L. Sunde: Toxicity studies on polychlorinated biphenyls in the chick. 1. Toxicity and symptoms. Poultry Sci.50, 1090 (1971).
Rehfeld, B. M., R. L. Bradley, Jr., and M. L. Sunde: Toxicity studies on polychlorinated biphenyls in the chick. 2. Biochemical effects and accumulations. Poultry Sci.51, 448 (1972).
Reynolds, L. M.: Polychlorobiphenyls (PCBs) and their interference with pesticide residue analysis. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol.4, 128 (1969).
Richardson, A., J. Robinson, A. N. Crabtree, and M. K. Baldwin: Residues of polychlorobiphenyls in biological samples. Pesticide Monit. J.4, 169 (1971).
Risebrough, R. W., P. Rieche, S. G. Herman, D. B. Peakall, and M. N. Kirven: Polychlorinated biphenyls in the global ecosystem. Nature220, 1098 (1968).
Scott, M. L., D. V. Vadchra, P. A. Mullenhoff, G. L. Rumsey, and R. W. Rice: Results of experiments on the effects of PCBs on laying hen performance. Proc. 1971 Cornell Nutrition Conf., Nov. 1971, p. 56.
Vos, J. G., and R. B. Beems: Dermal toxicity studies of technical polychlorinated biphenyls and fractions thereof in rabbits. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol.19, 617 (1971).
Vos, J. G., and J. H. Koeman: Comparative toxicologic study with polychlorinated biphenyls in chickens with special reference to porphyria, edema formation, liver necrosis, and tissue residues. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol.17, 656 (1970).
Vos, J. G., J. J. T. W. A. Strik, C. W. M. Van Holsteÿn, and J. H. Pennings: Polychlorinated biphenyls as inducers of hepatic porphyria in Japanese quail, with special reference toδ-aminolevulinic acid synthetase activity, fluorescence, and residues in the liver. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol.20, 232 (1971).
Zitko, V., and P. M. K. Choi: PCB and p, p′-DDE in eggs of cormorants, gulls, and ducks from the Bay of Fundy, Canada. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol.7, 63 (1972).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tumasonis, C.F., Bush, B. & Baker, F.D. PCB levels in egg yolks associated with embryonic mortality and deformity of hatched chicks. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1, 312–324 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01985433
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01985433