Abstract
Conventional and saturation transfer electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy (EPR and ST EPR) and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) were used to study the motional dynamics and segmental flexibility of cardiac myosins.
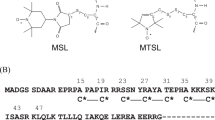
Cardiac myosins isolated from bovine and human heart muscle were spin-labelled with isothiocyanate- or maleimide-based probe molecules at the reactive sulfhydryl sites (Cys-697 and Cys-707) of the motor domain. The maleimide probe molecules attached to human cardiac myosin rotated with an effective rotational correlation time of 33 ns which was at least eight times shorter than the rotational correlation time of the same label on skeletal myosin (260 ns). In the presence of MgADP and MgADP plus orthovanadate, flexibility changes in the multisubunit structure of myosins were detected, but this did not lead to changes of the overall rotational property of the myosin heads. Significant difference in the internal flexibility was detected on myosin samples isolated from ischemic tissue, the rotational correlation time decreased to 25 ns.
DSC measurements supported the view that addition of nucleotides produced additional loosening in the multisubunit structure of cardiac myosin. It is postulated that there is an intersite communication between the nucleotide binding domain and the 20 kDa subunit where the reactive thiol sites are located.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. E. Huxley, Science, 202 (1969) 1356.
B. Brenner, Muscle mechanics and biochemical kinetics, in Molecular mechanism in muscular contraction (Squire, J. ed.) Mcmillan Press, London 1990, pp. 77.
M. Tada, G. Bailin and K. Bárány, Biochemistry, 8 (1969) 4842.
W. M. Kuehl, R. S. Adelstein, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 39 (1970) 956.
N. Bálint, F. A. Sréter and J. Gergely, Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 168 (1975) 557.
H. A. Katus, K. W. Diederich, M. Uellner, A. Remppis, G. Schuler and W. Kübler, Cardiovascular Res., 22 (1988) 456.
R. Nagai, C. C. Chiu, K. Yamaoki, Y. Ohuchi, S. Ueda, K. Imataka and Y. Yazaki, Am. J. Physiol., 245 (1983) 413.
M. Kaneko, H. Masuda, H. Suzuki, Y. Matsumoto, A. Kobayashi, N. Jamuzaki, Mol. Cell. Biochem., 125 (1993) 163.
U. Hoffmann and J. Belágyi, Hoppe-Seyler's Z. Physiol. Chem., 372 (1991) 679.
K. T. Shiverick, L. L. Thomas and N. R. Alpert, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 393 (1975) 124.
P. Bouvagnet, J. O. C. Léger, C. Dechesne, J. J. Léger, Circ. Res., 55 (1984) 794.
O. H. Lowry, N. J. Rosebrough, A. L. Farr and P. J. Randall, J. Biol. Chem., 193 (1951) 265.
P. Graceffa and J. C. Seidel, Biochemistry, 19 (1980) 33.
P. Fajer and D. Marsh, J. Mag. Res., 49 (1982) 212.
D. Raucher, C. P. Sar, K. Hideg and P. Fajer, Biochemistry, 33 (1994) 14317.
M. C. Schaub, J. G. Watterson and P. G. Waser, Hoppe-Seyler's Z. Physiol. Chem., 356 (1975) 325.
M. S. Crowder and R. Cooke, J. Mus. Res. Cell Motil., 5 (1984) 131.
D. D. Thomas, S. Ishivata, J. C. Seidel and J. Gergely, Biophys. J., 32 (1980) 873.
J. Belágyi, I. Frey and L. Pótó, Eur. J. Biochem., 224 (1994) 215.
S. A. Goldman, G. V. Bruno and J. H. Freed, J. Phys. Chem., 76 (1972) 1858.
J. Belágyi and E. Róth, Gen. Physiol. Biophys., 6 (1987) 571.
D. B. Stone, R. A. Mendelson, J. Botts and P. H. Cheung, Circ. Res., 49 (1981) 677.
I. Rayment, W. R. Rypniewski, K. Schmidt-Bäse, R. Smith, D. R. Tomchick, M. M. Benning, D. A. Winkelmann, G. Wesenberg and H. M. Holden, Science, 261 (1993) 50.
D. LŐrinczy, U. Hoffmann, L. Pótó, J. Belágyi and P. Laggner, Gen. Physiol. Biophys., 9 (1990) 589.
P. G. Fajer, E. D. Fajer, J. J. Matta and D. D. Thomas, Biophys. J., 55 (1989) 261a.
C. D. Rodger and R. T. Treager, J. Mol. Biol., 86 (1974) 495.
P. Vibert and C. Cohen, J. Musc. Res. Cell Motil., 9 (1988) 296.
A. Bertazzon, G. H. Tian and T. Y. Tsong, Biophys. J., 53 (1988) 236a.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported by grants from the National Research Foundation (OTKA T 017099) and Ministry of Social Welfare (ETT 737/1993). The Bruker ESP 300 E spectrometer and the SETARAM Micro DSC-II used in the experiments were purchased with funds provided by the National Research Foundation Grants CO-123 and CO-272. The computer (PC-386) was supported by POPEX Ltd., Pécs, Hungary. The authors thank to Prof. Dr. K. Hideg (Central Research Laboratory) for providing the iodoacetamide spin label.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
LŐrinczy, D., Belágyi, J. Internal flexibility of cardiac myosins. Journal of Thermal Analysis 47, 503–514 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01983992
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01983992