Abstract
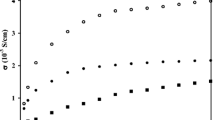
Poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO) based-polymeric solid electrolytes are of growing interest for their applications in electrochemical devices. Their major limitations are structural and electrochemical stability, and low cationic transport number. A possible response to these problems is given by composite or nanostructured materials. We present sol-gel synthesis, thermal and electrical characterization of new electrolytes made of a composite glass-polymer matrix doped with LiClO4 and LiBF4. Emphasis to the critical aspects of preparation is given. We obtain a conductivity at room temperature better than 10−5 ohm−1 cm−1, which is high enough to envisage technological applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Armand, Solid State Ionics, 69 (1994) 309.
B. Scrosati, “Solid State Ionic Materials”, B. V. R. Chowdari et al. eds., World Scientific, Singapore, 1994, pp. 111–118.
J. F. Le Nest, A. Gandini and C. Shoenenberger, Trends Polymer Sci., 2 (1994) 432.
C. A. Angell, C. Liu and E. Sanchez, Nature, 362 (1993) 137.
A. Magistris, “Fast Ion Transport in Solids”, B. Scrosati et al. eds., Nato Asi Series, Kluwer Acad. Publ., Dordrecht (1993), pp. 213–230 and references therein.
G. Chiodelli, A. Magistris and A. Schiraldi, Electrochim. Acta, 23 (1978) 585.
A. Vallee, S. Besner and J. Prud'homme, Electrochim. Acta, 37 (1992) 1579.
N. Venkatasubramanian, B. Wade, P. Desai, A. S. Abhiraman and L. T. Gelbaum, J. Non-Cryst. Solids, 130 (1991) 144.
A. Magistris, P. Ferloni, P. Mustarelli, M. Restelli and G. Chiodelli, “Solid State Ionic Materials”, B. V. R. Chowdari et al. eds., World Scientific, Singapore, 1994, pp. 361–367.
P. S. Gill, S. R. Sauerbrunn and M. Reading, J. Thermal Anal., 40 (1993) 931.
C. Tomasi, P. Mustarelli, N. A. Hawkins and V. Hill, Thermochim. Acta, in press.
Y. Ohta, M. Shimada and M. Koizumi, J. Amer. Ceram. Soc., 65 (1982) 572.
“Vogel's Textbook of Practical Organic Chemistry”, 4th Edition, B. S. Furniss et al. eds., Longman, Harlow, England, 1988.
P. Ferloni, G. Chiodelli, A. Magistris and M. Sanesi, Solid State Ionics, 18 & 19 (1986) 265.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
TG-FTIR experiments were kindly performed by V. Berbenni.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Quartarone, E., Tomasi, C., Mustarelli, P. et al. Sol-gel synthesis, thermal characterization and conductivity of new glass-polymer solid electrolytes. Journal of Thermal Analysis 47, 235–245 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01982702
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01982702