Summary
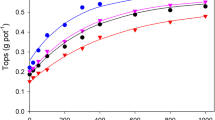
The accumulation of phosphate as a function of time has been followed for wheat plants when grown in small pots of Seddon sandy loam under conditions of controlled environment. Phosphate additions of 150, 300, 600 and 2400µg P/g soil were made to bulk samples of soil by spraying on appropriate amounts of calcium phosphate solution, followed by drying and thorough mixing.
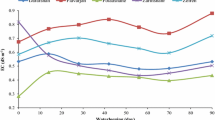
At intervals of two weeks from sowing to maturity (22 weeks) the plants in two pots of each treatment were harvested and the phosphorus content determined. For each level of phosphate addition the rate of phosphate uptake into the plant tops was almost constant for the period 2–12 weeks during which the average rates for the four phosphate levels were 65, 135, 290 and 530µg P/plant/day respectively.
The rates obtained under controlled conditions are compared with corresponding rates found for wheat plants when grown in field rotation trials.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Black, J. N., Seed size as a factor in the growth of subterranean clover (Trifolium subterranean L.) under spaced and sward conditions. Australian J. Agr. Research8, 335–351 (1957).
Boltz, D. F. and Mellon, M. G., Determination of phosphorus, germanium, silicon and arsenic by the heteropoly blue method. Anal. Chem.19, 873–877 (1947).
Carter, E. D., Fertilizer investigations with special reference to phosphate use on the lateritic soils of Kangaroo Island. Proc. Australian Agrostology Conf. (Armidale) 33.1–33.15 (1958).
Kanwar, J. S., Phosphate retention in some Australian soils. Soil Sci.82 43–50 (1956).
Lewis, D. G. and Quirk, J. P., Phosphate diffusion in soil and uptake by plants. I. Self-diffusion of phosphate in soils. Plant and Soil26, 99–118 (1967).
Tyson, A. G., Studies on the fertility of Seddon soil (Kangaroo Island, South Australia). Australian J. Agr. Research6, 398–422 (1955).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lewis, D.G., Quirk, J.P. Phosphate diffusion in soil and uptake by plants. Plant Soil 26, 119–128 (1967). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01978679
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01978679