Abstract
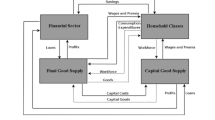
This paper attempts to analyze the implications of the organizational structure of the firms on economic growth and income distribution. The approach used byBeckmann [1977] is generalized and used explicitly as the starting point. The impact of the administrative structure on output growth is then studied using an extension of the Growth-Accounting-Method incorporating the quality of the labor force.
Regarding income distribution it is shown that the coefficients of Pareto distributions can be obtained from the characteristics of the administrative structure. Their contribution to growth is evaluated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beckmann, M.J.: Management Production Functions and the Theory of the Firm. Journal of Economic Theory14, 1977, 1–18.
Blau, P.M.: The Hierarchy of Authority in Organizations. American Journal of Sociology73 (4), 1968, 453–467.
Blau, P.M., andD.D. Duncan: The American Occupational Structure. New York 1967.
Blau, P.M. et al.: Technology and Organization in Manufacturing. Administrative Sciences Quarterly21, 1976, 20–40.
Bochum, H.: Choice of the Organization Structure: A Framework for Quantitative Analysis of Industrial Centralization/Decentralization Issues. Zeitschrift für Operations Research20, 1976, B17-B35.
Calvo, A.G., andS. Wellisz: Supervision, Loss of Control, and the Optimum Size of the Firm. Journal of Political Economy86 (5), 1976, 943–952.
Charnes, A., W.W. Cooper, andA. P. Schinnar: A Theorem on Homogeneous Functions and Extended Cobb-Douglas Forms. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science73 (1), 1976, 3747–3748.
Correa, H.: The Economics of Human Resources. Amsterdam 1963.
-: Sources of Economic Growth in Latin America. The Southern Economic Journal38 (1), 1970.
Denison, E.F.: The Sources of Economic Growth in the United States and the Alternatives Before Us. Supplementary Paper No. 13. New York, Committee for Economic Development, 1966.
-: Why Growth Rates Differ. Washington, D.C., 1967.
Dogramaci, A.: Research on the Size of Administrative Overhead and Productivity: Some Methodological Considerations. Administrative Science Quarterly22, 1977, 22–26.
Doreian, P., andN.P. Hummon: Modeling Social Processes. New York 1976. Chapt. 3.
Johansen, L.: Production Functions: An Integration of Micro and Macro, Short Run and Long Run Aspects. Amsterdam 1972.
Kasarda, J.D.: The Structural Implications of Social System Size: A Three-level Analysis. American Sociological Review39, 1974, 19–28.
Kennedy, C., andA.P. Thirlwall: Surveys in Applied Economics: Technical Progress. Economic Journal82 (325), 1972, p. 11, p. 72.
Kochem, M.: Decentralization by Function and Location. Management Science19 (8), 1973, 841–856.
Kochem, M., andK. W. Deutsch: Pluralization: A Mathematical Model. Operations Research20 (2), 1972, 276–292.
-: A Note on Hierarchy and Coordination: An Aspect of Decentralization. Management Science21 (1), 1974.
Lydall, H.: The Structure of Earnings. Oxford 1968.
Mandelbrot, B.: The Pareto-Levy Law, and the Distribution of Income. International Economic Review1(2), 76–106.
Mayer, T.: The Distribution of Ability and Earnings. The Review of Economics and Statistics42, 1960, 189–195.
Mincer, J.: The Distribution of Labor Incomes: A Survey with Special Reference to Human Capital Approach. Journal of Economic Literature8 (1), 1970, 1–26.
Nadiri, M.I.: Some Approaches to the Theory and Measurement of Total Factor Productivity: A Survey. Journal of Economic Literature8 (4), 1970, 1137–1177.
Pondy, L.: Effects of Size, Complexity, and Ownership on Administrative Intensity. Administrative Science Quarterly14, 1969, 47–60.
—: Reply to Dogramaci: Suggestions for Improving Administrative Research. Administrative Science Quarterly22, 1977, 27–29.
Sahota, G.S.: Theories of Personal Income Distribution: A Survey. Journal of Economic Literature16(1), 1978, 1–55.
Sato, K.: Production Functions and Aggregation. Amsterdam 1975.
Simon, H.A.: The Compensation of Executives. Sociometry20 (1), 1957, 32–35.
Solow, R.M.: Technical Change and the Aggregate Production Function. The Review of Economics and Statistics39 (3), 1957, 312–320.
Tinbergen, J.: On the Theory of Trend Movements. Weltwirtschaftliches Archiv, Band55, 1942. Reprinted in Selected Papers, Amsterdam 1959.
U.S. Department of Labor: Salary Structure Characteristics in Large Firms. Bulletin 1417. Washington, D.C., 1964.
Williamson, O.E.: Hierarchical Control and Optimum Firm Size. The Journal of Political Economy75 (2), 1967.
Yotopoulous, P.A., andJ.B. Nugent: Economics of Development: Empirical Investigations. New York 1976.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Correa, H. The firm's administrative structure: Theory, measurement and applications to growth accounting and income distribution. Empirical Economics 8, 93–109 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01973193
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01973193