Abstract
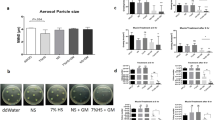
We investigated whether sulfuric acid inhalation would cause hyperresponsiveness to substance P. Guinea pigs became dyspneic during a 1 h sulfuric acid exposure, but recovered by 24 h when they were challenged with substance P or histamine aerosols. Eight minutes after the start of challenge, animals were killed and excised lung gas volumes measured. Sulfuric acid slightly increased histamine responsiveness compared to controls. However, sulfuric acid caused a much more pronounced leftward shift in the dose response to substance P. Coadministration of the neutral endopeptidase (NEP) inhibitor, thiorphan, did not reduce sulfuric acid-related hyperresponsiveness to substance P. By 72 h, sensitization to substance P was absent. Histological evaluation of sulfuric acid-treated lungs revealed mild alveolitis at 24 h, but not at 72 h. We conclude that sulfuric acid produces a marked sensitization to substance P. Inactivation of NEP does not appear to account for this effect.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. O. Amdur, R. Z. Schultz and P. Drinker,Toxicity of sulfuric acid mist to guinea pigs. Ind. Hyg. Occup. Med.5, 318–329 (1951).
D. G. Brownstein,Reflex-mediated desquamation of bronchiolar epithelium in guinea pigs exposed acutely to sulfuric acid aerosol. Am. J. Pathol.98, 577–590 (1979).
S. A. Silbaugh, J. L. Mauderly and C. A. Macken,Effects of sulfuric acid and nitrogen dioxide on airway responsiveness of the guinea pig. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health8, 31–45 (1981).
S. A. Silbaugh, P. W. Stengel, R. D. Dillard and K. G. Bemis,Pulmonary gas trapping in the guinea pig and its application in pharmacological testing. J. Pharmacol. Methods18, 295–303 (1987).
P. W. Stengel and S. A. Silbaugh,Mechanisms of gas loss from normal and hyperinflated excised guinea pig lungs. Respir. Physiol.63, 129–138 (1986).
A. M. Bendele, P. W. Stengel and S. A. Silbaugh,Quantitation of bronchiolar epithelial proliferation in A23187-exposed guinea pigs. Agents and Actions34, 194–196 (1987).
P. W. Stengel, A. M. Bendele, S. L. Cockerham and S. A. Silbaugh,Inhaled A23187 produces a preferential sensitization to substance P. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis.147, 196–201 (1993).
P. W. Stengel, G. D. Williams and S. A. Silbaugh,A23187-induced pulmonary gas trapping and inflammation in the guinea pig. Agents and Actions32, 270–276 (1991).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stengel, P.W., Bendele, A.M., Cockerham, S.L. et al. Sulfuric acid induces airway hyperresponsiveness to substance P in the guinea pig. Agents and Actions 39 (Suppl 1), C128–C131 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01972743
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01972743