Abstract
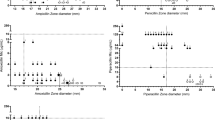
One hundred and forty isolates were identified using the GPI Card (Vitek Systems) and a conventional biochemical scheme. Agar dilution susceptibility testing was performed and isolates were screened for beta-lactamase production. The GPI Card was accurate in identifyingEnterococcus faecalis, but discrepant results were obtained for seven (29.1 %) of the 24non-Enterococcus faecalis isolates. Ampicillin resistance was present in 2.9 % of isolates and there were no beta-lactamase producers. There was no vancomycin resistance but 12.1 % of isolates showed high-level resistance to gentamicin.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hoffman S, Moellering R The enterococcus: “putting the bug in our ears”. Annals of Internal Medicine 1987, 106: 757–761.
Murray B The life and times of the enterococcus. Clinical Microbiology Reviews 1990, 3: 46–65.
Smyth E, Steven P, Holliman R Prevalence and susceptibility of highly gentamicin resistantEnterococcus faecalis in a South London teaching hospital. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 1989, 23: 633–639.
Nachamkin I, Axelrod P, Talbot G, Fischer S, Wennersten C, Moellering R, MacGregor R Multiple high-level aminoglycoside-resistant enterococci isolated from patients in a university hospital. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 1988, 26: 1287–1291.
Shlaes D, Al-Obeid S, Shlaes J, Boisivon A, Williamson R Inducible, transferable resistance to vancomycin inEnterococcus faecium, D399. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 1989, 23: 503–508.
Uttley A, George R, Naidoo J, Woodford N, Johnson A, Collins C, Morrison D, Gilfillan A, Fitch L, Heptonstall J High-level vancomycin-resistant enterococci causing hospital infections. Epidemiology and Infection 1989, 103: 173–181.
Facklam R, Collins M Identification ofEnterococcus species isolated from human infections by a conventional test scheme. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 1989, 27: 731–734.
Ruoff K, de la Maza L, Murtagh M, Spargo J, Ferraro M Species identities of enterococci isolated from clinical specimens. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 1990, 28: 435–437.
Rosenthal S, Freundlich L An aminoglycoside disk sensitivity test for use with enterococci. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 1982, 10: 459–462.
Clarke A, Zemcov SJV Comparative in vitro activity of lomefloxacin, a new difluoroquinolone. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases 1989, 8: 164–168.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bryce, E.A., Zemcov, S.J.V. & Clarke, A.M. Species identification and antibiotic resistance patterns of the enterococci. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 10, 745–747 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01972500
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01972500