Abstract
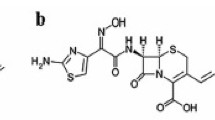
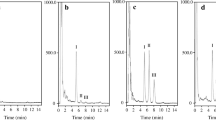
A simple reversed-phase high pressure liquid chromatographic method was developed for the determination of cefuroxime in the serum of patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting. The serum was cleaned up with a 3.3% solution of perchloric acid in water.
Cefalexine was used as an internal standard. Detection was made by a UV multi-wavelength detector. The optimum wavelength for cefuroxime is 275 nm. The absolute recovery of this method was 90.9%; the limit of quantification was 0.7 mg/l. This analytical method was used in a study to investigate the cefuroxime serum concentration-time curves in 26 patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting. It was found that one single dose is sufficient to obtain effective serum concentrations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Scheld WM, Sande MA. Endocarditis and intravascular infections. In: Mandell GL, Douglas RG, Bennett JE, eds. Principles and practice of infectious disease. New York: Churchill Livingstone, 1990:670–706.
Cockcroft CW, Gault MH. Prediction of creatinine clearance from serum creatinine. Nephron 1976;16; 31–41.
Brogard JM, Kopferschmitt JK, Pinget M, Arnaud JP, Lavillaureix J. Cefuroxime concentrations in serum, urine and bile: pharmacokinetic profile. Proc R Soc Med 1977;70:42–50.
O'Callaghan CH, Harding SM. The pharmacokinetics of cefuroxime in man in relation to its anti-bacterial activity. Proc R Soc Med 1977;70:4–10.
Tartaglione TA, Polk RE. Review of the new second-generation cephalosporins: cefonicid, ceforanide, and cefuroxime. Drug Intell Clin Pharm 1985;19:188–98.
Bundtzen RW, Toothaker RD, Nielson OS, Madsen PO, Welling PG, Craig WA. Pharmacokinetics of cefuroxime in normal and impaired renal function: comparison of high-pressure liquid chromatography and microbiological assays. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 1981;3:443–9.
Toothaker RD, Wright DS, Pachla LA. Recent analytical methods for cephalosporins in biological fluids. Minireview. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 1987;31:1157–63.
Brisson AM, Fourtillan JB. Determination of cephalosporins in biological material by reversed-phase liquid column chromatography. J Chromatogr 1981;223:393–9.
Lecaillon JB, Rouan MC, Souppart C, Febvre N, Juge F. Determination of cefsulodin, cefotiam, cephalexin, cefotaxime, desacetyl-cefotaxime, cefuroxime and cefroxadin in plasma and urine by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr 1982;228:257–67.
Hekster YA, Baars AM, Vree TB, Van Klingeren B, Rutgers A. Comparison of the determination ofβ-lactam antibiotic drugs in plasma of rabbits by means of HPLC and of a microbiological assay. Pharm Weekbl [Sci] 1979;1:95–100.
Gold B, Rodriguez WJ. Cefuroxime: mechanisms of action, antimicrobial activity, pharmacokinetics, clinical applications, adverse reactions and therapeutic indications. Pharmacotherapy 1983;3;82–100.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koot, M.J., Ijdenberg, F.N., Stuurman, R.M. et al. High pressure liquid chromatographic analysis of the serum concentration of cefuroxime after an intravenous bolus injection of cefuroxime in patients with a coronary artery bypass grafting. Pharmaceutisch Weekblad Scientific Edition 14, 360–364 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01970173
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01970173