Abstract
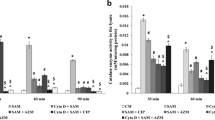
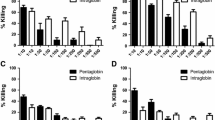
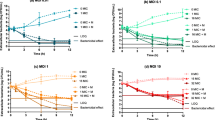
The intraphagocytic activity of erythromycin, roxithromycin and azithromycin against phagocytosedStaphylococcus aureus was compared. Erythromycin and roxithromycin both acted bacteriostatically at concentrations corresponding to 10×MIC. Azithromycin, however, did not prevent intracellular proliferation of the staphylococci. On comparison of the pH dependency of the antibacterial activity of the three drugs, azithromycin was found to be inactivated earlier in an acidic milieu.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson R, van Rensburg CEJ, Joone G, Lukey PT An in vitro comparison of the intraphagocytic bioactivity of erythromycin and roxithromycin. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 1987, 20, Supplement B: 57–68.
Carlier MB, Zenebergh A, Tulkens PM Cellular uptake and subcellular distribution of roxithromycin and erythromycin in phagocytic cells. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 1987, 20, Supplement B: 47–56.
Gladue RP, Bright GM, Isaacson RE, Newborg MF In vitro and in vivo uptake of azithromycin (CP-62, 993) by phagocytic cells: possible mechanism of delivery and release at sites of infection. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 1989, 33: 277–282.
Vildé JL, Dournon E, Rajagopalan P Inhibition ofLegionella pneumophila multiplication within human macrophages by antimicrobial agents. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 1986, 30: 743–748.
Rodgers FG, Elliot TSJ Antibiotic killing of legionella. Lancet 1984, i: 683–684.
Horwitz MA, Silverstein SC Intracellular multi-plication of Legionnaire's disease bacteria (Legionella pneumophila) in human monocytes is reversibly inhibited by erythromycin and rifampicin. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 1983, 71: 15–26.
Vosbeck K, James PR, Zimmermann W Antibiotic action on phagocytosed bacteria measured by a new method for determining viable bacteria. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 1984, 25: 735–741.
Hand WL, King-Thompson NL Contrasts between phagocyte antibiotic uptake and subsequent intracellular bactericidal activity. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 1986, 29: 135–140.
Hand WL, King-Tompson NL, Holman JW Entry of roxithromycin (RU 965), imipenem, cefotaxime, trimethoprim and metronidazole into human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 1987, 31: 1553–1557.
Bermudez LEM, Young LS Activities of amikacin, roxithromycin, and azithromycin alone and in combination with tumor necrosis factor againstMycobacterium avium complex, Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 1988, 32: 1149–1153.
Chang HR, Pechère JCF In vitro effects of four macrolides (roxithromycin, spiramycin, azithromycin [CP-62, 993] and A-56268) onToxoplasma gondii. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 1988, 32: 524–529.
Milatovic D. Effect of subinhibitory antibiotic concentrations on the phagocytosis ofStaphylococcus aureus. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology 1982, 1: 97–101.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Milatovic, D. Intraphagocytic activity of erythromycin, roxithromycin and azithromycin. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 9, 33–35 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01969530
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01969530