Abstract
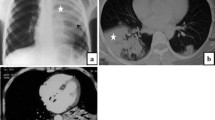
A direct method for detection ofPneumocystis carinii was evaluated in 14 patients with impaired immune function (3 seropositive for HIV, 8 with AIDS and 3 with heart transplants) and signs and symptoms suggestive ofPneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Direct examination by phase-contrast and interference-contrast microscopy of fresh clinical specimens obtained by sputum induction, bronchoalveolar lavage or transbronchial lung biopsy was found to be a simple and rapid method for detection ofPneumocystis carinii, the sensitivity of the method being comparable to that of the classical toluidine blue O and Diff-Quik staining methods. These findings suggest that this direct microscopy technique could be considered for routine clinical application in patients with suspectedPneumocystis carinii pneumonia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Edman JC, Kovacs JA, Masur H, Santi DV, Elwood HJ, Sogin ML: Ribosomal RNA sequence showsPneumocystis carinii to be a member of the fungi. Nature 1988, 334: 519–522.
Stringer SL, Stringer JR, Blase MA, Walzer PD, Cushion MT:Pneumocystis carinii: sequence from ribosomal RNA implies a close relationship with fungi. Experimental Parasitology 1989, 68: 450–461.
Walzer PD, Kim CK, Cushion MT:Pneumocystis carinii. In: Walzer PD, Genta RM (ed): Parasitic infections in the compromised host. Marcel Dekker, New York, 1989, p. 83–178.
Mills J:Pneumocystis carinii andToxoplasma gondii infections in patients with AIDS. Reviews of Infectious Diseases 1986, 8: 1001–1011.
Valerie L, Gartner I, Weymouth LA, Goodman CD, Hopewell PC, Hadley WK: The use of mucolyzed induced sputum for the identification of pulmonary pathogens associated with human immunodeficiency virus infection. Archives of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine 1989, 113: 488–493.
Bartlett JG, Ryan KJ, Smith TF, Wilson WR: Laboratory diagnosis of lower respiratory tract infections. Cumitech 7A. American Society for Microbiology, Washington DC, 1987, p. 1–18.
Pintozzi RL, Bleka LJ, Narros S: The morphologic identification ofPneumocystis carinii. Acta Cytologica Journal 1979, 23: 35–39.
Nielsen PB, Goyot P, Mojon M: The microscopic diagnosis ofPneumocystis carinii. Acta Pathologica Microbiologica Immunologica Scandinavica (B) 1986, 94: 19–23.
Fingerland A, Vortel V: Zur Kenntnis der Pneumozystis-Pneumonien. Pathologie und Bakteriologie 1954, 17: 201–220.
Pliess G: Das mikrokulturelle Verhalten von Alveolarzellen undPneumocystis carinii bei der interstitiellen plasmazellulären Säuglingspneumonie. Frankfurther Zeitschrift für Pathologie 1957, 68: 153–184.
Bommer W:Pneumocystis carinii in interstitial plasma-cell pneumonia. Studies of the organism. American Journal of Diseases of Children 1961, 102: 375–379.
Pifer LL, Hughes WT, Murphy MJ: Propagation ofPneumocystis carinii in vitro. Pediatric Research 1977, 11: 305–316.
Masur H, Jones TC: The interaction in vitro ofPneumocystis carinii with macrophages and L-cells. Journal of Experimental Medicine 1978, 147: 157–170.
Von Behren LA, Pesanti EL: Uptake and degradation ofPneumocystis carinii by macrophages in vitro. American Review of Respiratory Disease 1978, 118: 1051–1059.
Shiota T: Morphology and development ofPneumocystis carinii observed by phase-contrast microscopy and semiultrathin section light-microscopy. Japanese Journal of Parasitology 1984, 33: 443–455.
Shiota T, Yamada M, Yoshida Y: Morphology, development and behaviour ofPneumocystis carinii observed by light-microscopy in nude mice. Zentralblatt für Bakteriologie, Mikrobiologie und Hygiene (A) 1986, 262: 230–239.
Ruffolo JJ, Cushion MT, Walzer PD: Techniques for examiningPneumocystis carinii in fresh specimens. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 1986, 23: 17–21.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chichino, G., Bruno, A., Cevini, C. et al. Rapid microscopy technique for detection ofPneumocystis carinii in fresh clinical specimens. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 9, 601–605 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01967215
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01967215