Abstract
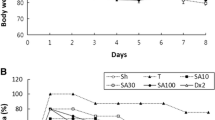
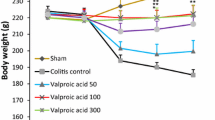
The efficacy of various drugs used to treat ulcerative colitis, (sulfasalazine, 5-aminosalicylate, hydrocortisone) was investigated in a model of acetic acid-induced colitis in the rat. Subsequently, we tested the ability of antioxidant/5-lipoxygenase inhibitors (gossypol and nordihydroguiaretic acid [NDGA]) and a cyclooxygenase inhibitor (indomethacin) to attenuate the macroscopic colonic damage and/or neutrophil influx (myeloperoxidase activity [MPO]) associated with this model of colitis. Oral pretreatment with either sulfasalazine, gossypol, or NDGA significantly decreased colonic MPO activity induced by acetic acid. Intrarectal administration of such drugs resulted in an even larger reduction of the colonic inflammation, with gossypol being the most potent compound. Oral or intrarectal administration of corticosteroids (dexamethasone, hydrocortisone) also attenuated the parameters of acetic acid induced colitis. In contrast, pretreatment with indomethacin was ineffective, or when administered daily after colitis induction, indomethacin actually increased colonic neutrophil influx significantly. Our data suggest that both the route of drug administration and dosing regimen employed affect the antiinflammatory potency and/or efficacy of compounds on colitis induced by acetic acid in the rat. Drugs which were effective against this colitis may act by scavenging of oxygen derived free radicals.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 5-ASA:
-
5-aminosalicylate
- HTAB:
-
hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide
- LTB4:
-
leukotriene B4
- MPO:
-
myeloperoxidase
- NDGA:
-
nordihydroguiaretic acid
References
B. MacPherson and C. J. Pfeiffer,Experimental colitis. Digestion14, 442–452 (1976).
C. J. Pfeiffer,Animal models of colitis. InAnimal Models of intestinal disease. (Ed. C. J. Pfeiffer) pp. 148–155, CRC Press, Florida 1985.
N. K. Boughton-Smith, J. L. Wallace, G. P. Morris and B. R. J. Whittle,The effect of antiinflammatory drugs on eicosanoid formation in a chronic model of inflammatory bowel disease. Br. J. Pharmac.94, 65–72 (1988).
B. MacPherson and C. J. Pfeiffer,Experimental production of diffuse colitis in rats. Digestion17, 135–150 (1978).
J. E. Krawisz, P. Sharon and W. F. Stenson,Quantitative assay for acute intestinal inflammation based on myeloperoxidase activity: assessment of inflammation in rat and hamster models. Gastroenterology87, 1344–1350 (1984).
P. Sharon and W. F. Stenson,Metabolism of arachidonic acid in acetic acid induced colitis in rats: similarity to human inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology88, 55–63 (1985).
R. B. Sartor, T. M. Bond and J. H. Schwab,Systemic uptake and intestinal inflammatory effects of luminal bacterial cell wall polymers in rats with acute colonic injury. Infect. Immun.52, 2101–2108 (1988).
C. H. Hobson, T. J. Butt, D. M. Ferry, J. Hunter, V. S. Chadwick and M. F. Broom,Enterohepatic circulation of bacterial chemotatic peptide in rats with experimental colitis. Gastroenterology94, 1006–1013 (1988).
A. Keshavarzian, S. Sedghi, G. Morgan, M. Doria and G. Urban,The role of oxygen free radicals in inflammatory colitis. Scand. J. Gastroenterology24, 158, 178 (1989).
G. Morgan, M. Doria and A. Keshavarzian,The source of oxygen free radicals (OFR) and the role of hydroxyl radicals (OH . ) in experimental colitis. Am. J. Gastroenterology84, 1185 (1989).
J. Watt, S. N. Marcus and A. J. Marcus,The comparative prophylatic effects of sulfasalazine, prednisolone, and azathiprine in experimental colonic ulceration. J. Pharm. Pharmacol.32, 873–874 (1980).
C. C. Nast, M. Pinzani, F. Cominelli and R. D. Zipser,Antiinflammatory effects of sulfasalazine in rabbit colitis are not mediated by prostaglandin or leukotriene inhibition. Gut (in press).
A. A. Norris, A. J. Lewis and I. J. Zeitlin,Actions of anticolitic drugs on a guinea pig model of immune colitis. Agents and Actions112, 239–242 (1982).
R. D. Zipser, C. C. Nast, M. Lee, H. W. Kao and R. Duke,In vivo production of leukotriene B 4 and leukotriene C 4 in rabbit colitis: relationship to inflammation.Gastroenterology 92, 33–39 (1987).
P. Conzentino, P. C. Will, A. Lin and T. S. Gaginella,Effect of 5-lipoxygenase inhibitors on acetic acid induced colitis in the rat. Pharmacologist28, 163 (1986).
N. S. Mann and L. M. Demers,Experimental colitis studied by colonoscopy in the rat: effect of indomethacin. Gastrointest. Endosc.29, 77–82 (1983).
L. R. Empey, C. A. McArthur, L. D. Jewell and R. N. Fedorak,Cytoproctive effect of prostaglandin E 1 analog in acetic acid colitis. Gastroenterology94, A616 (1988).
J. L. Wallace, W. K. MacKnaughton and P. L. Beck,Inhibition of leukotriene synthesis markedly accelerates heading in a rat model of inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology96, 29–36 (1989).
M. K. Church and P. Miller,Time course of anti-anaphylactic and antiinflammatory effects of dexamethasone in the rat and mouse. Br. J. Pharmac.62, 481–486 (1978).
Worthington Enzyme Manual, p. 93, Worthington Biochemical, Freehold 1972.
G. P. Morris, P. L. Beck, M. S. Herridge, W. T. Drew, M. R. Szewczuk and J. L. Wallace,Hapten-induced model of chronic inflammation and ulceration in the rat. Gastroenterology96, 795–803 (1989).
A. K. A. Khan, J. Pirist and S. C. Truelove,An experiment to determine the active moiety of sulfasalazine. LancetII, 892–895 (1977).
M. A. Peppercorn and P. Goldman,The role of intestinal bacteria in the metabolism of salicylazosulfapyridine. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther.181, 555–562 (1972).
M. B. Abou-Donia, C. M. Lyman and J. W. Dieckert,Metabolic fate of gossypol: the metabolism of 14 C-gossypol in rats. Lipids 3, 938–946 (1970).
I. Ahnfelt-Ronne and O. H. Nielsen,The antiinflammatory moiety of sulfasalazine, 5-aminosalicylic acid, is a free radical scavenger. Agents and Actions21, 191–194 (1987).
P. Craven, J. Pfansteil, R. Saito and F. DeRubertis,Actions of sulfasalazine and 5-aminosalicylic acid as reactive oxygen scavengers in the suppression of bile acid-induced increases in colonic epithelial cell loss and proliferative activity. Gastroeneterology92, 1998–2008 (1987).
Y. Miyachi, A. Yoshioko, S. Imamura and Y. Niwa,Effect of sulfasalazine and its metabolites on the generation of reac tive oxygen species. Gut28, 190–195 (1987).
Y. Ozaki, T. Ohashi and N. Yukie,A comparative study on the effects of inhibitors of the lipoxygenase pathway on neutrophil function: inhibitory effects on neutrophil function may not be attributed to inhibition of the lipoxygenase pathway. Biochem Pharmacol.35, 3481–3488 (1986).
B. L. Maloff, D. Peifer, M. Cooke and N. R. Ackerman,Inhibition of LTB 4 binding to human neutrophils by nordihydroguiaretic acid. Agents and Actions21, 358–360 (1987).
L. Levine,Inhibition of the A-23187-stimulated leukotriene and prostaglandin biosynthesis of rat basophil leukemia (RBL-1) cells by non-steroidal antiflammatory drugs, antioxidants, and calcium channel blockers. Biochem. Pharmacol.32, 3023–3026 (1983).
Y. Hamasaki and H. H. Tai,Gossypol, a potent inhibitor of arachidonate 5- and 12- lipoxygenases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta834, 37–41 (1985).
E. Sekizuka, M. B. Grisham, M. A. Li, E. A. Deitch and N. D. Granger,Inflammation-induced intestinal hyperemia in the rat: role of neutrophils. Gastroenterology95, 1528–1534 (1988).
R. Schumert, J. Towner and R. D. Zipser,Role of eicosanoids in human and experimental colitis. Dig. Dis. Sci.33, 58s-64s (1988).
E. Guth, K. Su and P. H. Guth,The effect of indomethacin on the normal and inflamed rat colon. Gastroenterology96, A191 (1989).
D. Engineer, U. Niederhauser, P. Piper and P. Sirois,Release of mediators of anaphylaxis: inhibition by prostaglandin synthesis and the modification of release of slow reacting substance of anaphylaxis and histamine. Br. J. Pharmacol.62, 61–66 (1978).
N. J. Greenberger, C. Arvanitakis and A. Hurwitz, InDrug treatment of gastrointestinal disorders. (Ed. D. Azarnoff) pp. 175–183, Churchill Livingston, NY (1978).
G. A. Higgs, R. J. Flower and J. R. Vane,A new approach to antiinflammatory drugs. Biochem. Pharmacol.28, 1959–1961 (1979).
G. J. Blackwell, R. Carnuccio, M. Di Rosa, R. J. Flower, C. S. J. Langham, L. Parente, P. Persico, N. C. Russel-Smith and D. Stone,Glucocorticoids induce the formation of anti-inflammatory and anti-phospholipase proteins into the peritoneal cavity of the rat. Br. J. Pharmac.76, 185–194 (1982).
R. M. McMillan and S. J. Foster,Leukotriene B 4 and inflammatory disease. Agents and Actions24 1/2, 114–119 (1988).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fitzpatrick, L.R., Bostwick, J.S., Renzetti, M. et al. Antiinflammatory effects of various drugs on acetic acid induced colitis in the rat. Agents and Actions 30, 393–402 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01966304
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01966304