Abstract
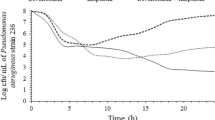
The postantibiotic effect of imipenem onPseudomonas aeruginosa was studied at different inocula using one ATCC strain and four clinical isolates. The postantibiotic effect was measured using two different methods: viable counts and bioluminescence assay of intracellular bacterial ATP. The postantibiotic effect could be demonstrated with both methods (viable counts 1–2 h, ATP assay 3–5 h) for all strains at an inoculum of 106 CFU/ml. When the inoculum was raised to 108 CFU/ml, no postantibiotic effect could be observed with either method using routine growth conditions. This disappearance of the postantibiotic effect coincided with a loss of bactericidal effect of imipenem when high inocula were used. Improved oxygenation of the cultures restored the bactericidal and postantibiotic effects of imipenem at high inocula.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bigger, J. W.: The bactericidal action of penicillin onStaphylococcus pyogenes. Irish Journal of Medical Science 1946, 227: 553–568.
Parker, R. F., Luse, S.: The action of penicillin on staphylococcus: further observations on the effect of a short exposure. Journal of Bacteriology 1948, 56: 75–81.
Eagle, H.: The recovery of bacteria from the toxic effects of penicillin. Journal of Clinical Investigation 1949, 28: 832–836.
Mc Donald, P. J., Craig, W. A., Kunin, C. M.: Persistent effect of antibiotics onStaphylococcus aureus after exposure for limited periods of time. Journal of Infectious Diseases 1977, 135: 217–223.
Wilson, D. A., Rolinson, G. N.: The recovery following exposure of bacteria to penicillin. Chemotherapy 1979, 25: 14–22.
Bundtzen, R. W., Gerber, A. U., Cohn, D. L., Craig, W. A.: Postantibiotic suppression of bacterial growth. Reviews of Infectious Diseases 1981, 3: 28–37.
Gerber, A. U., Craig, W. A.: Growth kinetics of respiratory pathogens after short exposures to ampicillin and erythromycin in vitro. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 1981, 8: 81–91.
Vogelman, B. S., Craig, W. A.: Postantibiotic effects. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 1985, 15, Supplement A: 37–46.
Craig, W. A., Gudmundsson, S.: The postantibiotic effect. In: Lorian, V. (ed.): Antibiotics in laboratory medicine. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, 1986, p. 515–536.
Gerber, A. U., Craig, W. A., Brugger, H. P., Feller, C., Vastila, A. P., Brandel, J.: Impact of dosing intervals on activity of gentamicin and ticarcillin againstPseudomonas aeruginosa in granulocytopenic mice. Journal of Infectious Diseases 1983, 147: 910–917.
Gerber, A. U., Feller-Seessenmann, C.: In vivo assessment of in vitro killing patterns ofPseudomonas aeruginosa. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 1985, 15, Supplement A: 201–206.
Odenholt, I., Holm, S. E., Cars, O.: An in vivo model for evaluation of the postantibiotic effect. Scandinavian Journal of Inectious Diseases 1988, 20: 97–103.
Mc Donald, P. J., Hakendorf, P., Pruul, H.: Recovery period of bacteria after brief exposure to N-formimidoylthienamycin and other antibiotics. In: Periti, P., Grassi, G. G. (ed.): Current chemotherapy and immunotherapy. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC, 1981, p. 741–743.
Bustamente, C. I., Drusano, G. L., Tatem, B. A., Standiford, H. C.: Postantibiotic effect of imipenem onPseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 1984, 5: 678–682.
Gudmundsson, S., Vogelman, B., Craig, W. A.: The in vivo postantibiotic effect of imipenem and other new antimicrobials. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 1986, 18, Supplement E: 67–73.
Manek, N., Andrews, J. M., Wise, R.: The postantibiotic effect of imipenem. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 1986, 18: 641.
Molin, Ö., Nilsson, L., Ånsehn, S.: Rapid detection of bacterial growth in blood cultures by bioluminescent assay of bacterial ATP. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 1983, 18: 521–525.
Cars, O., Henning, C., Holm, S. E.: Penetration of ampicillin and dicloxacillin into tissue cage fluid in rabbits. Scandinavian Journal of Infectious Diseases 1981, 13: 69–74.
Spratt, B. G., Tolanputra, V., Zimmerman, W.: Binding of thienamycin and clavulanic acid to penicillin-binding proteins ofEscherichia coli K-12. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 1977, 12: 406–409.
Kropp, H., Gerchens, L., Sundelof, J. G., Kahan, F. M.: Antibacterial activity of imipenem. The first thienamycin antibiotic. Reviews of Infectious Diseases 1985, 7, Supplement 3: 389–410.
Tuomanen, E.: The search forβ-lactam antibiotics that kill nongrowing bacteria. Reviews of Infectious Diseases 1986, 8, Supplement 3: 279–291.
Vogelman, B., Gudmundsson, S., Turnidge, J., Leggett, J., Craig, W. A.: In vivo postantibiotic effect. Journal of Infectious Diseases 1988, 157: 287–298.
Mattie, H.: Kinetics of antimicrobial action. Reviews of Infectious Diseases, 1981, 1: 19–27.
Eagle, H., Musselman, A. D.: The slow recovery of bacteria from the toxic effects of penicillin. Journal of Bacteriology 1949, 58: 475–490.
Freeman, B. A.: Pseudomonas and legionella. In: Freeman, B. A. (ed.): Textbook of microbiology. W. B. Saunders, Philadelphia, 1985, p. 544–551.
Luria, S. E.: A test for penicillin sensitivity and resistance inStaphylococcus. Proceedings in Sociology and Experimental Biology 1946, 61: 46–51.
Sabath, L. D., Garner, C., Wilcox, C., Finland, M.: Effect of inoculum and ofβ-lactamase on the anti-staphylococcal activity of thirteen penicillins and cephalosporins. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 1975, 8: 344–349.
Gwynn, M. N., Rolinson, G. N.: Selection of variants ofPseudomonas aeruginosa resistent toβ-lactam antibiotics. Infection 1980, 8: 73–80.
Greenwood, D., Eley, A.: A turbidity study of the response of select strains ofPseudomonas aeruginosa to eight anti-pseudomonasβ-lactam antibiotics. Journal of Infectious Diseases 1980, 145: 110–117.
Corrado, M. L., Landesman, S. H., Cherubin, C. E.: Influence of inoculum size on activity of cefoperazone, cefotaxime, moxalactam, piperacillin and N-formimidoyl thienamycin (MK 0787) againstPseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 1980, 18: 893–896.
Watanakunakorn, C.: Effects of inoculum size on the activity of carboxy- and ureido-penicillins and effects of combinations of ureido-penicillins with amino-glycosides against resistentPseudomonas aeruginosa. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 1986, 17: 91–95.
Eng, R. H. K., Smith, S. M., Cherubin, C. E.: Inoculum effect of newβ-lactam antibiotics onPseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 1984, 26: 42–47.
Neu, H. C., Labthavikul, P.: Comparative in vitro activity of N-formimidoyl thienamycin against gram-positive and gram-negative aerobic and anaerobic species and itsβ-lactamase stability. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 1982, 21: 180–187.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Odenholt, I., Isaksson, B., Nilsson, L. et al. Postantibiotic and bactericidal effect of imipenem againstPseudomonas aeruginosa . Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 8, 136–141 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01963897
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01963897