Abstract
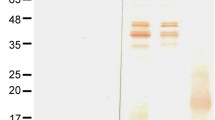
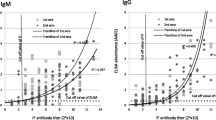
A sonicate antigen and two concentrations of a purified flagellum antigen ofBorrelia burgdorferi were compared for serological diagnosis of Lyme borreliosis by an enzyme immunoassay (EIA). Generally, the higher concentration of flagellum antigen was found to be superior to the lower concentration, which was diluted eight times compared to the higher concentration. The diagnostic sensitivity for IgG antibody detection increased from 13 % in the sonicate EIA to 31 % in the best flagellum EIA assay (p=0.01) in sera from patients with erythema migrans (n=70), and from 34 % to 55 % (p=0.01) in sera from patients with neuroborreliosis (n=77). However, the sensitivity for IgG in sera from patients with acrodermatitis chronica atrophicans (n=20) was high in both assays: 90 % in the sonicate EIA compared to 95 % in the flagellum EIA. Regarding IgM, there was no significant difference between the sensitivity of the assays in sera from any of the patient groups. The sensitivity values for IgM and IgG in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from patients with neuroborreliosis were also without significant differences. Sera and CSF from patients with meningitis/encephalitis of non-Borrelia etiology (n=35), multiple sclerosis (n=9) or syphilis (n=24), served as controls. The flagellum EIA showed a significantly improved specificity for IgG in CSF from controls with syphilis (p<0.01). It is concluded that purifiedBorrelia burgdorferi flagellum antigen is superior to a sonicate antigen, especially for serodiagnosis of the early stages of Lyme borreliosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burgdorfer W, Barbour AG, Hayes SF, Benach JL, Grunwaldt E, Davis JP: Lyme disease — a tick-borne spirochetosis? Science 1982, 216: 1317–1319.
Stiernstedt G: Tick-borneBorrelia infection in Sweden, Scandinavian Journal of Infectious Diseases 1985, 17, Supplement 45: 1–70.
Steere AC, Grodzicki RL, Kornblatt AN, Craft JE, Barbour AG, Burgdorfer W, Schmid GP, Johnson E, Malawista SE: The spirochetal etiology of Lymedisease. New England Journal of Medicine 1983, 308: 733–740.
Åsbrink E, Hovmark A, Hederstedt B: The spirochetal etiology of acrodermatitis chronica atrophicans Herxheimer. Acta Dermato-Venereologica 1984, 64: 506–512.
Benache JL, Bosler EM, Hanraha JP, Coleman JL, Bast TE, Habicht GS, Cameron DJ, Ziegler JL, Burgdorfer W, Barbour AG, Edelman R, Kaslow RA: Spirochetes isolated from the blood of two patients with Lyme Disease. New England Journal of Medicine 1983, 308: 740–742.
Pfister HW, Einhaupl K, Preac-Mursic V, Wilske B, Schiertz G: The spirochetal etiology of lymphocytic meningoradiculitis of Bannwarth (Bannwarth's syndrome). Journal of Neurology 1984, 118: 1–4.
Rawlings JA, Fournier PV, Teltow GA: Isolation ofBorrelia spirochetes from patients in Texas. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 1987, 25: 1148–1150.
Schmidli J, Hunziker T, Moesli P, Schaad UB: Cultivation ofBorrelia burgdorferi from joint fluid three months after treatment of facial palsy due to Lyme borreliosis. Journal of Infectious Diseases 1988, 158: 905–906.
Åsbrink E, Hovmark A: Successful cultivation of spirochetes from skin lesions of patients with erythema chronica migrans Afzelius and acrodermatitis chronica atrophicans. Acta Patologica Microbiologica Immunologica Scandinavica (B) 1985, 93: 161–163.
Russell H, Sampson JS, Schmid GP, Wilkinson HP, Plikaytis B: Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and indirect immunofluorescence assay for Lyme disease. Journal of Infectious Diseases 1984, 149: 465–470.
Craft JE, Grodzicki RL, Steere AC: Antibody response in Lyme disease. Evaluation of diagnostic tests. Journal of Infectious Diseases 1984, 149: 789–795.
Stiernstedt GT, Granström M, Hederstedt B, Sköldenberg B: Diagnosis of spirochetal meningitis by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and indirect immunofluorescence assay in serum and cerebrospinal fluid. Journal of clinical Microbiology 1985, 21: 819–825.
Åsbrink E, Hovmark A, Hederstedt B: Serological studies of erythema chronicum migrans Afzelius and acrodermatitis chronica atrophicans with indirect immunofluorescence and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays. Acta Dermatologica Venerologica 1985, 65: 509–514.
Magnarelli LA, Anderson JF, Barbour AG: Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for Lyme disease: reactivity of subunits ofBorrelia burgdorferi. Journal of Infectious Diseases 1989, 159: 43–49.
Magnarelli LA, Anderson JF, Johnson RC: Cross-reactivity in serological tests for Lyme disease and other spirochetal infections. Journal of Infectious Diseases 1987, 156: 183–188.
Hansen K, Bangsborg JM, Fjordvang H, Strandberg-Pedersen N, Hindersson P: Immunochemical characterization of and isolation of the gene for aBorrelia burgdorferi immunodominant 60-kilodalton antigen common to a wide range of bacteria. Infection and Immunity 1988, 56: 2047–2053.
Barbour AG, Burgdorfer W, Grunwaldt E, Steere AC: Antibodies of patients with Lyme disease to components of theIxodes dammini spirochete. Journal of Clinical Investigation 1983, 72: 504–515.
Craft JE, Fisher DK, Shimamoto GT, Steere AC: Antigens ofBorrelia burgdorferi recognized during Lyme disease. Appearance of a new immunoglobulin M response and expansion of the immunoglobulin G response late in the illness. Journal of Clinical Investigation 1986, 78: 934–939.
Wilske B, Preac-Mursic V, Schiertz G, Busch KV: Immunochemical and immunological analysis of EuropeanBorrelia burgdorferi strains. Zentralblatt für Bakteriologie, Mikrobiologie and Hygiene (A) 1986, 263: 92–102.
Coleman JL, Benach JL: Isolation of antigenic components of Lyme disease spirochete: their role in early diagnosis. Journal of Infectious Diseases 1987, 155: 756–765.
Karlsson M, Möllegård I, Stiernstedt G, Henriksson AM, Wretlind B: Characterization of antibody response in patients withBorrelia meningitis. Serodiagnosis and Immunotherapy in Infectious Disease 1988, 2: 375–386.
Grodzicki RL, Steere AC: Comparison of immunoblotting and indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using different antigen preparations for diagnosing early Lyme disease. Journal of Infectious Diseases 1988, 157: 790–797.
Hansen K, Hindersson P, Strandberg-Pedersen N: Measurement of antibodies to theBorrelia burgdorferi flagellum improves serodiagnosis in Lyme disease. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 1988, 26: 338–346.
Hansen K, Åsbrink E: Serodiagnosis of erythema migrans and acrodermatitis chronica atrophicans by theBorrelia burgdorferi flagellum enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 1989, 27: 545–551.
Sköldenberg B, Stiernstedt G, Gårde A, Kolmodin A, Carlström A, Nord CE: Chronic meningitis, caused by a penicillin-sensitive microorganism? Lancet 1983, ii: 75–78.
Stiernstedt G, Gustavsson R, Karlsson M, Svenungsson B, Sköldenberg B: Clinical manifestations and diagnosis of neuroborreliosis. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 1988, 539: 46–55.
Wilske B, Schierz G, Preac-Mursic V: Intrathecal production of antibodies againstBorrelia burgdorferi in patients with lymphocytic menigoradiculitis (Bannwarth's syndrome). Journal of Infectious Diseases 1986, 153: 304–314.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karlsson, M., Stiernstedt, G., Granström, M. et al. Comparison of flagellum and sonicate antigens for serological diagnosis of Lyme borreliosis. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 9, 169–177 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01963833
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01963833