Abstract
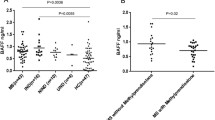
Kawasaki disease (KD) is an acute febrile illness of early childhood. Although the epidemiology of KD suggests an infectious agent, the cause still remains unknown. Intense immune activation during the acute disease has been well documented. Quantitative determination of soluble CD23 in serum can serve as an index of macrophage/monocyte or B-cell activation. To further characterize the immunological profile in KD, we investigated whether soluble CD23 levels in serum increase during the acute disease. In addition, we compared soluble CD23 levels in 33 patients with acute KD with levels in ten patients each with measles, rubella, infectious mononucleosis, and scarlet fever to determine if marked elevations in soluble CD23 were unique to acute KD. Patients with KD, rubella and infectious mononucleosis, but not patients with measles or scarlet fever, had increased soluble CD23 levels in serum during the acute stage, as compared to age-matched control subjects (P<0.01). These data suggest infection with Epstein-Barr virus and rubella and acute KD are all characterized by B-cell and macrophage/monocyte activation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CAL :
-
coronary-artery lesions
- IM :
-
infectious mononucleosis
- KD :
-
Kawasaki disease
- MAb :
-
monoclonal antibodies
References
Abe J, Kozin BL, Jujo K, Melish ME, Glode MP, Kohsaka T, Leung DYM (1992) Selective expansion of T-cells expressing T-cell receptor variable lesions Vß2 and Vß8 in Kawasaki disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:4066–4070
Al-Janadi M, Al-Wabel A, Raziuddin S (1994) Soluble CD23 and interleukin-4 levels in autoimmune chronic active hepatitis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 71:33–37
Bansal AS, Pumphrey RS, Mandal BK, Khoo SH, Wilson PB (1990) Serum measurements of soluble CD23 in HIV infection. Immunology 80:652–653
Bansal AS, Robert T, Hay EM, Kay R, Pumphrey RSH, Wilson PB (1992) Soluble CD23 levels are elevated in the serum of patients with primary Sjogren's syndrome and systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol 89:452–455
Delespesse G, Suter U, Mossalayi D, Bettler B, Sarfati M, Hofstetter H, Kilcherr E, Debre P, Dalloul A (1991) Expression, structure, and function of the CD23 antigen. Adv Immunol 49:149–191
Furukawa S, Matsubara T, Motohashi T, Nakachi S, Sasai K, Yabuta K (1990) Expression of FcεR2/CD23 on peripheral blood macrophages/monocytes in Kawasaki disease. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 56:280–286
Furukawa S, Matsubara T, Motohashi T, Sasai K, Nakachi S, Umezawa Y, Yabuta K (1991) Increased expression of FcεR2/CD23 on peripheral blood B lymphocytes and serum IgE levels in Kawasaki disease. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol 95:7–12
Furukawa S, Motohashi T, Matsubara T, Watanabe T, Obara T, Yabuta K (1992) Increased expression of CD23 on peripheral blood B cells and macrophages/monocytes during acute infectious mononucleosis. J Infect Dis 166:691–692
Furukawa S, Matsubara T, Yabuta K (1992) Mononuclear cell subsets and coronary artery lesions in Kawasaki disease. Arch Dis Child 67:706–708
Furukawa S, Matsubara T, Okumura K, Yabuta K (1993) Decreased expression of CD23 on peripheral blood macrophages/monocytes during acute Kawasaki disease with coronary artery lesions. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 102:335–339
Genot E, Sarfati M, Sigaux F, Petit-Kpskas E, Billard C, Mathiot C, Falcoff E, Delespesse G, and Kolb J-P (1989) Effect of interferon-α on the expression and release of the CD23 molecule in Hairy cell leukemia. Blood 74:2455–2463
Gordon J (1991) CD23: novel disease marker with a split personality. Clin Exp Immunol 86:356–359
Kawasaki T, Kosaki G, Osawa S, Shigematsu I, Yanagawa S (1974) A new infantile acute febrile mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome (MLNS) prevailing in Japan. Pediatrics 54:271–276
Kicza K, Fischer A, Pfeil T, Bujanowski-Weber J, Konig W (1989) Cell-cell interaction for CD23 expression and soluble CD23 release from peripheral lymphocytes of atopic donors. Immunology 68:532–539
Kikutani H, Suemura M, Owaki H, Nakamura H, Sato R, Yamasaki K, Barsumian EL, Hardy RR, Kishimoto T (1986) FcεR receptor, a specific differentiation marker transiently expressed on mature B cells before isotype switching. J Exp Med 164:1455–1469
Leung DYM, Meissner HC, Fulton DR, Murray DL, Kotzin BL, Schlievert PM (1994) Toxic shock syndrome toxin-secreting staphylococcus aureus in Kawasaki syndrome. Lancet 342:1385–1388
Matsumoto T, Miike T, Yamaguchi K, Murakami M, Kawabe T, Yodoi J (1991) Serum levels of IL-2 receptor, IL-4 and IgE-binding factors in childhood allergic diseases. Clin Exp Immunol 85:288–292
Melish ME, Parsonett J, Marchette N (1994) Kawasaki syndrome (KS) is not caused by toxic shock syndrome toxin-1 (TSST-1)+staphylococci (abstract). Pediatr Res 35:187A
Nadler LM (1986) B cell/leukemia panel workshops: Summary and comments? In: Reinherz EL, Haynes BF, Nadler LM, Bernstein ID (eds) Leukocyte typing II. Springer Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 4–43
Pietra BA, Inocencio JD, Giannini EH, Hirsch R (1994) TCR Vß family repertoire and T cell activation markers in Kawasaki disease. J Immunol 153:1881–1888
Research Committee on Kawasaki Disease (1984) Report of subcommittee on standardization of diagnostic criteria and reporting of coronary artery lesions in Kawasaki disease. Ministry of Health and Welfare, Tokyo, pp 56–66
Sarfati M, Nutman T, Fonteyn C, Delespesse G (1986) Presence of antigenic determinants common to Fc IgE receptors on human macrophages, T and B lymphocytes and IgE-binding factors. Immunology 59:569–575
Sarfati M, Lagneaux L, Fonteyn C, Frost H, Delespesse (1988) Elevation of IgE-binding factors in serum of patients with B cell-derived chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 71:94–98
Vercelli D, Jabara HH, Lee B-W, Woodland N, Geha RS, Leung DYM (1988) Human recombinant interleukin 4 induces FcεR2/CD23 on normal human monocytes. J Exp Med 167: 1406–1416
Yanagawa H, Nakamura Y, Yashiro M, Fujita Y, Nagai M, Kawasaki T, Aso S, Imada Y, Shigematsu I (1988) A nationwide incidence survey of Kawasaki disease in 1985–1986 in Japan. J Infect Dis 158:1296–1301
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matsubara, T., Furukawa, S., Motohashi, T. et al. Soluble CD23 antigen in Kawasaki disease and other acute febrile illnesses. Eur J Pediatr 154, 826–829 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01959791
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01959791