Abstract
Thirty-nine consecutive patients with symptoms suggestive of reflux esophagitis underwent a double contrast upper gastrointestinal series and subsequently had endoscopy with biopsy. In a control group of 164 consecutive patients without symptoms of esophagitis a double contrast examination was done with the same method.
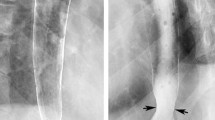
We have found a significant increase of the diameter of the esophagus in its distal or cardiac segment (IDCE) in patients with esophagitis of Grades 1 and 2 when compared with the control group (p<0.001). Radiology was found to have correctly diagnosed 35 of the 39 cases (89.7%) and the majority of the patients had endoscopic signs of mild esophagitis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Strawn T, Knutson CO, Max MH: The role of endoscopy in patients with suspected esophageal reflux.Am Surg 46:95–99, 1980
Ott DJ, Gelfand DW, Wu AC: Reflux esophagitis: radiographic and endoscopic correlation.Radiology 130:583–588, 1979
Koehler RE, Weyman PJ, Oakley HF: Single and doublecontrast techniques in esophagitis.AJR 135:15–19, 1980
Edwards DAW: The mechanism at the cardia.Br J Radiol 34:474–487, 1961
Edwards DAW: Diaphragm and hiatus hernia. In Shanks SC, Kerley P (eds):Textbook of X-ray Diagnosis, 4th Ed. London: Lewis, 1969, pp 266–319
Wolf BS: Sliding hiatal hernia: the need for redefinition.AJR 117:231–247, 1973
Graziani L, Pesaresi A, De Nigris E, Montesi A: Valutazione radiologica del giun to esofago-gastrico.Radiol Med 67:425–434, 1981
Liebermann-Meffert D, Allgöwer M, Schmid P, Math D, Blum AL: Muscular equivalent of the lower esophageal sphincter.Gastroenterology 76:31–38, 1979
Friedland GW: Historical review of the changing concepts of lower esophageal anatomy: 430B.C. – 1977.AJR 131:373–388, 1978
Berridge FR, Friedland GW, Tagart REB: Radiological landmarks at the oesophago-gastric junction.Thorax 21:499–509, 1966
Laufer I:Double Contrast Gastrointestinal Radiology. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders Co., 1979
Johnson LF, Demeester TR, Haggitt RC: Endoscopic signs for gastroesophageal reflux objectively evaluated.Gastrointest Endosc 22:151–155, 1976
Hogan WJ, Dodds WJ, Hoke SE, Reid DP, Kalkhoff RK, Arndorfer RC: Effect of glucagon on esophageal motor function.Gastroenterology 69:160–165, 1975
Demeester TR, Johnson LF, Joseph GJ, Toscano MS, Hall AW, Skinner DB: Patterns of gastroesophageal reflux in health and disease.Ann Surg 184:459–470, 1976
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Graziani, L., De Nigris, E., Pesaresi, A. et al. Reflux esophagitis: Radiologic-endoscopic correlation in 39 symptomatic cases. Gastrointest Radiol 8, 1–6 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01948078
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01948078