Summary
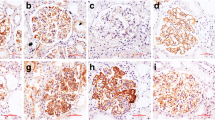
The BALB/c mouse developed mesangial deposits of immune constituents and light microscopical changes characteristic of immune complex glomerulonephritis after 8 weeks' treatment with mercuric chloride given by s.c. injection. There were no signs of linear of granular immune deposits along the glomerular capillary basement membrane after 2 or 8 weeks. The antigen could not be identified. No antibodies to nuclear or renal structures were found. Using a histochemical method (silver amplification) mercury was detected by light and electron microscopy in tubular and glomerular structures. Mercury was present in secondary lysosomes of the mesangial cells after eight weeks of mercury poisoning.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berlin, M., Mercury, in: Handbook on the Toxicology of Metals, pp. 503–539. Eds L. Friberg, G. F. Nordberg and V. B. Vouk, Elsevier/North-Holland Biomedical Press, Amsterdam/New York/Oxford 1979.
Bellon, B., Capron, M., Druet, E., Verroust, P., Vial, M.-C., Sapin, C., Girard, J. F., Foidart, M. M., Mahieu, P., and Druet, P. Mercuric chloride induced autoimmune disease in Brown-Norway rats: sequential search for anti-basement membrane antibodies and circulating immune complexes. Eur. J. clin. Invest.12 (1982) 127–133.
Bernaudin, J. F., Druet, E., Druet, P., and Masse, R., Inhalation or ingestion of organic or inorganic mercurials produces autoimmune disease in rats. Clin. Immun. Immunopath.20 (1981) 129–135.
Clarkson, T. W., The pharmacology of mercury compounds. A. Rev. Pharmac.12 (1972) 375–406.
Danscher, G., and Schröder, H. D., Histochemical demonstration of mercury induced changes in rat neurons. Histochemistry60 (1979) 1–7.
Danscher, G., Histochemical demonstration of heavy metals. Histochemistry71 (1981) 1–16.
Druet, E., Sapin, C., Günther, E., Feingold, N., and Druet, P., Mercuric chloride-induced anti-glomerular basement membrane antibodies in the rat. Genetic control. Eur. J. Immun.7 (1977) 348–351.
Druet, E., Sapin, C., Fournie, G., Mandet, C., Günther, E., and Druet, P., Genetic control of susceptibility to mercury-induced nephritis in various strains. Clin. Immun. Immunopath.25 (1982) 203–212.
Druet, P., Druet, E., Potdevin, F., and Sapin, C., Immune type glomerulonephritis induced by HgCl2 in the Brown Norway rat. Ann. Immun. (Inst. Pasteur)129 C (1978) 777–792.
Druet, P., Ayed, K., Bariety, J., Bernaudin, J. F., Druet, E., Girard, J. F., Hinglais, N., and Sapin, C., Experimental immune glomerulonephritis induced in the rat by mercuric chloride, in: Advances in Nephrology, pp. 321–342. Eds J. Hamburger et al. Year Book Medical Publisher 15, London 1979.
Druet, P., Teychenne, P., Mandet, C., Bascou, C., and Druet, E., Immune-type glomerulonephritis induced in the Brown-Norway rat with mercury-containing pharmaceutical products. Nephron28 (1981) 145–148.
Eneström, S., Avantages des coupes semi-fines des biopsies rénales incluses en paraffine et réalisées par coteaux en verre au large tranchant. Archs. Anat. Cytol. Path.29 (1981) 317–319.
Eneström, S., and Hultman, P., Mercury induced glumerulonephritis in mice. Abstract, 6th World Congress of Academic and Environmental Pathology, Miami Beach, Florida, September 2–7, 1984.
Fournié, G. J., Lulé, J., Gayral-Taminh, M., Mignon-Conté, M., Conté, J. J., Bellon, B., Druet, E., Hirsch, F., Sapin, C., Druet, P., Izui, S., and Lambert, P. H., Immunological pathogenesis of experimental glomerulonephritis induced by some infectious and toxic agents. Contr. Microbiol. Immun.7 (1983) 43–51.
Hinglais, N., Druet, P., Grossetete, J., Sapin, C., and Bariéty, J., Ultrastructural study of nephritis induced in Brown-Norway rats by mercuric chloride. Lab. Invest.41 (1979) 150–159.
Hirsch, J., Couderc, J., Sapin, C., Fournié, G., and Druet, P., Polyclonal effect of HgCl2 in the rat, its possible role in an eyperimental autoimmune disease. Eur. J. Immun.12 (1982) 620–625.
Hultman, P., and Eneström, S., Experimental Hg-nephropathy: correlation between histochemistry and analytical EM. J. Ultrastruct. Res.85 (1983) 118–119.
Lelental, M., and Gysling, H. J., Tellurium Physical Development (TPD): A dry non-silver amplification process. J. Photogr. Sci.28 (1980) 209–215.
Makker, S. P., and Aikawa, M., Mesangial glomerulonephropathy with deposition of IgG, IgM and C3 induced by mercuric chloride: A new model. Lab. Invest.41 (1979) 45–50.
Rodin, A. E., and Crowson, C. N., Mercury nephrotoxicity in the rat 1. Factors influencing the localization of the tubular lesions. Am. J. Path.41 (1962) 297–307.
romano-Franco, A. A., Turiello, M., Albini, B., Ossi, E., Milgrom, F., and Giuseppe, A. A., Anti-basement membrane antibodies and antigen-antibody complexes in rabbits injected with mercuric chloride. Clin. Immun. Immunopath.9 (1978) 464–481.
Sapin, C., Druet, E., and Druet, P., Induction of anti-glomerular basement membrane antibodies in the Brown-Norway rat by mercuric chloride. Clin. exp. Immun.28 (1977) 173–179.
Sapin, C., Mandet, C., Druet, G., Günther, G., and Druet P., Immune complex type disease induced by HgCl: genetic control of susceptibility. Transpl. Proc.13 (1981) 1404–1406.
Schreiner, G. A., and Maher, J. F., Toxic Nephropathy. Am. J. Med.38 (1965) 404–449.
Siegel, S., The Randomization test for two independent samples, in: Non-parametric statistics for the behavioral sciences, pp. 152–156. Ed. S. Siegel. McGraw-Hill, New York 1956.
Stejskal, J., Acute renal insufficiency in intoxication with mercury compounds III. Pathological findings. Acta med. scand.177 (1965) 75–84.
Thaw, H. H., Forslid, J., Hamberg, H., and Hed, J., The effect of reactive oxygen metabolites (ROM) on the attachment and indigestion phase of C3b- and IgG-mediated phagocytosis by macrophages. Acta path. microbiol. immun. scand.92 (1984) 1–8.
Weening, J. J., Fleuren, G. J., and Hoedemaeker, Ph. J., Demonstration of Antinuclear antibodies in mercuric-chloride-induced glomerulopathy in the rat. Lab. Invest.39 (1978) 405–411.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
We are deeply indebted to Dr. Gorm Danscher, Institute of Anatomy, B., University of Aarhus, Denmark, for valuable discussions and technical advice. This work was supported by the Swedish Medical Research Council, project no 6536.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eneström, S., Hultman, P. Immune-mediated glomerulonephritis induced by mercuric chloride in mice. Experientia 40, 1234–1240 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01946653
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01946653