Summary
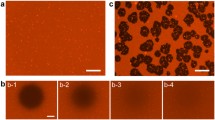
Concentrated mixtures of lipid vesicles and pigeon erythrocyte membrane were cosonicated in order to produce functional hybrid vesicles. From the properties of the resulting material, we conclude that hybrids were very probably formed. These properties were as follows: (i) The presence of membrane increased the sonic fragmentability of lipid vesicles. Sonic fragmentability was assessed by measuring sonication-induced release of previously trapped [14C]-choline and trapping of external [3H]-choline. (ii) Space enclosed by lipid was served by the membrane-like properties of36Cl− permeability and ATP-dependent45Ca++ uptake activity. (iii)36Cl-permeability was more readily and fully induced into the more easily fragmented lipid vesicles. Further sonication caused loss of the induced36Cl−-permeability. This loss was less rapid with the less easily fragmented lipid vesicles; i.e., less easily fragmented lipids protected36Cl−-permeability better. (iv) Glycine uptake activity was partially protected from sonic damage by the presence of lipid vesicles. (v) On centrifugation in bovine serum albumin density gradients, cosonicated material showed lipid properties (enclosed choline and32Pi space and [3H]-cholesterol) and membrane properties (36Cl−-permeability and ATP-dependent45Ca2+ uptake) coinciding at a density intermediate between those reached by separately sonicated membrane and lipid vesicles. (vi) Electron micrographs showed the disappearance of pure membrane-like structures and the appearance of large amounts of new vesicles whose appearance is consistent with a hybrid structure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahkong, Q.F., Cramp, F.C., Fisher, D., Howell, J.I., Lucy, J.A. 1972. Studies on chemically-induced cell fusion.J. Cell Sci. 10:769
Ahkong, Q.S., Cramp, F.C., Fisher, D., Howell, J.I., Tampion, W., Verrinder, M., Lucy, J.A. 1973. Chemically-induced and thermally-induced cell fusion: Lipid-lipid interactions.Nature New Biol. 242:215
Ahkong, Q.F., Howell, J.I., Lucy, J.A., Safwat, F., Davey, M.R., Cocking, E.C. 1975. Fusion of hen erythrocytes with yeast protoplasts induced by polyethylene glycol.Nature (London) 255:66
Bosch, J. van der, McConnell, H.M. 1975. Fusion of dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine vesicle membranes induced by concanavalin A.Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 72:4409
Fodor, K., Alföldi, L. 1976. Fusion of protoplasts ofBacillus Megaterium.Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 73:2147
Frye, L.D., Edidin, M. 1970. The rapid intermixing of cell surface antigens after formation of mouse-human heterokaryons.J. Cell Sci. 7:319
Grant, C.W.M., McConnell, H.M. 1973. Fusion of phospholipid vesicles with viableacholeplasma laidlawii.Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 70:1238
Hayat, M.A. 1972. Basic Electron Microscopy Techniques. Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York
Howell, J.I., Ahkong, Q.F., Cramp, F.C., Fisher, D., Tampion, W., Lucy, J.A. 1972. Membrane fluidity and membrane fusion.Biochem. J. 130:44P
Howell, J.I., Fisher, D., Goodall, A.H., Verrinder, M., Lucy, J.A. 1973. Interactions of membrane phospholipids with fusogenic lipids.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 332:1
Huang, C. 1969. Studies on phosphatidylcholine vesicles. Formation and physical characteristics.Biochemistry 8:344
Kantor, H.L., Mabrey, S., Prestegard, J.H., Sturtevant, J.M. 1977. A calorimetric examination of stable and fusing lipid bilayer vesicles.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 466:402
Kantor, H.L., Prestegard, J.H. 1975. Fusion of fatty acid containing lecithin vesicles.Biochemistry 14:1790
Koprowski, H., Croce, C.M. 1973. Fusion of somatic and gametic cells with lysolecithin.In: Methods in Cell Biology. Vol. 7, pp. 251–260. D.M. Prescott, editor. Academic Press, New York
Lau, A.L.Y., Chen, S.I. 1974. Nuclear magnetic resonance studies of the interactions of alomethicin with lecithin bilayers.Biochemistry 13:4942
Lee, J.W., Beygu-Farber, S., Vidaver, G.A. 1973. Glycine transport by membrane vesicles from pigeon red cells.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 298:446
Lee, J.W., Vidaver, G.A. 1977. A method for demonstrating the heterogeneity of pigeon red cell membrane vesicles based on their glycine transport activity.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 446:441
Lowry, O.H., Rosebrough, N.J., Farr, A.L., Randall, R.J. 1951. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent.J. Biol. Chem. 193:265
Miller, C., Racker, E. 1976. Fusion of phospholipid vesicles reconstituted with cytochromec oxidase and mitochondrial hydrophobic protein.J. Membrane Biol. 26:319
Orly, J., Schramm, M. 1976. Coupling of catecholamine receptors from one cell with adenylate cyclase from another cell by cell fusion.Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 73:4410
Pagano, R.E., Huang, L., Wey, C. 1974. Interaction of phospholipid vesicles with cultured mammalian cells.Nature (London) 252:166
Papahadjopoulos, D., Mayhew, E., Poste, G., Smith, S., Vail, W.J. 1974. Incorporation of lipid vesicles by mammalian cells provides a potential for modifying cell behavior.Nature (London) 252:163
Papahadjopoulos, D., Poste, G., Schaeffer, B.E. 1973. Fusion of mammalian cells by unilamellar lipid vesicles: Influence of lipid surface charge, fluidity and cholesterol.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 323:23
Papahadjopoulos, D., Vail, W.J., Pangborn, W.A., Poste, G. 1976. Studies on membrane fusion. II. Induction of fusion in pure phospholipid membranes by calcium ions and other divalent ions.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 448:265
Racker, E. 1973. A new procedure for the reconstitution of biologically active phospholipid vesicles.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 55:224
Racker, E., Eytan, E. 1973. Reconstitution of an efficient calcium pump without detergents.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 55:174
Reynolds, E.S. 1963. The use of lead citrate at high PH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy.J. Cell Biol. 17:208
Schacterle, G.R., Pollack, R.L. 1973. A simplified method for the quantitative assay of small amounts of protein in biological material.Anal. Biochem. 51:654
Schaeffer, P., Cami, B., Hotchkiss, R.D. 1976. Fusion of bacterial protoplasts.Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 73:2151
Shortman, K. 1968. The separation of different cell classes from lymphoid organs. II. The purification and analysis of lymphocyte populations by equilibrium density gradient centrifugation.Aust. J. Exp. Biol. Med. Sci. 46:375
Sorensen, E.N., Weisman, G., Vidaver, G.A. 1977. A sephadex column procedure for measuring uptake and loss of low molecular weight solutes from small, lipid-rich vesicles.Anal. Biochem. 82:376
Vanderkooi, J.M., Ierokomas, A., Nakamura, H., Martenosi, A. 1977. Fluorescence energy transfer between Ca2+ transport ATPase molecules in artificial membranes.Biochemistry 16:1262
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sorensen, E.N., Vidaver, G.A. Hybridization by cosonication of pigeon erythrocyte membrane with exogenous lipid vesicles. J. Membrain Biol. 44, 47–65 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01940573
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01940573