Summary
During open heart surgery, needle biopsy material was obtained in four patients, and electron microscopic preparations of the mitochondrial ATPases (coupling factors 1) in human myocardial cells were performed.
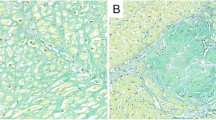
The pre-ischemic, normal structure of the mitochondrial ATPases and the changes which occur during the ischemic interval were described. An increase in the center-to-center space was shown in the post-ischemic phase. This result was discussed for the pathogenesis of subcellular injuries due to ischemia.
Zusammenfassung
Während Operationen am offenen Herzen wurden bei vier Patienten Myokardbiopsien durchgeführt. Die Biopsien wurden zur elektronenmikroskopischen Darstellung der mitochondrialen ATPasen (coupling factors 1) aufgearbeitet.
Die präischänische Normalstruktur der mitochondrialen ATPasen und deren Veränderungen während Ischämie werden beschrieben. Dabei zeigt sich postischämisch eine Vergrößerung der Zentrum-Zentrum-Abstände.
Diese ultrastrukturellen Ergebnisse werden im Hinblick auf ihre Bedeutung für die Pathogenese der subzellulären Schäden erörtert.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avron, M.: Energy transduction in Chloroplasts. Ann. Rev. Biochem.46, 143 (1977).
Bittar, N., J. R. Koke, H. A. Berkoff, D. R. Kahn: Histochemical and Structural Changes in Human Myocardial Cells After Cardiopulmonary Bypass. Circulation51/52, 16 (1975).
Elert, O.: Untersuchungen des Myokardstoffwechsels während verschiedener Formen induzierter Kardioplegie an gesunden und vorgeschädigten menschlichen und tierischen Herzen. Med. Habil. Schr. Frankfurt/M. (1976).
Fernández-Morán, H.: Cell Membrane Ultrastructure. Circulation26, 1039 (1962).
Fernández-Morán, H., T. Oda, P. V. Blair, D. E. Green: A Macromolecular Repeating Unit of Mitochondrial Structure and Function. J. Cell. Biol.22, 63 (1964).
Kagawa, Y.: Crystallization of ATPase (TF1) from a thermophilic bacterium. Methods Enzym.55, 372 (1979).
Kagawa, Y., E. Racker: Partial Resolution of the Enzymes Catalyzing Oxidative Phosphorylation. VIII. Properties of a Factor Conferring Oligomycin Sensitivity on Mitochondrial Adenosine Triphosphatase. J. Biol. Chem.241, 2461 (1966).
Kagawa, Y., E. Racker: Partial Resolution of the Enzymes Catalyzing Oxidative Phosphorylation. IX. Reconstruction of Oligomycin-sensitive Adenosine Triphosphatase. J. Biol. Chem.241, 2467 (1966).
Kagawa, Y., E. Racker: Partial Resolution of the Enzymes Catalyzing Oxidative Phosphorylation. XXV. Reconstitution of Vesicles Catalyzing32Pi-Adenosine Triphosphatase Exchange. J. Biol. Chem.246, 5477 (1971).
Kagawa, Y., E. Racker, R. E. Hauser: Partial Resolution of the Enzymes Catalyzing Oxidative Phosphorylation. X. Correlation of Morphology and Function in Submitochondrial Particles. J. Biol. Chem.241, 2475 (1966).
Lehninger, A. L.: The Mitochondria (W. A. Benjamin Inc., New York and Amsterdam 1964).
Mitchell, P.: Coupling of Phosphorylation to Electron and Hydrogen Transfer by a Chemiosmotic Type of Mechanism. Nature191, 144 (1961).
Mitchell, P.: Chemiosmotic Coupling in Oxidative and Photosynthetic Phosphorylation. Biochem. Rev. Cambridge Philos. Soc.41, 445 (1962).
Nermut, M. V.: Methods of Negative Staining. In: Methodensammlung der Elektronenmikroskopie, pp. 3–22 (3.1.2.3.) (Schimmel, G. & Vogell, W., Eds.) (Wissenschaftliche Verlagsgesellschaft Stuttgart 1971).
Park, B.: Subunits of Chloroplast structure and quantum Conversion in Photosynthesis. Int. Rev. Cytol.20, 67 (1967).
Parsons, D. F.: Mitochondrial Structure: Two Types of Subunits on Negatively Stained Mitochondrial membranes. Science140, 985 (1963).
Parsons, D. F.: Negative Staining of Thinly Spread Cells and Associated Virus. J. Cell. Biol.16, 620 (1963).
Penefsky, H. S., R. C. Warner: Partial Resolution of the Enzymes Catalyzing Oxidative Phosphorylation. VI. Studies of the Mechanism of Cold Inactivation of Mitochondrial Adenosine Triphosphatase. J. Biol. Chem.240, 4694 (1965).
Pullman, M. E., H. S. Penefsky, A. Datta, E. Racker: Partial Resolution of the Enzymes Catalyzing Oxidative Phosphorylation. I. Purification and Properties of Soluble, Dinitrophenol-Stimulated Adenosine Triphosphatase. J. Biol. Chem.235, 3322 (1960).
Racker, E.: Resolution and Reconstitution of the Inner Mitochondrial Membrane. Fed. Proc.26, 1335 (1967).
Racker, E.: The Two Faces of the Inner Mitochondrial Membrane. Essays Biochem.6, 1 (1970).
Racker, E.: Membranes of Mitochondria and Chloroplasts (New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold Company 1970).
Racker, E., D. D. Tyler, R. W. Estabrook, T. E. Conover, D. F. Parsons, B. Chance: Correlation between Electrontransport Activity, ATPase and Morphology of Submitochondrial Particles. In: Oxidases and Related Redox Systems. (King, T. E., H. S. Mason, M. Morrison, Eds.) pp. 1077–1094 (New York-London-Sydney: J. Wiley & Sons Inc.1965).
Racker, E., L. L. Horstmann: Partial Resolution of the Enzymes Catalyzing Oxidative Phosphorylation. II. Structure and Function of Submitochondrial Particles completely Resolved with Respect to Coupling Factor 1. J. Biol. Chem.242, 2547 (1967).
Schaper, J., F. Hehrlein, M. Schlepper, K.-H. Thiedemann: Ultrastructural Alterations During Ischemia and Reperfusion in Human Hearts During Cardiac Surgery. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol.9, 175 (1977).
Seno, S., K. Utsumi, E. Yokomura: Swelling and Contraction of Mitochondria Related to the Metabolism. In: Intracellular Membraneous Structure. (Seno, S., E. D. Cowdry, Eds.) pp. 155–165 (Okayama: Chugoku Press Ltd. 1964).
Spitsberg, U. L., J. E. Blair: Evidence supporting the identity of beef heart mitochondrial chloroform-released adenosine-triphosphatase (ATPase) with coupling factor 1. Biochim. Biophys. Acta460, 136 (1977).
Stoeckenius, W.: Some observations on Negatively Stained Mitochondria. J. Cell. Biol.17, 443 (1963).
Telford, J. N., E. Racker: A Method for Increasing Contrast of Mitochondrial Inner Membrane Spheres in Thin Sections of Epon-Araldite Embedded Tissue. J. Cell. Biol.57, 580 (1973).
Whalen, D. A., D. G. Hamilton, C. E. Ganote, R. B. Jennings: Effect on a transient period of Ischemia on Myocardial Cells: I. Effect on Cell Volume Regulation. Amer. J. Pathol.74, 381 (1974).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
With 5 figures and 1 table
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beyersdorf, F., Gauhl, C., Elert, O. et al. Electron microscopic visible ischemic changes of the mitochondrial ATPases in human myocardial cells during extracorporal circulation. Basic Res Cardiol 76, 106–113 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01908166
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01908166