Abstract
Laboratory studies were undertaken to determine the differential response and suitability of 2 types of host larvae ofSesamia cretica (hibernating and active) to the development of the braconid,B. brevicornis.
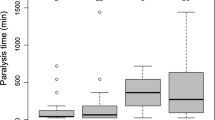
The parasitoid was able to immobilize the 2 forms of larvae. However, hibernating larvae were significantly less sensitive to the parasitoid's venom than active larvae. Parasitoid parents (specially females) which associated with hibernating larvae were significantly longer-lived than those kept with active larvae.
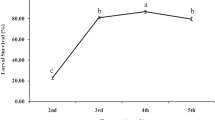
Life cycle period of the parasitoid did not affect with any of the 2 types of larvae. However, numbers of each of cocoons and emerged adults/larva were significantly higher in case of hibernating than in case of active larvae. Moreover, the produced adults from hibernating larvae were significantly larger in their size. Therefore the hibernating host larvae will serve better for mass colonization of this braconid.
Zusammenfassung
Laboruntersuchungen über die Beziehungen zwischen der SchlupfwespeBracon brevicornis und im Freiland gesammelter Ruhe- (überwinternder) und aktiver Raupen vonSesamia cretica ergaben daß weder die Eiablage noch der Lebenszyklus des Parasitoiden zwischen den beiden Wirtsformen verschieden waren. Dagegen waren die Kokonzahl, die Zahl geschlüpfter Parasitoiden sowie die Länge und das Gewicht (und damit die Produktivität) der Schlupfwespen bei Verwendung der Ruheraupen als Wirte signifikant größer als bei Verwendung der aktiven Raupen. Dies bietet wichtige Hinweise für eine Massenzucht für evtl. biologische Bekämpfungsversuche.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literaturverzeichnis
Babcock, K. W., Vance, A. M., 1929: The corn borer in central Europe. USDA Tech. Bull. No.135, pp. 54.
Fahmy, I., 1936: The European corn borer,Pyrausta nubilalis (Hübner), a major pest of maize in Egypt. Bull. Soc. ent. Egypte20, 58–60
Kamal, M., 1936: Recent advances in the control of the pink bollwormPlatyedra gossypiella Saunders, by natural enemies. Boll. Soc. ent. Egypte20, 259–293.
Kamal, M., 1951: Biological control projects in Egypt, with a list of introduced parasites and predators. Bull. Soc. ent. Egypte35, 205–220.
Tawfiek, M. S., 1977: Natural enemies ofHeliothis armigera HB., with special reference to the larval parasite,B. brevicornis Wesm. (Hymenoptera, Braconidae) M. Sc.-Thesis, Coll. of Agric., Univ. of Cairo, Egypt.
Thompson, W. R., Parker, H. L., 1928: The European corn borer and its controlling factors in Europe. USDA, Tech. Bull. No.59, pp. 63.
Temerak, S. A., 1976: Studies on certain mortality factors affecting distribution and abundance of sugarcane borers in upper Egypt. Ph. D. Thesis Coll. of Agric., Univ. of Assiut, Egypt.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Mit 2 Tabellen
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Temerak, S.A. Über Eignung und Reaktion überwinternder und aktiver Raupen von Sesamia cretica Led. (Lepid., Noctuidae) in bezug auf den Parasitoiden Bracon brevicornis Wesm. (Hymen., Braconidae). Anz. Schadlingskde., Pflanzenschutz, Umweltschutz 54, 149–151 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01907700
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01907700