Summary
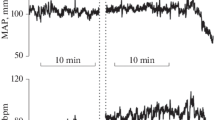
Despite the fact that the blood flow maintained during cardiopulmonary bypass is rather steady in the extracorporeal pump output, the arterial pressure under high-dose fentanly anaesthesia quite often shows sinusoidal oscillations. In the present study the duration of an oscillatory cycle was on average 17.6±3.6 s, its amplitude 7.3±1.6 mm Hg and mean systemic arterial pressure 75±12 mm Hg. The oscillation is affected by the drugs used under bypass conditions. In our series of clinical observations the blood pressure oscillation disappeared under the influence of chlorpromazine, phentolamine, droperidol, and enflurane, and it disappeared or at least was distinctly attenuated under fentanyl, thiopental, diazepam, sodium nitroprusside, nitroglycerine, acebutolol, and potassium chloride. Pancuronium, atropine and furosemide appeared to be practically incffective. In spite of the fact that the drugs used affected several sites of the sympathetic efferent chain, the disappearance and attenuation of the oscillation were associated with a simultaneous decrease of blood pressure. Hence, it is suggested that the occurrence of the oscillations requires some level of peripheral vascular tone.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson B, Kenney RA, Neil E (1950) The role of the chemoreceptors of the carotid and aortic regions in the production of Mayer waves. Acta Physiol Scand 20:203–220
Barcroft J, Khanna LC, Nisimaru Y (1932) Rhythmical contraction of the spleen. J. Physiol (Lond) 74:294–298
Barcroft J, Nisimaru Y, Steggerda FR (1932) The effects of intestinal rhythm on general bloodpressure. J Physiol (Lond) 74:490–498
Blakeley C, Tinker J (1983) Vasodilators in acute circulatory failure. Inten Care Med 9:5–11
Dornhorst AC, Howard P, Leathart GL (1952) Respiratory variations in blood pressure. Circulation 6:553–558
Gebber GL (1980) Central oscillators responsible for sympathetic nerve discharge. Am J Physiol 239:H143-H155
Gilston A (1984) Cyclic variations in blood pressure. Letter. Crit Care Med 12:925–926
Golenhofen K, Hilderbrandt G (1958) Die Bezichungen des Blutdrucksrhythmus zu Atmung und peripherer Durchblutung. Pflügers Arch 267:27–45
Guyton AC, Harris JW (1951) Pressoreceptor-autonomic oscillation: a probable cause of vasomotor waves. Am J Physiol 165:158–166
Guyton AC, Satterfield JH (1952) Vasomotor waves possibly resulting from CNS ischemic reflex oscillation. Am J Physiol 170:601–605
Kaminski RJ, Meyer GA, Winter DL (1970) Sympathetic unit activity associated with Mayer waves in the spinal dog. Am J Physiol 219:1768–1771
Koepchen HP (1984) History of studies and concepts of blood pressure waves. In: Miyakawa K, Koepchen HP, Polosa C (eds) Mechanisms of blood pressure waves. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg New York Tokyo, pp 3–23
Mayer S (1876) Studien zur Physiologie des Herzens und Blutgefäße: V. Über spontane Blutdruckschwankungen. S-B Akad Wiss Wien, math-nat Kl 74:281–307
Miller RR, Vismara LA, Williams DO, Amsterdam EA, Mason DT (1976) Pharmacological mechanisms for left ventricular unloading in clinical congestive heart failure. Differential effects of nitroprusside, phentolamine, and nitroglyccrin on cardiac function and peripheral circulation. Circ Res 39:127–133
Preiss G, Iscoe S, Polosa C (1975) Analysis of a periodic breathing pattern associated with Mayer waves. Am J Physiol 228:768–774
Preiss G, Polosa C (1974) Patterns of sympathetic neuron activity accociated with Mayer waves. Am J Physiol 226:724–730
Schwartz AJ, Conahan III TJ, Jobes DR, Andrews RW, MacVaugh III H, Ominsky AJ (1980) Pcripheral vascular response to potassium administration during cardiopulmonary bypass. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 79:237–240
Sehested J, Schultze G (1982) Vasomotor waves and blood pressure response to crect posture after operation for aortic coarctation. Br Heart J 48:357–363
Seller H, Langhorst P, Polster J, Koepchen HP (1967) Zcitliche Eigenschaften der Vasomotorik II. Erscheinungsformen und Entstehung spontaner und nervös induzierter Gefäßrhythmen. Pflügers Arch 296:110–132
Suwa K, Asahara H (1978) Vasomotor waves during cardiopulmonary bypass. Tohoku J Exp Med 125:45–51
Tuzel IH (1974) Sodium nitroprusside: a review of its clinical effectiveness as a hypotensive agent. J Clin Pharmacol 14:494–503
Vainionpää V, Timisjärvi J, Saarela E (1985) Spontaneous oscillations of systemic arterial pressure during cardiopulmonary bypass in man. Basic Res Cardiol 80:37–46
Wallin BG, Nerhed C (1982) Relationship between spontaneous variations of muscle sympathetic activity and succeeding changes of blood pressure in man. J Auton Nerv Syst 6:293–302
Wesseling KH, Scttels JJ, Walstra HG, van Esch JHJ, Donders JJ (1982) Baromodulation as the cause of short term blood pressure variability? In: Alberi G, Bajzer Z, Baxa P (eds) Proceed Internat Conf Applied Physics Med Biol, Trieste, Italy, pp 247–275
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vainionpää, V., Timisjärvi, J. Spontaneous oscillation of the systemic arterial pressure during cardiopulmonary bypass in man. The effects of some drugs used during the operation. Basic Res Cardiol 82, 178–185 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01907065
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01907065