Summary
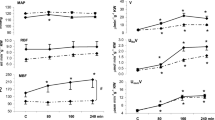
Experiments were carried out in seven conscious macaque monkeys undergoing a water diuresis to determine the effects of raising carotid blood sodium concentration on renal sodium excretion and free water clearance. On separate days each animal received an intracarotid infusion of hypertonic sodium chloride (90 Eq NaCl/kg·body wt./min) for 5 to 10 min, the same hypertonic infusion intravenously, and an intracarotid infusion of isotonic NaCl. None of the infusions produced a change in sodium excretion. However, the intracarotid hypertonic infusion produced a sustained decrease in free water excretion while the other infusion did not. Creatinine clearance was not affected by any of the infusions. The results of these experiments support the view that while the brain of the primate contains an osmotic sensing mechanism it does not contain a mechanism which modulates sodium excretion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersson B, Dallman MF, Olsson K (1969) Evidence for a hypothalamic control of renal sodium excretion. Acta Physiol Scand 75:496–510
Andersson B, Jobin M, Olsson K (1966) Stimulation of urinary salt excretion following injections of hypertonic NaCl-solution into the 3rd brain ventricle. Acta Physiol Scand 67:127–128
Bealer SL (1983) Hemodynamic mechanisms in CNS-induced natriuresis in the conscious rat. Am J Physiol 244:F376-F382
Blaine EH, Denton DA, McKinley MJ, Weller S (1975) A central osmosensitive receptor for renal sodium excretion. J Physiol (London) 244:497–509
Bruning JL, Kintz BL (1977) Computational handbook of statistics. In: Glenview IL, Scott, Foresman and Co, 2nd ed, pp 119–122
Chiu PJS, Sawyer WH (1974) Third ventricular injection of hypertonic NaCl and natriuresis in cats. Am J Physiol 226:463–469
Dorn JB, Levin N, Kaley G, Rothballer AB (1969) Natriuresis induced by injection of hypertonic saline into third cerebral ventricle of dogs. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 131:240–244
Gilmore JP (1983) Neural control of extracellular volume in the human and nonhuman primate. In: Handbook of Physiology — The Cardiovascular System, III Ch 24 pp 885–915
Gilmore JP, Nemeh MN (1984) Salt depletion inhibits cerebral-induced natriuresis in the dog. Am J Physiol 247:F725-F728
Herd A, Barger CA (1964) Simplified technique for chronic catheterization of blood vessels. J Appl Physiol 19:791–792
Kumar MA, Swaminathan S (1977) Search for a natriuretic mechanism sensitive to sodium in the brain of the monkey. J Physiol (London) 272:563–572
Mouw DR, Vander AJ (1970) Evidence for brain Na receptors controlling renal Na excretion and plasma renin activity. Am J Physiol 219:822–832
Mouw DR, Vander AJ, Bourgoignic JJ, Kutschinski SS, Mathias NP (1979) Nonpressor mechanisms in CNS-induced natriuresis. Am J Physiol 237:F157-F166
Olsson K (1973) Further evidence for the importance of cerebrospinal fluid Na concentration in central control of fluid balance. Acta Physiol Scand 88:183–188
Sncdecor GW, Cochran WG (1967) In: Ames IA (ed) Statistical Methods, 6th Iowa State University Press
Swaminathan S (1980) Osmoreceptors or sodium receptors: An investigation into ADH release in the rhesus monkey. J Physiol 307:71–83
Thornborough JR, Passo SS, Rothballer AB (1973) Receptors in cerebral circulation affecting sodium excretion in the cat. Am J Physiol 225:138–141
Wesley CR, Huffman LJ, Gilmore JP (1982) Responsiveness of cerebral osmoreceptors in the anesthetized dog. Proc Soc. Exp Biol Med 171:238–241
Winer BJ (1971) Statistical principles in experimental design. 2nd ed, McGraw-Hill, New York
Zucker IH, Kaley G (1976) Natriuresis induced by intracarotid infusion of hypertonic NaCl, Am J Physiol 230:427–433
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by National Institutes of Health Grant No. HL-13427