Summary
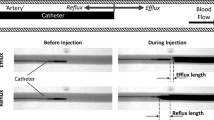
This experimental study described myocardial echo contrast enhancement through coronary venous injections. Retrograde administration of renografin was performed in 15 closed-chest dogs. Two-dimensional echocardiography was used to study myocardial echo contrast enhancement before and after coronary artery occlusion. Digital subtraction venography was used to assess delivery, drainage and shunting of the retrograde injectate. Systolic/diastolic blood pressure in the great cardiac vein measured 7±3/1±0.6 mm Hg and increased to 29±11/5±3 after coronary sinus occlusion and to 55±2.3/15±12 mm Hg during coronary sinus contrast injection. Myocardial contrast echo appearance in a midpapillary left ventricular short axis cross-section was limited to the anteroseptal region, extending to 28.4±11.3% of the section circumference after great cardiac vein injections and 35.3±17% after coronary sinus injections (difference NS). After occlusion of the left anterior descending coronary artery, great cardiac vein contrast injections resulted in opacification of 36.6±9.7% of the section circumference (N.S. vs preocclusion control) and opacified most, but not all asynergic segments. After occlusion of the circumflex coronary artery, myocardial echo contrast uptake was restricted to the septum and the anterior wall. The ischemic and asynergic posterolateral myocardial segments were not opacified. Digital subtraction coronary venography revealed rapid drainage of retrogradely injected contrast to the right atrium, in spite of coronary sinus balloon occlusion via venovenous anastomoses.
Retrograde coronary venous contrast injections may help define myocardial regions which are accessible with retrograde coronary venous interventions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anrep GV, Blalock A, Hammouda M (1923) The distribution of the blood in the coronary blood vessels. J Physiol 67:87–96
Berdeaux A, Farcot SC, Bourdarias JK, Barry M, Bardet J, Giudicelli JF (1981) Effects of diastolic synchronized retroperfusion on regional coronary blood flow in experimental myocardial ischemia. Am J Cardiol 47:1033–1040
Cibulski AA, Markov A, Lehan PH, Galycan J, Smith R, Powers W, Hellems H (1974) Retrograde radioisotope myocardial perfusion patterns in dogs. Circulation 50:159–166
Cibulski AA, Markov A, Lehan PH (1974) External measurement and mapping of myocardial isotopes after coronary venous 85 Krypton and 133 Xenon injections. Am J Cardiol 34:545–551
Evans ME, Christensen GC (1979) Blood vessels of the heart. In: Saunders, W. B. (ed) Miller's Anatomy of the Dog. Philadelphia, pp 647–651
Gregg DE, Dewald D (1938) The immediate effects of the occlusion of the coronary veins on the dynamics of the coronary circulation. Am J Physiol 124:444–456
Feinstein SB, Ten Cate FJ, Zwehl W, Ong K, Maurer G, Tei C, Shah PM, Meerbaum S, Corday E (1984): Two-dimensional contrast echocardiography. I. In vitro development and quantitative analysis of echo contrast agents. J Am Coll Cardiol 3:14–20
Karagueuzian HS, Ohta M, Drury JK, Fishbein MC, Corday E, Meerbaum S, Mandel WS, Peter T (1984) Comparative efficacy of intravenous and coronary venous retroinfusion of procainamide for the management of inducible sustained ventricular tachycardia in conscious dogs during chronic myocardial infarction. In: Mohl W (ed) The Coronary Sinus. Darmstadt: Steinkopff. New York: Springer, pp 385–391
Maurer G, Ong K, Haendchen R, Torres M, Tei C, Wood F, Meerbaum S, Shah PM, Corday E (1984) Myocardial contrast two-dimensional echocardiography: comparison of contrast disappearance rates in normal and underperfused myocardium. Circulation 69:418–429
Maurer G, Punzengruber C, Haendchen RV, Torres MA, Heublein B, Meerbaum S, Corday E (1984) Retrograde coronary venous contrast echocardiography: Assessment of shunting and delineation of regional myocardium in the normal and ischemic canine heart. J Am Coll Cardiol 4:577–586
Meerbaum S, Haendchen RV, Corday E, Pozhitkov M, Fishbein M, Rit J, Lang T, Uchiyama T, Aosaki N, Broffmann J (1982) Hypothemic coronary venous phased retroperfusion: a closed-chest treatment of acute regional myocardial ischemia. Circulation 65:1435–1445
Meerbaum S, Lang TW, Pozhitkov M, Haendchen R, Uchiyama T, Broffmann J, Corday E (1983) Retrograde lysis of coronary artery thrombus by coronary venous streptokinase administration. J Am Coll Cardiol 1:1262–1267
Menasche P, Kural S, Fauchet M (1982) Retrograde coronary sinus perfusions: a safe alternative for ensuring cardioplegic delivery in aortic valve surgery. Ann Thorac Surg 34:647–659
Mohl W, Glogar D, Mayr H, Losert U, Sochor H, Pachinger O, Kaindl F (1984) Reduction of infarct size by intermittent coronary sinus occlusion. Am J Cardiol 53:923–928
Mohl W, Punzengruber C, Moser M, Kenner T, Heimisch W, Haendchen R, Meerbaum S, Maurer G, Conday E (1985) Effects of pressure-controlled intermitted coronary sinus occlusion on regional ischemic myocardial function. J Am Coll Cardiol 5:939–947
Wiggers CJ (1954) The interplay of coronary vascular resistance and myocardial compression in regulating coronary flow. Circ Res 2:271–278
Wyatt HL, Heng MK, Meerbaum S, Hestenes SD, Cobo SM, Davidson RM, Corday E (1979) Cross-sectional echocardiography. I. Analysis of mathematical models for quantifying the mass of the left ventricle in dogs. Circulation 60:1104–1113
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Dr. Punzengruber was supported by a Grant from the Max Kade Foundation, New York
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Punzengruber, C., Maurer, G., Chang, B.L. et al. Factors affecting penetration of retrograde coronary venous injections into normal and ischemic canine myocardium: assessment by contrast echocardiography and digital angiography. Basic Res Cardiol 85, 21–32 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01907011
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01907011