Summary
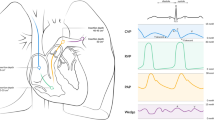
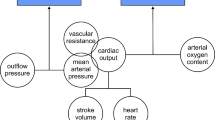
Extracorporeal blood circulation (ECC) provides a steady flow and minimal pulmonary circulation in the absence of cardiac function. Oscillations of systemic arterial pressure were observed in 70 patients during ECC. At the onset of oscillations the frequency was as a rule 4 cycles per minute but depended on the temperature and showed a positive correlation with it. Correspondingly, the amplitude was about 6 mm Hg and depended on aortic pressure and showed a positive correlation with it. During the cooling phase of ECC the frequency decreased and the amplitude increased. The oscillations were independent of central venous pressure and ventilation. The oscillations disappeared either at the beginning of restitution of cardiac function or with decreasing arterial pressure caused by drug administration or rewarming. Arterial blood pressure oscillations have been described in experimental animals under various conditions but also in conscious man. The mechanisms underlying these oscillations are suggested to be nervous in origin, as is possible also in the present findings.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson B, Kenney RA, Neil E (1950) The role of the chemoreceptors of the carotid and aortic regions in the production of Mayer waves. Acta Physiol Scand 20:203–220
Dornhorst AC, Howard P, Leathart GL (1952) Respiratory variations in blood pressure. Circulation 6:553–558
Ferretti R, Cherniak NS, Longobardo G, Levine OR, Morkin E, Singer DH, Fishman AP (1965) Systemic and pulmonary vasomotor waves. Am J Physiol 209:37–50
Gedeon A, Odselius L, Lindblad LE, Wallin G (1983) A mathematical model and some measured characteristics of the carotid baroreceptor control of blood pressure in man. Med Biol Eng Comput 21:65–73
Guyton AC, Harris JW (1951) Pressoreceptor-autonomic oscillation: a probable cause of vasomotor waves. Am J Physiol 165:158–166
Guyton AC, Satterfield JH (1952) Vasomotor waves possibly resulting from CNS ischemic reflex oscillation. Am J Physiol 170:601–605
Hering E (1869) Über den Einfluß der Atmung auf den Kreislauf. S-B Akad Wiss Wien, math-nat Kl 60:829–856
Kaminski RJ, Meyer GA, Winter DL (1970) Sympathetic unit activity associated with Mayer waves in the spinal dog. Am J Physiol 219:1768–1771
Kenner T, Hinghofer-Szalkay H and Hinghofer-Szalkay L (1977) The continuous high-precision measurement of the density of flowing blood. Pflügers Arch 370:25–29
Killip III T, (1962) Oscillation of blood flow and vascular resistance during Mayer waves. Circ Res 11:987–993
Kollai M, Koizumi K (1981) Cardiovascular reflexes and inter-relationships between sympatheti and parasympathetic activity. J auton Nerv Syst 4:135–148
Mayer S (1876) Studien zur Physiologie des Herzens und Blutgefäße: V. Über spontane Blutdruck schwankungen. S-B Akad Wiss Wien, math-nat Kl 74:281–307
Preiss G, Iscoe S, Polosa C (1975) Analysis of a periodic breathing pattern associated with Maye waves. Am J Physiol 228:768–774
Preiss G, Polosa C (1974) Patterns of sympathetic neuron activity associated with Mayer waves. Ann J Physiol 226:724–730
Quintin L, Whalley DG, Wynands JE, Morin JE, Burke J (1981) High dose fentanyl anaesthesis with oxygen for aorto-coronary bypass surgery. Can Anaesth Soc J 28:314–320
Reves JG, Karp RB, Buttner EE, Tosone S, Smith LR, Samuelson PN, Kreusch GR, Oparic S (1982) Neuronal and adrenomedullary catecholamine release in response to cardiopulmonan bypass in man. Circulation 66:49–55
Sebel PS, Bovill JG, Schellekens APM, Hawker CD (1981) Hormonal responses to high-dose fentanyl anaesthesia. A study in patients undergoing cardiac surgery. Br J Anaesth 53:941–948
Sharpey-Schafer EP (1965) Effect of respiratory acts on the circulation. In: Hamilton WF (ed) Handbook of Physiology, sect 2, vol III. American Physiological Society, Washington, D.C., pp 1875–1886
Stanley TH, Philbin DM, Coggins CH (1979) Fentanyl-oxygen anaesthesia for coronary artery surgery: cardiovascular and anti-diuretic hormone responses. Can Anaesth Soc J 26:168–172
Stanley TH, Webster LR (1978) Anaesthetic requirements and cardiovascular effect of fentanyl-oxygen and fentanyl-diazepam-oxygen anaesthesia in man. Anest Analg (Cleve) 57:411–416
Suwa K, Asahara H (1978) Vasomotor waves during cardiopulmonary bypass. Tohoku J Exp Med 125:45–51
Taylor KM (1981) Why pulsatile flow during cardiopulmonary bypass. In: Longmore DB (ed) Towards safer cardiac surgery. MTP Press Ltd, Lancaster (England), pp 483–500
Taylor KM, Bairn WH, Russel M, Brannan JJ, Morton IJ (1979) Peripheral vascular resistance and angiotensin II levels during pulsatile and nonpulsatile cardiopulmonary bypass. Thorax 34:594–598
Traube L (1865) Über periodische Thätigkeits-Äusserungen des vasomotorischen und Hemmungs-Nerven-Zentrums. Zentralbl med Wiss 56:881–908
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vainionpää, V., Timisjärvi, J. & Saarela, E. Spontaneous oscillations of systemic arterial pressure during cardiopulmonary bypass in man. Basic Res Cardiol 80, 37–46 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01906742
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01906742