Summary
Changes of the mineral concentrations of the heart muscle can point at disturbances of myocardial metabolism. Disturbances of heart muscle with functional loss and without coronary of inflammatory heart disease are called myocardosis, especially cardioplegic myocardosis after open-heart surgery with extracorporal bypass.
30 dogs were examined in three groups varying the method of induced cardiac arrest: 1. ischemic cardiac arrest by clamping the ascending aorta, 2. functional cardiac arrest by electrically induced fibrillation and 3. ischemic cardiac arrest and in addition injection of a Mg-aspartate-procain-solution.
Sodium, potassium, magnesium, calcium, copper and zinc were analyzed by atomic absorption spectrophotometry. Specimens from the left and right ventricular wall were examined before and after extracorporal circulation. After a recovery period for one hour the dogs were killed and specimens from the right and left ventricular wall and from the basis and apex of the interventricular septum were taken and reduced to ashes with mineral acids.
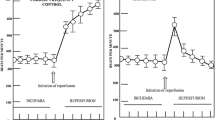
In all animals changes of the mineral content were most marked after the recovery period. In all forms of cardiac arrest mineral metabolism showed monotone reactions: water content increased, potassium and magnesium decreased. Variations of mineral concentrations were more expressed in the right ventricular wall than in the left. Animals with cardiac arrest by electrically induced fibrillation indicated the smallest deviations from the basic values.
The comparison of the values of dogs with sufficient circulation at the end of the experiments and those dogs with medicamentally or mechanically supported circulation at this time showed a more increased water content and simultaneously a decrease of all cations in the group with supported circulation. The decrease of the osmolality of the cations seems to be the metabolic answer to the increased cardioplegic damage of heart muscle.
Zusammenfassung
Bei drei Gruppen von je 10 Hunden wurde der Herzstillstand auf verschiedene Weise verursacht:
-
1.
Ischämische Kardioplegie durch Abklemmen der Aorta
-
2.
Funktioneller Herzstillstand durch elektrisch induziertes Kammerflimmern
-
3.
Injektionskardioplegie mit Cardioplegin
Natrium, Kalium, Magnesium, Kalzium, Kupfer und Zink des Herzgewebes wurden vor und nach dem Bypass und nach einstündiger Erholungsphase in intravital entnommenen Gewebsproben gemessen. Veränderungen im Elektrolytgehalt waren eine Stunde nach Beendigung der extrakorporalen Zirkulation bei allen Gruppen am größten: Der Wassergehalt nimmt zu, Kalium und Magnesium nehmen ab. Bei allen Kardioplegieformen verlaufen die Elektrolytstörungen monoton. Im rechten Ventrikel sind die Veränderungen ausgeprägter als im linken. In der Gruppe Kardioplegie durch elektrisch induziertes Flimmern sind die Abweichungen am geringsten. Der Vergleich von Hunden mit stabilen Kreislaufverhältnissen eine Stunde nach Beendigung des Herzstillstandes, mit solchen Hunden, deren Kreislauf medikamentös oder maschinell gestützt wurde, zeigt eine vermehrte Wasseraufnahme bei gleichzeitig verminderter Konzentration aller Kationen bei den letzteren. Die herabgesetzte Kationenosmolalität ist offenbar Ausdruck der stärkergradigen metabolischen Schädigung der Herzmuskulatur.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Baczyk, S., B. Borzycka, B. Kosicki, Z. Lorkiewicz, Z. inn. Med.27, 369–696 (1974).
Ban, T., N. Tatsuta, J. Kawai, K. Noguchi, K. Tatemichi, Thoraxchirurgie18, 253–265 (1970).
Bersin, Th., Biochemie der Mineral- und Spuren-elemente (Frankfurt 1963).
Bing, R. J., Physiol. Rev.45, 171–213 (1965).
Bretschneider, H. J., Verh. Dtsch. Ges. Kreislaufforschg.30, 11–34 (1964).
Case, R. B., Myocardial potassium loss during ischemia. In: Myocardiology, edt. byE. Bajusz andG. Rona, p. 665–672 (München 1972).
Das, J. B., A. J. Eraklis, J. C. Adams, R. E. Gross, J. Thoracic. Cardiovasc. Surg.62, 449–453 (1971).
Dittrich, H., Beitr. path. Anat.121, 426–435 (1959).
Doerr, W., Z. Kreislaufforschg.40, 92–98 (1951).
Fleckenstein, A., J. Janke, H. J. Döring, O. Leder, Verh. Dtsch. Ges. Kreislaufforschg.37, 345–353 (Steinkopff Verlag Darmstadt 1971).
Forbes, G. B., Natrium. In: Mineral Metabolism, edt.C. L. Comar andF. Bronner B. (New York and London 1962).
Hacker, R. W., In Vorbereitung (1975).
Hartmann, V., Praktische Anästhesie und Wiederbelebung6, 22–34 (1971).
Hazlewood, C. F., D. C. Chang, B. L. Nichols, H. E. Rohrschach, J. of Molecular and Cellular Cardiol.2, 51–53 (1971).
Holden, M. P., M. I. Ionescu, G. H. Wooler, Thorax27, 212–218 (1972).
Isselhard, W., K. L. Lauterjung, J. Witte, O. Giersberg, T. Ban, E. Heugel, Langenbecks Arch. Chir. Suppl. Chir. Forum 293–295 (1972).
Jansen, H. H., Verh. Dtsch. Ges. Path.44, 195–197 (1960).
Jansen, H. H., Basic Res. Cardiol.37, 1–87 (1962).
Jansen, H. H., L. Stapenbeck, Die regionäre Verteilung von Kalium und Natrium im Herzmuskel. Klin. Wschr.44, 470–72 (1962).
Kirsh, M. M., J. Morales, D. R. Kahn, O. Gago, W. Y. Moores, J. H. Dufek, H. Sloan, Arch. Surg.101, 500–502 (1970)
Kübler, W., P. G. Spieckermann, Dtsch. med. Wschr95, 1279–1285 (1970)
Kühn, H., G. Conradi. Zbl. allg. Path.114, 184–188 (1971).
Lossnitzer, K., Zur quantitativen Bestimmung von Kalium, Natrium, Magnesium und Calcium im Herzmuskelgewebe. In: Kalium Magnesium Aspartat, hrsg. von K. Horatz und P. Rittmeyer (Berlin 1973).
Marcial, M. B., R. C. Vedoya, E. Z. Zerbini, G. Verginelli, D. Bittencourt, R. G. do Amaral, Amer. J. Cardiology23, 400–408 (1969).
Meister, H., W. Fischer, Zbl. allg. Path.109, 240–244 (1966).
Mendler, N., S. Hagl, F. Sebening, K.-P. Theobald, Arzneim-Forschung (Drug Res.)22, 909–912 (1972).
Müller, C., H. Lutz, W. Schmitz, F. Reiss, Thoraxchirurgie16, 264–271 (1968).
Paschen, K., Chr. Fuchs, H.-E. Hoffmeister, D. Regensburger, J. Koncz, Thoraxchirurgie20, 43–50 (1972).
Scheinmann, M. M., R. W. Sullivan, J. C. Hutchinson, K. H. Hyatt, The J. of Thoracic and Cardiovasc. Surg.61, 135–140 (1971).
Schuhmann, H. J., G. Conradi, Virchows Arch. Abt. A. Path. Anat.346, 50–53 (1969).
Sebening, F., Langenbecks Arch. klin. Chir.317, 169–208 (1967)
Seelig, M. S., Myocardial loss of functional magnesium. I. Effect on mitochondrial integrity and potassium retention. In: Myocardiology, edt. byE. Bajusz andG. Rona 615–625 (München 1972).
Singh, C. M., C. T. G. Flear, A. Nandra, D. N. Roos, Cardiology56, 128–135 (1971/72).
Struck, E., P. Bottermann, F. Sebening, Thoraxchirurgie17, 388–391 (1969).
Wilde, W. S., Potassium. In: Mineral Metabolism, edt. byC. L. Comar andF. Bronner II B. (New York and London 1962).
Wollenberger, A., E. G. Krause, Amer. J. Cardiol.22, 359–349 (1968).
Wuhrmann, F., Die Myocardose (Basel 1956).
Ziegelhofer, A., K. Siska, V. Holec, M. Fedelesova, I. Frollo, Influence of associated circulation on cardiac metabolism. In: Myocardiology, edt. byE. Bajusz andG. Rona 484–491 (München 1972).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Herrn Prof. Dr. med.W. Doerr zum 60. Geburtstag gewidmet.
Mit 6 Abbildungen und 1 Tabelle
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brandt, G., Hacker, R.W., Mantel, A. et al. Herzmuskelelektrolyte bei der “kardioplegischen Myokardose”. Basic Res Cardiol 70, 671–684 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01906476
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01906476