Abstract
The relation between the pathogenBacillus thuringiensis and the predatorOrius albidepennis (Hem.: Anthocoridae) associated with the greasy cutwormAgrotis ypsilon (Lep.) has been investigated.
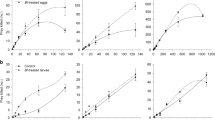
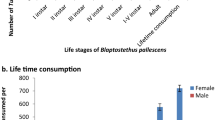
The biology of the predator showed to be affected in terms of nymphal duration, rate of food consumption and egg production when the predator larvae were fed on treated eggs or neonate larvae of the host (A. ypsilon). The effect of B-exotoxin (thuringiensin) on the predator has been also demonstrated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed, S.;O-Neill, J.;Mague, D.L.;Nowalk, R.K., 1978: Toxicity ofBacillus thuringiensis to gypsy moth larvae parasitized byApanteles melanoscelus. Envir. Ent.7, 73–76.
Bucher, G. E., 1963: Transmission of bacterial pathogens by oviposition of a hymenopterous parasite. J. Ins. Pathol.5, 277–283.
Franz, J. M.;Bogenschütz, H.;Hassan, S. A.;Huang, P.;Naton, E.;Suter, H.;Viggiani, G., 1980: Results of joint pesticide test programme by the working group: Pesticides and Benificial Arthropodes. Entomophaga25, 231–236.
Hamel, D. R., 1977: The effects ofBacillus thuringiensis on parasitoids of the western spruce budwormChoristoneura occidentalis (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae), and the spruce conewormDioryctria reniculoides (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae), in Montana. Can. Entomol.100, 1409–1415.
Hassan, S. A.;Bigler, F.;Bogenschütz, H.;Born, J. U.;Birth, S. I.;Huang, P.;Ledieu, M. S.;Naton.,E.;Oomen, P. A.;Ovérmeer, W. P.;Rieckmann, W.;Samson-Petersen, L.;Viggiani, G.;Zon, A.;Van A. O., 1983: Results of the second joint pesticide testing programme by the IOBC/WPRS working group: Pesticides and Benifitcial Arthropods. Z. ang. Ent.95, 151–158.
Herbert, D. A.;Harper, J. D., 1986: Bioassay of B-exotoxion ofBacillus thuringiensis againstGeocoris punctipes (Hemiptera: Lygaeidae). J. ec. Ent.79, 592–595.
Ignofo, G. M.;Gregory, B., 1972: Effect ofBacillus thuringiensis B-exotoxin on larval maturations, adult longevity, fecundity and egg viability in several species of lepidoptera. Envir. Ent.1, 269–272.
Morris, O. N., 1988: Comparative toxicity of S-endotoxin and thuringiensin ofBacillus thuringiensis and mixture for the two for bertha army worm (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J. econ. Ent.81, 135–141.
Salama, H. S.;Zaki, F. N.;Sharaby, A. F., 1982: Effect ofBacillus thuringlensis Berl. on parasites and predators of the cotton leafwormSpodoptera littoralis (Boisd.). Z. ang. Ent.94, 498–504.
Salama, H. S.;Zaki, F. N., 1983: Interaction betweenBacillus thuringiensis Berliner and the parasites and predators ofSpodoptera littoralis (Boisd.) in cotton fields. Z. Ang. Ent.97, 485–490.
Salama, H. S.;Zaki, F. N., 1985: Biological effects ofBacillus thuringiensis on the egg parasitoid,Trichogramma evanescens. Ins. Sci. Appl.6, 145–148.
Salama, H. S.;Salem, S.;Zaki, F. N.;Matter, M., 1990: Control ofAgrotis ypsilon (Hufn.) (Lep.: Noctuidae) on some vegetable crops in Egypt using the microbial agentBacillus thuringiensis. Anz. Schädl., Umweltsch.63, 147–151.
Salama, H. S.;El-Moursy, A.;Zaki, F. N.;Abdelrazek, A., 1991: Parasites and predators of the meal mothPlodia interpunctella Hbn. as affected byBacillus thuringiensis. Berl. J. Appl. Ent.112, 244–253.
Salama, H. S.;Zaki, F. N.;Salem, S.;Ragaei, M., 1995: The use ofBacillus thuringiensis to control two lepidopterous insect pests (Agrotis ypsilon andSpodoptera littoralis). Anz. Schädl., Pflanz., Umwelt.68, 15–17.
Tawfik, M. F. S.;Ata, A. M., 1973: The life history ofOrius albidepennis (Reut.)(Hemiptera: Anthocoridae). Bull. Soc. Ent. Egypt57, 117–126.
Temerak, S. A., 1980: Determination effects of rearing a braconid parasitoid on the pink boror larvae inoculated by different concentrations of the bacteriumBacillus thuringiensis Berl. Z. Ang. Ent.89, 315–319.
Wayne, A G.;Andrew, E. P.;Gregory, K. S., 1986: Interaction betweenBacillus thuringiensis and its B-exotoxin in fall army worm (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) neonate larvae. Flo. Ent.69, 531–536.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hafez, M., Abol-Ela, R., Zaki, F.N. et al. The potential of the predatorOrius albidepennis onAgrotis ypsilon as affected byBacillus thuringiensis . Anz. Schadlingskde., Pflanzenschutz, Umweltschutz 70, 127–130 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01904748
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01904748