Abstract
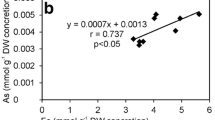
Heavy metal concentrations of a recent salina on the shore of the Mediterranean Sea near Port Said (Egypt) were investigated. Samples for the heavy metal study were taken in different ponds of the salina. It was found that microbial mat dominated brine sediments concentrated and enriched heavy metal 2–3 times more than sediments lacking microbial mat developments, suggesting that cyanobacteria play a major role in this enrichment. Heavy metal enrichment by cyanobacteria was therefore also studied in the laboratory environment. This study is compared with a recent study of Solar Lake and Sabkha Gavish sediments (Sinai, Egypt). Our conclusion is that recent hypersaline environments with ambient microbial mat (potential stromatolite) developments are ideal examples of present-day environments of metal accumulations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartholomé, P. et al. (1993) Diagenetic ore-forming processes at Kamoto, Katango, Republic of the Cango. In: Amstutz, G. C., Bernard, A. J. (eds.) Ores in sediments. Internat. Union Geol. Sci., ser. A, no. 3. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 21–41
Clemmey, H. (1981) Some aspects of the genesis of heavy mineral assemblages in lower Proterozoic uranium-gold conglomerates. Mineralog. Mag. London 44:399–408
Davis, J. H. (1977) Genesis of the southeast Missouri Lead Deposits. Econ. Geol. 22:443–450
Dexter-Dyer, B., Kretzschmar, M., Krumbein, W. E. (1984) Possible microbial pathways playing a role in the formation of Precambrian ore deposits. J. Geol. Soc. 141:251–262
Ehrlich, H. L. (1981) Geomicrobiology, 2nd edn. Dekker, New York, pp 393
Gibbons, M. J. (1978) The geochemistry of sabkha and related deposits. Unpublished PhD Thesis, Newcastle, UK
Horikoshi, T., Nakajima, A., Sakaguchi, T. (1981) Studies on the accumulation of heavy elements in biological systems XIX. Accumulation of uranium by microorganisms. European J. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 12:90–96
Jackson, S. A., Beales, F. W. (1967) An aspect of sedimentary basin evolution — The concentration of Mississippi Valley-type ores during late stages of diagenesis. Bull. Canadian Petroleum Geology. 15:383–433
Jones, G. E., Murray, L., Carr, N. G. (1978) Trace element composition of five cyanobacteria. In: Environmental Biogeochemistry and Geomicrobiology. Krumbein, W. E. (ed.) Ann. Arbor Sci., Ann Arbor, pp 967–973
Krumbein, W. E. (1982) Biogeochemistry and Geomicrobiology of lagoons and lagoonary environments; Seminar on present and future research in coastal lagoons, Beaufort. Unesco Tech. Pap. Mar. Sci. 33:97–109
Krumbein, W. E. (1986) Biotransfer of minerals by microbes and microbial mats. In: Leadbeater, B. S. C., Riding, R. (eds.) Biomineralization in lower plants and animals. Clarendon, Oxford, pp 55–72
Krumbein, W. E., Cohen, Y., Shilo, M. (1977) Solar Lake (Sinai). 4. Stromatolitic cyanobacterial mats. Limnol. Oceanogr. 22:635–656
Krumbein, W. E., Buchholz, H., Franke, P., Giani, D., Giele, C., Wonneberger, K (1979) O2 and H2S coexistence in stromatolites. A model for the origin of mineralogical lamination in stromatolites and banded iron formations: Naturwissenschaften 66:381–389
Lange, I. M., Murray, R. C. (1977) Evaporite brine reflux as a mechanism for moving deep warm brines upward in the formation of Mississippi Valley type base metal deposits. Econ. Geol. 72:107–109
Lorenz, M. G., Krumbein, W. E. (1985) Uranium mobilization from low-grade ore by cyanobacteria. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 21:374–377
Lyons, W. B., Gaudette, H. E. (1985) Trace metal concentrations in sediments from the Gavish Sabkha. In: Friedman, G. M., Krumbein, W. E. (eds.) Hypersaline ecosystems, The Gavish Sabkha. Ecological Studies 53:346–349
Renfro, A. R. (1974) Genesis of evaporite associated stratiform metalliferous deposits — a sabkha process. Econ. Geol. 69:33–45
Sonnenfeld, P., Hudec, P. P., Turek, A., Boon, J. A. (1976) Basemetal concentration in a density stratified evaporite pan. In: Fisher, J. H. (ed.) Reefs and evaporites — concepts and depositional models. Tulsa, O. K.: A.A.P.G., pp 181–187
Smith, G. E. (1976) Sabkha and tidal flat facies control of stratiform Copper deposits in North Texas. In: Walf, K. H. (ed.) Handbook of strata-bound and stratiform ore deposit. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 407–446
Thomson, J., Turekian, K. K., McCaffrey, R. J. (1975) The accumulation of metals in and release from sediments of Long Island Sound. In: Cronin, L. E. (ed.) Estuarine research, vol. 1. Academic Press, New York, pp 28–44
Thiede, D. S., Cameron, E. N. (1978) Concentration of heavy metals in the Elk Point Evaporite Sequence, Saskatchewan. Econ. Geol. 73:405–415
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taher, A.G., Abd el Wahab, S., Philip, G. et al. On heavy metal concentrations and biogenic enrichment in microbial mat environments. Mineral. Deposita 29, 427–429 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01886961
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01886961