Abstract
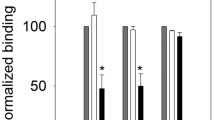
The interaction between epidermal growth factor (EGF) and its receptor molecule is not completely understood and has received much attention recently. Studies combining site-directed mutagenesis and NMR spectroscopy have identified a number of EGF residues that are required for activity and are believed to interact directly with the receptor. Instead of focusing on these residues, this study combines site-directed mutagenesis and NMR spectroscopy to probe the role of the type Iβ-bend located between residues 25 and 26 of the N-terminal subdomain of the protein. Ser25 of murine EGF is replaced by Pro in an attempt to stabilize this turn conformation to produce a variant of mEGF with increased activity relative to that for the native protein. Ser25 is also replaced by Ala, which is found at position 25 in human EGF (hEGF), as a more conservative replacement. Receptor binding studies demonstrate that both mutations produce about a 30% reduction in binding affinity, which is shown to result from local changes within the loop or minor perturbations of residues neighboring the loop rather than from long-range perturbations of theβ-sheet of the N-terminal subdomain. The type Iβ-turn appears to remain intact in both mutants; however, replacement with Pro seems to introduce more flexibility into this region of the protein. These results demonstrate that perturbation of thisβ-turn has little effect on EGF-receptor interactions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EGF:
-
epidermal growth factor
- h:
-
human
- m:
-
murine
- TGFα :
-
typeα transforming growth factor
- NMR:
-
nuclear magnetic resonance
- [S2A]mEGF:
-
mEGF missing the N-terminal asparagine and with the serine at position 2 replaced by alanine
- [S2A,S25A]mEGF and [S2A, S25P]mEGF:
-
replacement of serine at position 25 in [S2A]mEGF by alanine and proline, respectively
- 125I-mEGF:
-
125I-labeled mEGF
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium
- FCS:
-
fetal calf serum
- HEPES:
-
N-(2-hydroxyethyl)piperazine-N′-2-ethanesulfonic acid
- BSA:
-
bovine serum albumin
- COSY:
-
correlated spectroscopy
- DQCOSY:
-
double-quantum filtered COSY
- NOESY:
-
nuclear Overhauser spectroscopy
- NOE:
-
nuclear Overhauser effect
- TOCSY:
-
total correlation spectroscopy
- 3 J(Hα-HN):
-
vicinal spin-spin coupling constant between amide proton and α-proton
- DSS:
-
2,2-dimethyl-2-silapentane-5-sulfonate
- δ:
-
chemical shift in ppm
- ppm:
-
parts per million,
References
Bundi, A., and Wüthrich, K. (1979).Biopolymers 18, 285–297.
Burgess, A. W., Lloyd, C. J., Smith, S., Stanley, E., Walker, F., Fabri, L., Simpson, R. J., and Nice, E. C. (1988).Biochemistry 27, 4977–4985.
Campbell, I. D., and Bork, P. (1993).Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 3, 385–392.
Campion, S. R., Matsunami, R. K., Engler, D. A., and Niyogi, S. K. (1990).Biochemistry 29, 9988–9993.
Campion, S. R., Geck, M. K., and Niyogi, S. K. (1993).J. Biol. Chem. 268, 1742–1748.
Carpenter, G., and Cohen, S. (1990).J. Biol. Chem. 265, 7709–7712.
Carver, J. A., Cooke, R. M., Esposito, G., Campbell, I. D., Gregory, H., and Sheard, B. (1986).FEBS Lett. 205, 77–81.
Celda, B., Biamonti, C., Arnua, M. J., Tejero, R., and Montelione, G. T. (1995).J. Biomol. NMR 5, 161–172.
Cooke, R. M., Wilkinson, A. J., Baron, M., Pastore, A., Tappin, M. J., Campbell, I. D., Gregory, H., and Sheard, B. (1987).Nature 327, 339–341.
Davis, D. G., and Bax, A. (1985).J. Am. Chem. Soc. 107, 2820–2821.
Dyson, H. J., Rance, M., Houghten, R. A., Lerner, R. A., and Wright, P. E. (1988).J. Mol. Biol. 201, 161–200.
Engler, D. A., Matsunami, R. K., Campion, S. R., Stringer, C. D., Stevens, A., and Niyogi, S. K. (1988).J. Biol. Chem. 263, 12384–12390.
Engler, D. A., Montelione, G. T., and Niyogi, S. K. (1990).FEBS Lett. 271, 47–50.
Gao, Y., Boyd, J., Williams, R. J. P., and Pielak, G. J. (1990).Biochemistry 29, 6994–7003.
Higashiyama, S., Abraham, J. A., Miller, J., Fiddes, J. C., and Klagsbrun, M. (1991).Science 251, 936–939.
Hommel, U., Dudgeon, T. J., Fallon, A., Edwards, R. M., and Campbell, I. D. (1991).Biochemistry 30, 8891–8898.
Hommel, U., Harvey, T. S., Driscoll, P. C., and Campbell, I. D. (1992).J. Mol. Biol. 227, 271–282.
Hoyt, D. W., Harkins, R. N., Debanne, M. T., O'Connor McCourt, M., and Sykes, B. D. (1994).Biochemistry 33, 15283–15292.
Jeener, J., Meier, B. H., Bachmann, P., and Ernst, R. R. (1979).J. Chem. Phys. 71, 4546–4553.
Kohda, D., and Inagaki, F. (1988).J. Biochem. 103, 554–571.
Kohda, D., and Inagaki, F. (1992).Biochemistry 31, 11928–11939.
Koide, H., Muto, Y., Kasai, H., Kohri, K., Hoshi, K., Takahashi, S., Tsukumo, K., Sasaki, T., Oka, T., Miyake, T., Fuwa, T., Kohda, D., Inagaki, F., Miyazawa, T., and Yokoyama, S. (1992).Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1120, 257–261.
Koide, H., Yokoyama, S., Katayama, Y., Muto, Y., Kigawa, T., Kohno, T., Takusari, H., Oishi, M., Takahashi, S., Tsukumo, K., Sasaki, T., Miyake, T., Fuwa, T., Kawai, G., and Miyazawa, T. (1994).Biochemistry 33, 7470–7476.
Komoriya, A., Hortsch, M., Meyers, C., Smith, M., Kanety, H., and Schlessinger, J. (1984).Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 81, 1351–1355.
Lewis, P. N., Momany, F. A., and Scheraga, H. A. (1971).Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 68, 2293–2297.
Lewis, P. N., Momany, F. A., and Scheraga, H. A. (1973).Biochim. Biophys. Acta 303, 211–229.
Matsunami, R. K., Campion, S. R., Niyogi, S. K., and Stevens, A. (1990).FEBS Lett. 264, 105–108.
Montelione, G. T., Wüthrich, K., Nice, E. C., Burgess, A. W., and Scheraga, H. A. (1986).Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci USA 83, 8594–8598.
Montelione, G. T., Wüthrich, K., Nice, E. C., Burgess, A. W., and Scheraga, H. A. (1987).Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84, 5226–5230.
Montelione, G. T., Wüthrich, K., and Scheraga, H. A. (1988).Biochemistry 27, 2235–2243.
Montelione, G. T., Wüthrich, K., Burgess, A. W., Nice, E. C., Wagner, G., Gibson, K. D., and Scheraga, H. A. (1992).Biochemistry 31, 236–249.
Moy, F. J., Scheraga, H. A., Liu, J.-F., Wu, R., and Montelione, G. T. (1989).Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86, 9836–9840.
Moy, F. J., Li, Y.-C., Rauenbuehler, P., Winkler, M. E., Scheraga, H. A., and Montelione, G. T. (1993).Biochemistry 32, 7334–7353.
Ösapay, K., and Case, D. A. (1994).J. Biomol. NMR 4, 215–230.
Rance, M., Sørensen, O. W., Bodenhausen, G., Wagner, G., Ernst, R. R., and Wüthrich, K. (1983).Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 117, 479–485.
Ray, P., Moy, F. J., Montelione, G. T., Liu, J. F., Narang, S. A., Scheraga, H. A., and Wu, R. (1988).Biochemistry 27, 7289–7295.
States, D. J., Haberkorn, R. A., and Ruben, D. J. (1982).J. Magn. Reson. 48, 286–292.
Wagner, G., Pardi, A., and Wüthrich, K. (1983).J. Am. Chem. Soc. 105, 58–59.
Wang, B., Yang, X., and Wu, R. (1993).Protein Expression Purification 4, 223–231.
Wilmot, C. M., and Thornton, J. M. (1988).J. Mol. Biol. 203, 221–232.
Wishart, D. S., Sykes, B. D., and Richards, F. M. (1992).Biochemistry 31, 1647–1651.
Wishart, D. S., Bigam, C. G., Holm, A., Hodges, R. S., and Sykes, B. D. (1995).J. Biomol. NMR 5, 67–81.
Wüthrich, K. (1986).NMR of Proteins and Nucleic Acids, Wiley, New York, pp. 169–170.
Zimmerman, S. S., and Scheraga, H. A. (1977).Biopolymers 16, 811–843.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lester, C.C., Wang, B., Wu, R. et al. Structure-function studies of mEGF: Probing the type Iβ-turn between residues 25 and 26. J Protein Chem 14, 753–762 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01886915
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01886915