Summary
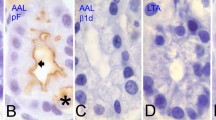
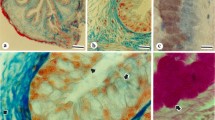
Histochemical studies performed on specimens of intestine from 12 to 37-week human foetuses showed that the epithelial glycoproteins of the goblet cells of the small intestine are non-sulphated sialoglycoproteins containing neutral sugar (hexose, 6-deoxy hexose or N-acetyl hexosamine residues with Periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) reactive vicinal diols), sialic acids without O-acyl substituents, smaller and variable quantities of sialic acids with O-acyl substituents at positions C8 or C9 (or with two or three side chain substituents) and O-acyl sugars (neutral sugars with an ester substituent blocking PAS reactivity). In the lower small intestine glycoproteins containing 8 (or 9)-O-acyl sialic acids are first observed in goblet cells at the tips of the villi. As the foetus matures their quantity increases and they are found in goblet cells located along the length of the villi. Smaller quantities of O-acyl sialic acids and traces of O-acyl sugars occur in the goblet cells of the upper small intestine. The colonic goblet cells contain sulphosialoglycoproteins of two types. The first type, found in the majority of specimens, contains O-sulphate ester, neutral sugar, O-acyl sugars and 8 (or 9)-O-acyl sialic acids. The second type contains O-sulphate ester, neutral sugars, and sialic acids which are either without side chain O-acyl substituents or are a mixture of such acids and 8 (or 9)-O-acyl sialic acids; O-acyl sugars are reduced or absent. The degree of sulphation of the foetal colonic goblet cell epithelial glycoproteins differs with the region of the colon, the level of the crypt and the gestational age of the foetus in a manner consistent with that described by Lev & Orlic (1974). The detection of O-acyl sugars in foetal intestinal glycoproteins adds to the known examples of such sugars and strengthens the suggestion that they are a normal constituent of colonic epithelial glycoproteins.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barger, J. D., &de Lamater, E. D. (1984) The use of thionyl chloride in the preparation of Schiff's reagent.Science 108, 121–2.
Bogomoletz, W. V., Williams, D. T. &Potet, F., (1987) HID-bleu alcian (‘high iron diamine-alcian blue’) et histochemie des mucines en pathologie colique vingt ans apresGastroenterol.Clin. Biol 11, 865–8.
Culling, C. F. A. (1974)Handbook of Histopathological and Histochemical Technique, 3rd edn. London: Butterworth.
Culling, C. F. A., Reid, P. E., Clay, M. G. &Dunn, W. L. (1974) The histochemical demonstration of O-acetylated sialic acid in gastrointestinal mucins. Their association with the potassium hydroxide-periodic acid schiff effect.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 22, 826–31.
Culling, C. F. A., Reid, P. E., Dunn, W. L. &Freeman, H. J. (1981a) The relevance of the histochemistry of colonic mucins based upon their PAS reactivity.Histochem. J. 13, 889–903.
culling, c. f. a., reid, p. e. & worth, a. j. (1981b) Carbohydrate markers in the lower gastrointestinal tract. InMethods and Achievements in Experimental Pathology. Cell Markers (edited byjasming g. & catin, m.) Vol. 10, pp. 77–100.
Filipe, M. I. (1984) Transitional mucosa.Histopathology 8, 707–8.
Filipe, M. I. (1979) Mucins in the human gastrointestinal epithelium: a review.Invest. Cell Pathol. 2, 195–216.
Filipe, M. I. &Branfoot, A. C. (1976) Mucin histochemistry of the colon.Curr. Top. Path. 63, 143–78.
Filipe, M. I. &Fenger, C. (1979) Histochemical characteristics of mucins in small intestine. A comparative study of normal mucosa, benign epithelial tumours and carcinomas.Histochem. J. 11, 277–87.
Garbarsch, C. H. (1969) Histochemical studies on the early development of the human small intestine.Acta Anat. 72, 257–375.
Garbarsch, C. H. &von Bulow, F. A. (1969) Histochemical and electron microscopic studies on the epithelium of the foetal colon with special reference to the occurrence of lipids.Histochemistry 20, 201–10.
Lev, R. (1968) A histochemical study of glycogen and mucin in developing human foetal epithelia.Histochem. J. 1, 152–65.
Lev, R. &Orlic, D. (1974) Histochemical and radio autographic studies of normal human foetal colonHistochemistry 39 301–11.
Lev, R., Siegel, H. I. &Bartman, J. (1972) Histochemical studies of developing human foetal small intestine.Histochemie 29, 103–19.
Lev, R. &Weisberg, H. (1969) Human foetal epithelial glycogen: a histochemical and electron microscopic study.J. Anat. 105, 337–49.
Lillie, R. D. &Pizzolato, P. (1972) Histochemical use of borohydrides as aldehyde blocking reagents.Stain Technol. 43, 13–16.
Park, C. M., Reid, P. E., Walker, D. C. &MacPherson, B. (1987a) A simple practical ‘Swiss roll’ method of preparing tissues for paraffin and methacrylate embedding.J. Microsc. 145, 115–20.
Park, C. M., Reid, P. E., Owen, D. A., Volz, D. &Dunn, W. L. (1987b) Histochemical studies of epithelial cell glycoproteins in normal rat colon.Histochem. J. 19, 546–54.
Reid, P. E., Culling, C. F. A. &Dunn, W. L. (1973) Saponification induced increase in the periodic acid-Schiff reactivity in the gastrointestinal tract: mechanism and distribution of the reactive substance.J. Histochem Cytochem. 21, 473–82.
Reid, P. E., Culling, C. F. A., Dunn, W. L. &Clay, M. G. (1984) Chemical and histochemical studies of normal diseased human gastrointestinal tract II. A comparison between histologically normal small intestine and Crohn's disease of the small intestine.Histochem. J. 16, 253–64.
Reid, P. E., Owen, D. A., Dunn, W. L., Ramey, C. W., Lazosky, D. A. &Clay, M. G. (1985a) Chemical and histochemical studies of normal and diseased human gastrointestinal tract III. Changes in the histochemical and chemical properties of the epithelial glycoproteins in the mucosa close to colonic tumours.Histochem. J. 17, 171–81.
Reid, P. E., Owen, D. A., Ramey, C. W., Dunn, W. L., Jones, E. A., Lazosky, D. A., Allen, E., Park, C. M. &Clay, M. G. (1985b) Chemical and histochemical studies of normal and diseased gastrointestinal tract V. A. differential diagnostic method for the histochemical classification of glycoproteins.Histochem. J. 17, 891–903.
Reid, P. E., Volz, D., Park, C. M., Owen, D. A. &Dunn, W. L. (1987) Methods for the identification, of side chain O-acyl substituted sialic acids and for the simultaneous visualisation of sialic acid, its side chain O-acyl variants and O-sulphate ester.Histochem. J. 19, 396–8.
Reid, P. E., Volz, D., Cho, K. Y. &Owen, D. A. (1988a) A new method for the histochemical demonstration of O-acyl sugars in human colonic epithelial glycoproteins.Histochem. J. 20, 510–18.
Reid, P. E., Walker, D. C., Terpin, T.. &Owen, D. A. (1988b) Histochemical studies of the colonic epithelial glycoproteins of the normal rabbit.Histochem. J. 20, 535–50.
Sugihara, K. &Jass, J. R. (1986) Colorectal goblet cell sialomucin heterogeneity; its relation to malignant disease.J. Clin. Path. 39, 1088–95.
Volz, D., Reid, P. E., Park, C. M., Owen, D. A. &Dunn, W. L. (1987a) Histochemical procedures for the simultaneous visualisation of neutral sugars and either sialic acid and its side chain O-acyl variants or O-sulphate ester I methods based upon the selective periodate oxidation of sialic acids.Histochem. J. 19, 249–56.
Volz, D., Reid, P. E., Park, C. M., Owen, D. A. &Dunn, W. L. (1987b) A new histochemical method for the selective periodate oxidation of total tissue sialic acids.Histochem. J. 19, 311–18.
Williams, G. T. (1985) Transitional mucosa of the large intestine.Histopathology 9, 1237–43.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reid, P.E., Owen, D.A., Magee, F. et al. Histochemical studies of intestinal epithelial goblet cell glycoproteins during the development of the human foetus. Histochem J 22, 81–86 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01885785
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01885785