Summary
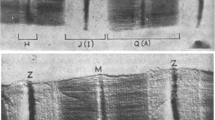
Myosin co-assembles with paramyosin in the thick filaments of invertebrate muscles. The molar ratio of the two proteins varies greatly but where sufficient paramyosin is present it forms the filament core with myosin arranged on its surface. In the fastest acting striated muscles, paramyosin is present in small amounts, and neither its location nor the nature of its interactions with myosin has previously been established. Antibodies to paramyosin have now been used in an attempt to locate the protein in thick filaments that have been isolated from the striated adductor muscle of the scallop and then frayed apart into their constituent subfilaments. Using a gold-conjugated secondary antibody, the location of paramyosin in relation to the subfilaments has been determined by electron microscopy of negatively stained samples. The labelling indicates that paramyosin extends throughout the length of the scallop filaments and appears to be associated with each subfilament, raising the possibility that in these filaments paramyosin may not be confined to a central core domain.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atkinson, S. J. &Stewart, M. (1991) Molecular basis of myosin assembly: coiled-coil interactions and the role of charge periodicities.J. Cell Sci. 14 (Suppl.), 7–10.
Beinbrech, G., Meller, U. &Sasse, W. (1985). Paramyosin content and thick filament structure in insect muscles.Cell and Tissue Res. 241, 607–14.
Bullard, B., Luke, B. &Winkelman, L. (1973) The paramyosin of insect flight muscle.J. Mol. Biol. 75, 359–67.
Bullard, B., Hammond, K. S. &Luke, B. M. (1977) The site of paramyosin in insect flight muscle and the presence of an unidentified protein between myosin filaments and Z-line.J. Mol. Biol. 115, 417–40.
Castellani, L. &Cohen, C. (1987) Rod phosphorylation favours folding in a catch muscle myosin.Proc. Nail. Acad. Sci. USA 84, 4058–62.
Castellani, L., Vibert, P. &Cohen, C. (1983) Structure of myosin/paramyosin filaments from a molluscan smooth muscle.J. Mol. Biol. 167, 853–72.
Cohen, C. (1982) Matching molecules in the catch mechanism.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 79, 3176–89.
Cohen, C. &Holmes, K. C. (1963) X-ray diffraction evidence for α-helical coiled coils in native muscle.J. Mol. Biol. 6, 423–32.
Cohen, C. &Castellani, L. (1988) New perspectives on catch.Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 91C, 31–3.
Cohen, C., Szent-Györgyi, A. G. &Kendrick Jones, J. (1971) Paramyosin and the filaments of molluscan ‘catch’ muscles. I. Paramyosin structure and assembly.J. Mol. Biol. 56, 223–37.
Cohen, C., Lanar, D. E. &Parry, D. A. D. (1987) Amino acid sequence and structural repeats in schistosome paramyosin match those of myosin.Biosci. Rep. 7, 11–16.
Collins, J. H. &Kork E. D. (1980) Actin activation of Ca2+-sensitive Mg2+-ATPase activity ofAcanthamoeba myosin II is enhanced by dephosphorylation of its heavy chains.J. Biol. Chem. 255, 8011–14.
Cooley, L. B., Johnson, W. H. &Krause, S. (1979) Phosphorylation of paramyosin and its possible role in the catch mechanism.J. Biol. Chem. 254, 2195–8.
Craig, R., Padrón, R. &Alamo, L. (1991) Direct determination of myosin filament symmetry by rapid freezing and freeze-substitution electron microscopy.J. Mol. Biol. 220, 125–32.
Davis, J. S. (1988) Assembly processes in vertebrate skeletal thick filament formation.Ann. Rev. Biophys. Chem. 17, 217–39.
Elliott, A. &Bennett, P. M. (1984) Molecular organization of paramyosin in the core of molluscan thick filaments.J. Mol. Biol. 176, 477–93.
Epstein, H. F. (1988) Modulation of myosin assembly.BioEssays 9, 197–200.
Epstein, H. F., Miller, D. M., Ortiz, I. &Berliner, G. C. (1985) Myosin and paramyosin are organized about a newly identified core structure.J. Cell Biol. 100, 904–15.
Epstein, H. F., Ortiz, I. &Berliner, G. C., (1987) Assemblages of multiple thick filaments in nematode mutants.J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 8, 527–36.
Epstein, H. F., Berliner, G. C., Casey, D. L. &Ortiz, I. (1988) Purified thick filaments from the nematodeCaenorhabditis elegans; evidence for multiple proteins associated with core structures.J. Cell Biol. 106, 1985–95.
Gengyo-Ando, K. &Kagawa, H. (1991) Single charge change on the helical surface of the paramyosin rod dramatically disrupts thick filament assembly inCaenorhabditis elegans.J. Mol. Biol. 219, 429–41.
Hanson, J. &Lowy.J. (1961) The structure of the muscle fibres in the translucent part of the adductor of the oysterCrassostrea angulata.Proc. Roy. Soc. Series B. 154, 173–96.
Hardwicke, P. M. D. &Hanson, J. (1971) Separation of thick and thin myofilaments.J. Mol. Biol. 59, 509–16.
Kagawa, H., Gengyo, K., McLachlan, A. D., Brenner, S. &Karn, J. (1989) Paramyosin gene (unc-15) ofCaenorhabditis elegans. Molecular cloning, nucleotide sequence and models for thick filament structure.J. Mol. Biol. 207, 311–33.
Kiehart, D. P. &Pollard, T. D. (1984) Stimulation ofAcanthamoeba actomyosin ATPase activity by myosin-II polymerization.Nature 308, 864–6.
Levine, R. J. C., Elfvin, M., Dewey, M. M., &Walcott, B. (1976) Paramyosin in invertebrate muscles. II. Content in relation to structure and function.J. Cell Biol. 71, 273–9.
Levine, R. J. C., Kensler, R. W., Stewart, M. &Haselgrove, J. C. (1982) Molecular organization ofLimulus thick filaments. InBasic Biology of Muscles: a Comparative Approach (edited by Twarog, B. M., Levine, R. J. C. & Dewey, M. M.) pp. 37–52. New York: Raven Press.
Levine, R. J. C., Kensler, R. W. &Levitt, P. (1986) Crossbridge and backbone structure of invertebrate thick filaments.Biophys. J. 49, 135–8.
Levine, R. J. C., Chantler, P. D. &Kensler, R. W. (1988) Arrangement of myosin heads onLimulus thick filaments.J. Cell Biol. 107, 1739–47.
Lowey, S., Kucera, J. &Holtzer, A. M. (1963) On the structure of the paramyosin molecule.J. Mol. Biol. 7, 234–44.
Mackenzie, J. M. Jr. &Epstein, H. F. (1980) Paramyosin is necessary for determination of nematode thick filament length.Cell 22, 747–55.
Miller, D. M., Ortiz, I., Berliner, G. C. &Epstein, H. F. (1983) Differential localization of two myosins within nematode thick filaments.Cell 34, 477–90.
Millman, B. M. &Bennett, P. M. (1976) Structure of the cross-striated adductor muscle of the scallop.J. Mol. Biol. 103, 439–67.
Nonomura, Y. (1974) Fine structure of the thick filament in molluscan catch muscle.J. Mol. Biol. 88, 445–55.
Nunzi, M. G. &Franzini-Armstrong, C. (1981) The structure of smooth and striated portions of the adductor muscles of the valves in a scallop.J. Ultrastruct. Res. 76, 134–48.
Nyitray, L., Mocz, G., Szilagyi, L., Balint, M., Lu, R. C., Wong, A. &Gergely, J. (1983) The proteolytic substructure of light meromyosin: localization of a region responsible for the low ionic strength insolubility of myosin.J. Biol. Chem. 258, 13213–20.
Pepe, F. A., Ashton, F. T., Street, C. &Weisel, J. (1986) The myosin filament. X. Observation of nine subfilaments in transverse sections.Tissue Cell 18, 499–508.
Sinard, J. H., Rimm, D. L. &Pollard, T. D. (1990) Identification of functional regions on one tail ofAcanthamoeba myoxin-II using recombinant fusion proteins. II. Assembly properties of tails with NH2- and COOHterminal deletions.J. Cell Biol. 111, 2417–26.
Sohn, R. &Leinward, R. (1990) Sequence requirements for myosin filament assembly.J. Cell. Biochem. 14A, 14 (Abstract).
Squire, J. M. (1981)The Structural Basis of Muscular Contraction. pp. 698. New York: Plenum Press.
Szent-Györgyi, A. G., Cohen, C. &Kendrick-Jones, J. (1971) Paramyosin and the filaments of molluscan ‘catch’ muscles. II. Native filaments: isolation and characterization.J. Mol. Biol. 56, 239–58.
Vibert, P. J. &Craig, R. W. (1983) Electron microscopy and image analysis of myosin filaments from scallop striated muscle.J. Mol. Biol. 165, 303–20.
Vibert, P. &Craig. R. (1985) Structural changes that occur in scallop myosin filaments upon activation.J. Cell Biol. 101, 830–7.
Vibert, P. &Castellani, L. (1989) Substructure and Accessory proteins in scallop myosin filaments.J. Cell Biol. 109, 539–47.
Wallimann, T. &Szent-Györgyi, A. G. (1981) An immunological approach to myosin light-chain function in thick filament linked regulation. 1. Characterization, specificity and cross-reactivity of anti-scallop myosin heavy- and light-chain antibodies by competitive, solid-phase radioimmunoassay.Biochemistry 20, 1176–87.
Waterston, R. H., Epstein, H. F. &Brenner, S. (1974) Paramyosin ofCaenorhabditis elegans.J. Mol. Biol. 90, 285–90.
Wray, J. S. (1979) Structure of the backbone in myosin filaments of muscle.Nature (Lond.) 277, 37–40.
Wray, J. S., Vibert, P. J. &Cohen, C. (1975) Diversity of crossbridge configurations in invertebrate muscles.Nature 257, 561–4.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Castellani, L., Vibert, P. Location of paramyosin in relation to the subfilaments within the thick filaments of scallop striated muscle. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 13, 174–182 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01874154
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01874154