Summary
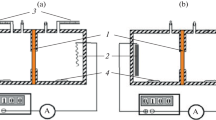
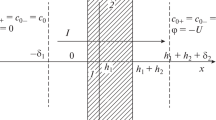
A new way of measuring high diffusional membrane permeabilities of intact erythrocytes is presented using THO and14C-glycol as test solutes. The technique combines the theoretical approach used by Redwood, Rall and Perl (J. Gen. Physiol. 64:706–729, 1974) and an experimental procedure introduced by Wang (J. Am. Chem. Soc. 73:510–513, 1951), which greatly simplifies the performance of the experiments. Permeability coefficients obtained by the new technique compare well to data derived by the approaches hitherto available. In view of its simplicity our method may be appropriate for the serial experiments necessary to characterize the transport mechanisms of water and other highly permeable lipophilic nonelectrolytes and for studies on other single cell systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barton, T.C., Brown, D.A.J. 1964. Water permeability to the fetal erythrocyte.J. Gen. Physiol. 47:839
Chien, S., Dellenback, R.J., Gregersen, S.U., Gregersen, M.I. 1965. Plasma trapping in hematocrit determination. Differences among animal species.Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 119:115
Conlon, T., Outhred, R. 1972. Water diffusion permeability of erythrocytes using an NMR technique.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 288:354–361
Conlon, T., Outhred, R. 1978. The temperature dependence of erythrocyte water diffusion permeability.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 511:408–418
Deuticke, B. 1977. Properties and structural basis of simple diffusion pathways in the erythrocyte membrane.Rev. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 78:1–97
Garrick, R.A., Redwood, W.R. 1977. Membrane permeability of isolated lung cells to nonelectrolytes.Am. J. Physiol. 233:104–109
Garrick, R.A., Patel, B.C., Chinard, F.R. 1980. Permeability of dog erythrocytes to lipophilic molecules: Solubility and volume effects.Am. J. Physiol. 238:107–113
Kutchai, H., Cooper, R.A., Forster, R.E. 1980. Erythrocyte water permeability. The effects of anesthetic alcohols and alterations in the level of membrane cholesterol.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 600:542–552
Mills, R. 1973. Self diffusion in normal and heavy water in the range 1–45°.J. Phys. Chem. 77:685–688
Osberghaus, U. 1980. Messung schneller Transportvorgänge an Erythrozytenmembranen. Doktordissertation. Rheinisch-Westfälische Technische Hochschule. Aachen
Paganelli, C.V., Solomon, A.K. 1957. The rate of exchange of tritiated water across the human red cell membrane.J. Gen. Physiol. 41:259–277
Pirkle, J.L., Ashley, D.L., Goldstein, J.H. 1979. Pulse nuclear magnetic resonance measurements of water exchange across the erythrocyte membrane employing a low Mn concentration.Biophys. J. 25:389–406
Redwood, W.R., Rall, E., Perl, W. 1974. Red cell membrane permeability deduced from bulk diffusion coefficients.J. Gen. Physiol. 64:706–729
Rich, G.T., Sha'aif, R.I., Barton, T.C., Solomon, A.K. 1967. Permeability studies on red cell membranes of dog, cat and beef.J. Gen. Physiol. 50:2391–2405
Saraf, D.N., Witherspoon, P.A., Cohen, L.H. 1963. Diffusion coefficients of hydrocarbons in water: Method for measuring.Science 142:955–956
Savitz, D., Solomon, A.K. 1971. Tracer determinations of human red cell membrane permeability to small nonelectrolytes.J. Gen. Physiol. 58:259–266
Sha'afi, R.I., Rich, G.T., Mikulecky, D.C., Solomon, A.K. 1970. Determination of urea permeability in red cells by minimum method.J. Gen. Physiol. 55:427–450
Sha'afi, R.I., Gary-Bobo, C.M., Solomon, A.K. 1971. Permeability of red cell membranes to small hydrophilic and lipophilic solutes.J. Gen. Physiol. 58:238–258
Vieira, F.L., Sha'afi, R.I., Solomon, A.K. 1970. The state of water in human and dog red cell membranes.J. Gen. Physiol. 55:451–466
Wang, J.H. 1951. Self-diffusion and structure of liquid water with deuterium as tracer.J. Am. Chem. Soc. 73:510–513
Wang, J.H. 1952. Tracer-diffusion of tracer amount of sodium ion in aqueous potassium chloride solutions.J. Am. Chem. Soc. 74:1182–1186
Wang, J.H., Robinson, C.V., Edelman, I.S. 1953. Self-diffusion and structure of liquid water with2H,3H and18O as tracers.J. Am. Chem. Soc. 75:466–470
Witherspoon, P.A., Saraf, D.N. 1965. Diffusion of methane, ethane, propane, andn-butane in water from 25 to 43°C.J. Phys. Chem. 69:3752–3755
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Osberghaus, U., Schönert, H. & Deuticke, B. A simple technique of measuring high membrane permeabilities of human erythrocytes. J. Membrain Biol. 68, 29–35 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01872251
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01872251