Summary
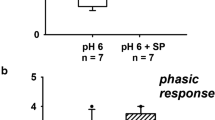
An extracellular adenosine responsive site that stimulates adenylate cyclase activity has been identified in several tissues. There is limited information on the presence and physiologic significance of adenosine receptors in well-defined segments of the mammalian nephron. We therefore examined the effect of adenosine and selected analogues on basal hydraulic conductivity in rabbit cortical collecting tubules (CCT) perfused in vitro. Adenosine and analogues with an intact ribose moiety produced a significant, sustained increase in hydraulic conductivity. No increase in hydraulic conductivity was seen in either time control CCT's or CCT's exposed to an adenosine analogue with an altered ribose moiety. These experiments are compatible with the presence of a functional adenosine receptor which requires an intact ribose moiety and acts to increase hydraulic conductivity in the mammalian CCT.
An intracellular adenosine responsive site, termed the “P site,” which inhibits adenylate cyclase activity, has also been described in several tissues. We therefore examined the effect of aP site agonist on hydraulic conductivity responses to arginine vasopressin, forskolin and cAMP.P site stimulation with 2′5′ dideoxyadenosine inhibited the effect of AVP and of forskolin but not of cAMP to increase hydraulic conductivity. These results are compatible with a functionalP site in the rabbit CCT which acts at the catalytic subunit of adenylate cyclase to inhibit hydraulic conductivity. Together, these results demonstrate purinergic modulation of basal and arginine vasopressin-stimulated water flux in the mammalian collecting tubule.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abboud, H.E., Dousa, T.P. 1983. Action of adenosine on cyclic 3′, 5′-nucleotides in glomeruli.Am. J. Physiol. 244:F633-F638
Al-Zahid, G., Schafer, J.A., Troutman, S. L. Andreoli, T.E. 1977. Effect of antidiuretic hormone on water and solute permeation, and the activation energies for these processes, in mammalian cortical collecting tubules. Evidence for parallel ADH-sensitive pathways for water and solute diffusion in luminal plasma membranes.J. Membrane Biol. 31:103–129
Burg, M., Grantham, J., Abramow, M., Orloff, J. 1966. Preparation and study of fragments of single rabbit nephrons.Am. J. Physiol. 210:1293–1298
Daly, J.W. 1982. Adenosine receptors: Targets for future drugs.J. Mea. Chem. 25:197–207
Diem, K., Lentner, C. 1970. Documenta Geigy: Scientific Tables. (7th ed.) p. 32 Geigy Pharmaceuticals, Ardsley (N.Y.)
Dillingham, M.D., Kim, J.K., Horster, M.F., Anderson, R.J. 1984. Forskolin increases osmotic water permeability in rabbit cortical collecting tubule.J. Membrane Biol. 80:243–248
Dixon, B.S., Anderson, R.J. 1985. Flow rate dependence of net volume flux and hydraulic conductivity response to arginine vasopressin in rabbit cortical collecting tubules. (abstr.)Kid. Int. 27:325
Dobbins, J.W., Laurenson, J.P., Forrest, J.N., Jr. 1984. Adenosine and adenosine analogues stimulate adenosine cyclic 3′, 5′ monophosphate-dependent chloride secretion in the mammalian ileum.J. Clin. Invest. 74:929–935
Hall, D.A., Grantham, J.J. 1980. Temperature effect on ADH response of isolated perfused rabbit collecting tubules.Am. J. Physiol. 239:F595-F601
Hir, M.L., Dubach, U.C. 1984. Sodium gradient-energized concentrative transport of adenosine in renal brush border vesicles.Pfluegers Arch. 401:58–63
Horster, M.F., Zink, H. 1982. Functional differentation of the medullary collecting tubule: Influence of vasopressin.Kid. Int. 22:360–365
Londos, C., Cooper, D.M.F., Wolff, J. 1980. Subclasses of external adenosine receptors.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 77:2551–2554
Londos, C., Wolff, J. 1977. Two distinct adenosine-sensitive sites on adenylate cyclase.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 74:5482–5485
Londos, D., Wolff, J., Cooper, D.M.F. 1983. Adenosine receptors and adenylate cyclase activation.In: Regulatory Function of Adenosine. R.M. Berne, R.T.W. Rall, and R. Rubio, editors. pp.17–32. Martinus Nighoff, Boston
Pohlman, T., Yates, J. Needleman, P., Klahr, S. 1983. Effects of prostacyclin on short-circuit current and water flow in the toad urinary bladder.Am. J. Physiol. 244:F270-F277
Roy, C. 1984. Regulation by adenosine of the vasopressin-sensitive adenylate cyclase in pig-kidney cells (LLC-PKIL) grown in defined mediaEur. J. Biochem. 143:243–250
Seamon, K.B., Padgett, W., Daly, J.W., 1981. Forskolin: Unique diterpene activator of adenylate cyclase in membranes and intact cellsProc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 78:3363–3367
Stivelman, J.C., Skorecki, K.L., Ausiello, D.A., Brenner, B.M. 1984. Adenosine stimulates cyclic AMP production in cultured renal epithelial cells. (abstr.) Proc. 9th. Int. Cong. Nephrol. (Los Angeles) p. 375A
Swinscow, T.D.V. 1980. Statistics at square one. pp. 1–86. Mendip, Bath (England)
Trimble, M.E., Coulson, R. 1984 Adenosine transport in perfused rat kidney and renal cortical membrane vesicles.Am. J. Physiol. 246:F794-F803
Woodcock E.A., Loxley, R., Leung, E., Johnston, C.I. 1984. Demonstration of RA-adenosine receptors in rat renal papillae.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 121:434–440
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dillingham, M.A., Anderson, R.J. Purinergic regulation of basal and arginine vasopressin-stimulated hydraulic conductivity in rabbit cortical collecting tubule. J. Membrain Biol. 88, 277–281 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01871091
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01871091