Abstract
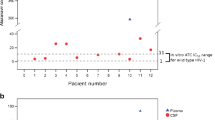
It has been hypothesized that didanosine has a low efficacy in the prevention and treatment of patients with the dementia complex of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) because “...the drug has not been detected in the cerebrospinal fluid”. We investigated didanosine concentrations in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and plasma of four patients with AIDS who were using didanosine chronically. Didanosine levels, 4 h after the last drug administration, averaged 0.16 (±0.03) μmol/l in CSF and 0.70 (±0.27) μmol/l in plasma. When compared with historical data from patients using zidovudine, didanosine concentrations in CSF appeared to be approximately half (on a molar base) those of zidovudine concentrations in the CSF. Whether this difference in CSF levels is the explanation for the presumed lower efficacy of didanosine in the prevention and treatment of AIDS dementia complex remains to be proven. However, it is clear from this study, in contrast with earlier suggestions, that didanosine is able to pass the blood-CSF barrier in human immunodeficiency virus-infected individuals.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yarchoan R, Berg G, Brouwers P, Fischl MA, Spitzer AR, Wichman A, et al. Response of human-immunodeficiencyvirus-associated neurological disease to 3′-azido-3′-deoxythymidine. Lancet 1987;1:132–5.
Pizzo PA, Eddy J, Falloon J, Balis FM, Murphy RF, Moss H, et al. Effect of continuous intravenous infusion of zidovudine (AZT) in children with symptomatic HIV infection. N Engl J Med 1988;319:889–96.
Schmitt FA, Bigley JW, McKinnis R, Logue PE, Evans RW, Drucker JL. Neuropsychological outcome of zidovudine (AZT) treatment of patients with AIDS and AIDS-related complex. N Engl J Med 1988;319:1573–8.
Portegies P, De Gans J, Lange JMA, Derix MM, Speelman H, Bakker M, et al. Declining incidence of AIDS dementia complex after introduction of zidovudine treatment. BMJ 1989;299:819–21.
Tartaglione TA, Collier AC, Coombs RW, Opheim KE, Cummings DK, Mackay SR, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid findings in patients before and during long-term oral zidovudine therapy. Arch Neurol 1991;48:695–9.
Gray F, Geny C, Dournon C, Fenelon G, Lionnet F, Gherardi R. Neuropathological evidence that zidovudine reduces incidence of HIV infection of brain. Lancet 1991;337:852–3.
Vago L, Castagna A, Lazzarin A, Trabattoni G, Cinque P, Costanzi G. Reduced frequency of HIV-induced brain lesions in AIDS patients treated with zidovudine. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 1993;6:42–5.
Sidtis JJ, Gatsonis C, Price RW, Singer EJ, Collier AC, Richamn DD, et al. Zidovudine treatment of the AIDS dementia complex: results of a placebo-controlled trial. Ann Neurol 1993;33:343–9.
Tozzi V, Narciso P, Galgani S, Galgani S, Sette P, Balestra P, et al. Effects of zidovudine in 30 patients with mild to endstage AIDS dementia complex. AIDS 1993;7:683–92.
Portegies P, Enting RH, De Gans J, Algra PR, Derix MM, Lange JMA, et al. Presentation and course of AIDS dementia complex: 10 years of follow-up in Amsterdam, The Netherlands. AIDS 1993;7:669–75.
Geleziunas R, Schipper HM, Wainberg MA. Pathogenesis and therapy of HIV-1 infection of the central nervous system. AIDS 1992;6:1411–26.
Morse GD, Shelton MJ, O'Donnell AM. Comparative pharmacokinetics of antiviral nucleoside analogues. Clin Pharmacokinet 1993;24:101–23.
Portegies P, Enting RH, De Jong MD, Danner SA, Reiss P, Goudsmit J, et al. AIDS dementia complex and didanosine. Lancet 1994;344:759–60.
Burger DM, Kraayeveld CL, Meenhorst PL, Mulder JW, Koks CHW, Bult A, et al. Penetration of zidovudine into the cerebrospinal fluid of patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus. AIDS 1993;7(12):1581–7.
Beijnen JH, Meenhorst PL, Rosing H, Van Gijn R, Los G, Underberg WJM. Analysis of 2′,3′-dideoxyinosine (ddl) in plasma by isocratic high-performance liquid chromatography with ultraviolet detection. J Drug Dev 1990;3:127–33.
Yarchoan R, Mitsuya H, Thomas RV, Pluda JM, Hartman NR, Perno CF, et al.In vivo activity against HIV and favorable toxicity profile of 2′,3′-dideoxyinosine. Science 1989;245:412–5.
Hartman NR, Yarchoan R, Pluda JM, Thomas RV, Marczyk KS, Broder S, et al. Pharmacokinetics of 2′,3′-dideoxyadenosine and 2′,3′-dideoxyinosine in patients with severe human immunodeficiency virus infection. Clin Pharmacol Ther 1990;47:647–54.
Balis FM, Pizzo PA, Butler KM, Hawkins ME, Brouwers P, Husson RN, et al. Clinical pharmacology of 2′,3′-dideoxyinosine in human immunodeficiency virus-infected children. J Inf Dis 1992;165(1):99–104.
Tuntland T, Ravasco RJ, Al-Habet S, Unadkat JD. Efflux of zidovudine and 2′,3′-dideoxyinosine out of the cerebrospinal fluid when administered alone and in combination toMacaca nemestrina. Pharm Res 1994;11(2):312–7.
Wientjes MG, Placke ME, Chang MJ, Page JG, Kluwe WM, Tomaszewski JE. Pharmacokinetics of 2′,3′-dideoxyinosine in dogs. Invest New Drugs 1991;9(2):159–68.
Anderson BD, Hoestery BL, Baker DC, Galinsky RE. Uptake kinetics of 2′,3′-dideoxyinosine into brain and cerebrospinal fluid of rats: intravenous infusion studies. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1990;253(1):113–8.
Butler KM, Husson RN, Balis FM, Brouwers P, Eddy J, El-Amin D, et al. Dideoxyinosine in children with symptomatic human immunodeficiency virus infection. N Engl J Med 1991;324(2):137–44.
Morgan ME, Chi SC, Murakami K, Mitsuya H, Anderson BD. Central nervous system targeting of 2′,3′-dideoxyinosine via adenosine deaminase-activated 6-halo-dideoxypurine prodrugs. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 1992;36(10):2156–65.
Galinsky RE, Flaharty KK, Houstery BL, Anderson BD. Probenecid enhances central nervous system uptake of 2′,3′-dideoxyinosine by inhibiting cerebrospinal fluid efflux. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1991;257(3):972–8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Burger, D.M., Kraayeveld, C.L., Meenhorst, P.L. et al. Study on didanosine concentrations in cerebrospinal fluid. Pharm World Sci 17, 218–221 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01870615
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01870615