Summary
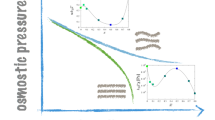
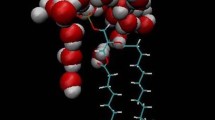
The role of large amounts of membrane-bound water in regulating various functions of the membrane is not clear at present. We have investigated the effect of perturbing the interfacial water structure on the osmotic shrinkage properties, such as water permeability and extent of shrinkage of egg lecithin liposomes. Water structure was perturbed by a series of reagents which have been earlier reported to affect phase transition of dipalmitoyl phosphatidylcholine liposomes by perturbing interfacial water structure. Anomalous variations of osmotic shrinkage properties with concentration of structure maker and breaker reagents have been interpreted to arise from concentration-dependent structural transitions of the ordered water at the membrane-aqueous interface. Various modes of interaction of these reagents on interfacial structured water have been suggested. Influence of molecular size and functional groups on the molecule in actions of some structure makers and breakers were also observed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andreoli, J.E., Troutman, S.L. 1971. An analysis of unstirred layers in series with ‘tight’ and ‘porous’ lipid bilayer membranes.J. Gen. Physiol. 57:464–478
Bean, R., Chan, H. 1969. Thermal transitions in conductivity of ultra-thin membranes.In: The Molecular Basis of Membrane Function. D.C. Tosteson, editor. pp. 133–146. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey
Blok, M.C., Van Deenen, L.L.M., De Gier, J. 1976. Effect of gel to liquid-crystalline phase transition on the osmotic behaviour of phosphatidylcholine liposomes.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 433:1–12
Blok, M.C., Van Der Neut-Kok, E.C.M., Van Deenen, L.L.M., De Gier, J. 1975. The effect of chain length and lipid phase transitions on the selective permeability properties of liposomes.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 406:187–196
Boggs, J.M. 1980. Intermolecular hydrogen bonding between lipids: Influence on organization and function of lipids in membranes.Can. J. Biochem. 58:755–770
Cass, A., Finkelstein, A. 1967. Water permeability of thin lipid membranes.J. Gen. Physiol. 50:1765–1784
Cerbon, J. 1970. The influence of pH and temperature on the limited rotational freedom of the structured water and lipid hydrocarbon chains of natural membranes.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 211:389–395
Clifford, J., Pethica, B.A., Smith, E.G. 1968. A nuclear magnetic resonance investigation of molecular motion in erythrocyte membranes.In: Membrane Models and the Formation of Biological Membranes. L. Bolis and B.A. Pethica, editors. pp. 19–42. North-Holland, Amsterdam
Coster, H.G.L., Simons, R. 1970. Anomalous dielectric dispersion in bimolecular lipid membranes.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 203:17–27
Das, S., Singhal, G.S. 1981. Effect of change of water structure on the phase transition of liposomes of dipalmitoyl phosphatidylcholine.Int. J. Quant. Chem. 20:495–504
Drost-Hansen, W. 1971. Structure and properties of water at biological interfaces.In: Chemistry of the Cell Interface. H.D. Brown, editor. Part B, pp. 1–184. Academic, New York
Drost-Hansen, W., Thorhaug, A.K. 1967. Temperature effects in membrane phenomena.Nature (London) 215:506–508
Finch, E.D., Schneider, A.S. 1975. Mobility of water bound to biological membranes: A proton NMR relaxation study.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 406:146–154
Franks, F. 1966. Solute-water interactions and the solubility behaviour of long chain paraffin hydrocarbons.Nature (London) 210:87–88
Glasel, J.A. 1970. Deuteron magnetic relaxation studies on the solution properties of some denaturing agents and surfactants.J. Am. Chem. Soc. 92:372–375
Glasel, J.A. 1970. Participation of water in conformational changes of biopolymers as studied by deuteron magnetic relaxation.J. Am. Chem. Soc. 92:375–381
Hauser, H. 1975. Lipids.In: Water—A Comprehensive Treatise. F. Franks, editor. Vol. 4, pp. 209–303. Plenum, New York
Horne, R.A. 1969. Marine Chemistry: The Structure of Water and the Chemistry of the Hydrosphere. Wiley-Interscience, New York
Inoue, K. 1974. Permeability properties of liposomes prepared from dipalmitoyl lecithin, dimyristoyl lecithin, egg lecithin, rat liver lecithin and beef brain sphingomyelin.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 339:390–402
Jeffrey, G.A., Jordan, T.H., McMullan, R.K. 1967. Clathrate hydrates of some amines.Science 155:689–691
Jung, O.Y., Carlson, L.M., Balzer, C.J. 1973. Characteristics of the permeability barrier of human erythrocyte ghosts to nonelectrolytes.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 298:101–107
Kaatze, U., Henze, R., Pottel, R. 1979. Dielectric relaxation and molecular motions in C14-lecithin-water systems.Chem. Phys. Lipids 25:149–177
Katz, Y., Diamond, J.M. 1974. Nonsolvent water in liposomes.J. Membrane Biol. 17:87–100
Kjellander, R. 1978. Water—A structural element in model membrane systems: An approach to some structural changes in the lecithin-water system.J. Colloid Interface Sci. 66:303–312
Klotz, I.M. 1970. Water: Its fitness as molecular environment.In: Membranes and Ion Transport. E.E. Bittar, editor. Vol. 1, pp. 93–122. Wiley-Interscience. London
Ladbrooke, B.D., Chapman, D. 1969. Thermal analysis of lipids, proteins and biological membranes. A review and summary of some recent studies.Chem. Phys. Lipids 3:304–367
Lyman, G.H., Papahadjopoulos, D., Preisler, H.D. 1976. Phospholipid membrane stabilization by dimethylsulfoxide and other inducers of Friend leukemic cell differentiation.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 448:460–473
Lyman, G.H., Preisler, H.D., Papahadjopoulos, D. 1976. Membrane action of DMSO and other chemical inducers of Friend leukemic cell differentation.Nature (London) 262:360–363
Macey, R.I., Karan, D.M., Farmar, R.E.L. 1972. Properties of water channels in human red cells.In: Biomembranes—Passive Permeability of Cell Membranes. F. Kreuzer and J.F.G. Slegers, editors. L.A. Manson, series editor. Vol. 3, pp. 331–340. Plenum, New York
Micelli, S., Galucci, E., Lippe, C. 1978. Nonelectrolyte permeability through black lipid membranes with different surface charge.Arch. Int. Physiol. Biochim. 86:755–759
Naftalin, R.J. 1971. The role of unstirred layers in control of sugar movements across red cell membranes.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 233:635–643
Nelson, S.S., Blei, I. 1966. Model Membrane Studies Related to Ionic Transport in Biological Systems. Office of Saline Water, Research and Development Progress Report 221. U.S. Govt. Printing Office, Washington, D.C.
Nichols, J.W., Deamer, D.W. 1980. Net proton-hydroxyl permeability of large unilamellar liposomes measured by an acid-base titration technique.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 77:2038–2042
Oku, N., Nojima, S., Inoue, K. 1980. Selective release of nonelectrolytes from liposomes upon perturbation of bilayers by temperature change or polyene antibiotics.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 595:277–290
Papahadjopoulos, D., Nir, S., Ohki, S. 1971. Permeability properties of phospholipid membranes: Effect of cholesterol and temperature.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 266:561–583
Petersen, D.C. 1980. Water permeation through the lipid bilayer membrane: Test of the liquid hydrocarbon model.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 600:666–677
Phillips, M.C., Finer, E.G., Hauser, H. 1972. Differences between conformations of lecithin and phosphatidylethanol-amine polar groups and their effects on interactions of phospholipid bilayer membranes.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 290:397–402
Redwood, W.R., Haydon, D.A. 1969. Influence of temperature and membrane composition on the water permeability of phospholipid bilayers.J. Theor. Biol. 22:1–8
Schneider, A.S., Middaugh, C.R., Oldewurtel, M.D. 1979. Role of bound water in biological membrane structure: Fluorescence and infrared studies.J. Supramol. Struct. 10:265–275
Schneider, M.J.T., Schneider, A.S. 1972. Water in biological membranes: Adsorption isotherms and circular dichroism as a function of hydration.J. Membrane Biol. 9:127–140
Solomon, A.K. 1972. Properties of water in red cell and synthetic membranes.In: Biomembranes—Passive Permeability of Cell Membranes. F. Kreuzer and J.F.G. Slegers, editors. L.A. Manson, series editor. Vol. 3, pp. 299–330.
Stein, W.D. 1967. The Movement of Molecules Across Cell Membranes. Academic, New York
Szmant, H.H. 1975. Physical properties of dimethyl sulfoxide and its function in biological systems.In: Biological Actions of Dimethylsulfoxide. S.W. Jacob, and R. Herschler, editors.Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 243:20–23
Thompson, T.E. 1964. The properties of bimolecular phospholipid membranes.In: Cellular Membranes in Development. M. Locke, editor. pp. 83–96. Academic, New York
Yeagle, P.L., Hutton, W.C., Huang, C., Martin, R.B. 1975. Head group conformation and lipid cholesterol association in phosphatidylcholine vesicles: A31P (1H)-nuclear Overhauser effect study.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 72:3477–3481
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Das, S., Singhal, G.S. Role of interfacial structured water in membrane: Osmotic properties ofl-α-egg lecithin liposomes. J. Membrain Biol. 86, 221–227 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01870601
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01870601