Summary
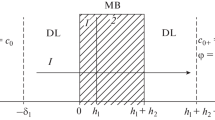
A generalized form of the electrodiffusion equation, allowing for any shape of symmetrical energy barrier and any spatial dependence of the diffusion coefficient, is used to deduce theoretically the carrier-mediated conductance for thin (e.g., bilayer) membranes in the limit of low applied current. Both the Nernst-Planck and the Eyring single-barrier treatments are special cases of this more general approach, which allows for the effect of non-uniform properties of the lipid and non-uniform profiles of the forces acting within the membrane interior. Two independent mechanisms for ions to cross the membrane-solution interfaces are considered; namely, (1) the reaction at the interface between ions from solution and carriers from the membrane, and (2) the partition across the interfaces of complexes already formed in the solution. The rates of these reactions are taken into account using the rate equations of chemical kinetics; and the Poisson-Boltzmann equation is integrated in the aqueous solutions to evaluate the effect of charged polar head groups of the lipid. The analysis leads to an expression for the conductance, which, in the approximation of constant field, is an explicit function of such experimentally variable parameters as the concentrations and types of permeant ions and carriers in the aqueous phases, the total ionic strength and the nature of the polar head groups of the lipid. The functional relationship observable in an unknown membrane can, in principle, enable one to deduce such information as the mechanism of ion permeation across the interfaces, the magnitude of the surface charge, and the degree of ion-carrier complexation in the aqueous solutions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ciani, S. M., Eisenman, G., Laprade, R., Szabo, G. 1973. Theoretical analysis of carrier-mediated electrical properties of bilayer membranes.In: Membranes—A Series of Advances. G. Eisenman, editor. Vol. 2, p. 61. Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York.
Ciani, S. M., Eisenman, G., Szabo, G. 1969. A theory for the effect of neutral carriers such as the macrotetralide actin antibiotics on the electric properties of bilayer membranes.J. Membrane Biol. 1:1.
Diebler, H., Eigen, M., Ilgenfritz, G., Maas, G., Winkler, R. 1969. Kinetics and mechanism of reactions of main group metal ions with biological carriers.Pure Appl. Chem. 20:93.
Eisenman, G., Ciani, S., Szabo, G. 1968. Some theoretically expected and experimentally observed properties of lipid bilayer membranes containing neutral molecular carriers of ions.Fed. Proc. Symposia 27:1289.
Feinstein, M. B., Felsenfeld, H. 1971. The detection of ionophorous antibiotic-cation complexes in water with fluorescent probes.Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 68:2037.
Hall, J. E., Mead, C. A., Szabo, G. 1973. A barrier model for current flow in lipid bilayer membranes.J. Membrane Biol. 11:75.
Haydon, D. A., Hladky, S. B. 1972. Ion transport across thin lipid membranes: A critical discussion of mechanisms in selected systems.Quart. Rev. Biophys. 5:187.
Laprade, R., Ciani, S. M., Szabo, G., Eisenman, G. 1972. Equilibrium and kinetic “domains” for trinactin effects on bilayer membranes.Biophys. Soc. Abstr. Sixteenth Annual Meeting, Vol. 12, p. 44a.
Läuger, P., Stark, G. 1970. Kinetics of carrier mediated ion transport across lipid bilayer membranes.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 211:75.
LeBlanc, O. H., Jr. 1971. The effect of uncouplers of oxidative phosphorylation on lipid bilayer membranes: Carbonylcyanidem-Chlorophenylhydrazone.J. Membrane Biol. 4:227.
Markin, V. S., Kristalik, L. I., Liberman, E. A., Topaly, V. P. 1969. Mechanisms of conductivity of artificial phospholipid membranes in the presence of ion carriers.Biofizika 14:256.
Markin, V. S., Pastushenko, V. F., Kristalik, L. I., Liberman, E. A., Topaly, V. P. 1969. Membrane potential and short circuit current in phospholipid membranes in the presence of agents uncoupling oxidative phosphorylation.Biofizika 14:462.
McConnell, H. M. 1970. Molecular motion in biological membranes.In: The Neurosciences: Second Study Program. F. O. Schmitt, editor. p. 697. Rockefeller University Press, New York.
McLaughlin, S. G. A., Szabo, G., Eisenman, G. 1971. Divalent ions and the surface potential of charged phospholipid membranes.J. Gen. Physiol. 58:667.
McLaughlin, S. G. A., Szabo, G., Eisenman, G., Ciani, S. M. 1970. Surface charge and the conductance of phospholipid membranes.Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 67:1268.
Neumcke, B. 1971. Diffusion polarization at lipid bilayer membranes in the presence of a homogeneous chemical reaction in the solutions.Life Sci. 1:85.
Neumcke, B., Läuger, P. 1969. Non-linear electrical effects in lipid bilayer membranes. II. Integration of the generalized Nernst-Planck equation.Biophys. J. 9:1160.
Parlin, R. B., Eyring, H. 1954. Membrane permeability and electrical potential.In: Ion Transport Across Membranes. Hans T. Clarke, editor. p. 103. Academic Press, Inc., New York.
Planck, M. 1890. Über die potential differenz zwischen zwei verdünnten Lösungen binärer Electrolyte.Ann. Phys., Lpz. 40:561.
Stark, G., Benz, R. 1971. The transport of potassium through lipid bilayer membranes by the neutral carriers valinomycin and monactin. Experimental studies to a previously proposed model.J. Membrane Biol. 5:133.
Stark, G., Ketterer, B., Benz, R., Läuger, P. 1971. The rate constants of valinomycin-mediated ion transport through thin lipid membranes.Biophys. J. 11:981.
Szabo, G., Eisenman, G., McLaughlin, S. G. A., Krasne, S. 1972. Ionic probes of membrane structure.Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 195:273.
Verwey, E. J. W., Overbeek, J. Th. G. 1948. Theory of the Stability of Lyophobic Colloids. Elsevier Publishing Co., New York.
Walz, D., Bamberg, E., Läuger, P. 1969. Non-linear electrical effects in lipid bilayer membranes. I. Ion injection.Biophys. J. 9:1150.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ciani, S., Laprade, R., Eisenman, G. et al. Theory for carrier-mediated zero-current conductance of bilayers extended to allow for nonequilibrium of interfacial reactions, spatially dependent mobilities and barrier shape. J. Membrain Biol. 11, 255–292 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01869826
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01869826