Summary
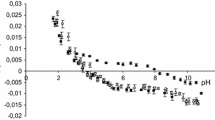
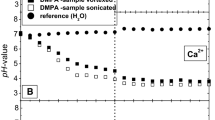
Mn2+ binding to phosphatidylserine (PS) vesicles was measured by EPR as a function of [Na+] and pH. At nearly physiological monovalent salt concentration the apparent Mn2+ affinity (K a) increased monitonically over the pH range 5.7–8.35, withK a roughly α[H+]−1 above pH 7.3. It was found, moreover, thatK a fell off more rapidly with added NaCl at pH 6.1 than at pH 7.87. Qualitatively, these results are consistent with two types of Mn2+-PS binding: (i) simple adsorption and (ii) adsorption with the release of an amino proton from PS. The existence of Mn2+-induced H+ displacement from PS was verified through titration measurements, employing a pH electrode.
When H+ displacement is taken into account, the variation inK a with [Na+] observed at pH 6.1 is found to be in reasonably good agreement with that expected from the Gouy-Chapman-Stern theory of ionic binding to charged surfaces.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramson, M., Katzman, R., Gregor, H.P. 1964. Aqueous dispersions of phosphatidylserine.J. Biol. Chem. 239:70
Eisenberg, M., Gresalfi, T., Riccio, T., McLaughlin, S. 1979. Adsorption of monovalent cations to bilayer membranes containing negative phospholipids.Biochemistry 18:5213
Kurland, R., Newton, C., Nir, S., Papahadjopoulos, D. 1979. Specificity of Na+ binding to phosphatidylserine vesicles from a23Na NMR relaxation rate study.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 551:137
MacDonald, R.C., Simon, S.A., Baer, E. 1976. Ionic influences on the phase transition of dipalmitoylphosphatidylserine.Biochemistry 15:885
McLaughlin, S. 1977. Electrostatic potentials at membranesolution interfaces.In: Current Topics in Membranes and Transport. Vol. 9, p. 71. F. Bronner and A. Kleinzeller, editors. Academic Press, New York
McLaughlin, A., Grathwohl, C., McLaughlin, S. 1978. The adsorption of divalent cations to phosphatidylcholine bilayer membranes.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 513:338
McLaughlin, S., Szabo, G., Eisenman, G. 1971. Divalent ions and the surface poential of charged phospholipid membranes.J. Gen. Physiol. 58:667
Nir, S., Newton, C., Papahadjopoulos, D. 1978. Binding of cations to phosphatidylserine vesicles.Bioelectrochem. Bioenerg. 5:116c
Papahadjopoulos, D. 1968. Surface properties of acidic phospholipids: Interaction of monolayers and hydrated liquid crystals with uni- and bi-valent metal ions.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 163:240
Puskin, J.S. 1977. Divalent cation binding to phospholipids: An EPR study.J. Membrane Biol. 35:39
Puskin, J.S., Martin, T. 1979. Divalent cation binding to phospholipid vesicles. Dependence on temperature and lipid fluidity.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 552:53
Watts, A., Marsh, D., Knowles, P.F. 1978. Characterization of dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine vesicles and their dimensional changes through the phase transition: Molecular control of membrane morphology.Biochemistry 17:1792
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Puskin, J.S., Coene, M.T. Na+ and H+ dependent Mn2+ binding to phosphatidylserine vesicles as a test of the Gouy-Chapman-Stern theory. J. Membrain Biol. 52, 69–74 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01869007
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01869007