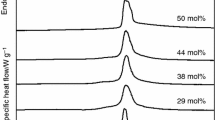
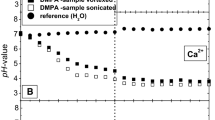
Summary
Na+ and sugar permeabilities of egg lecithin bilayers were measured using curved bilayers and planar bilayers as represented by single-bilayer vesicles and black lipid films, respectively. The Na+ permeability coefficient measured with single-bilayer vesicles at 25°C is (2.1±0.6)×10−13 cm sec−1. Because of technical difficulties it has been impossible to measure ionic permeabilities of values lower than about 10−10 cm sec−1 in planar (black) lipid bilayers using tracer methods. Thed-glucose andd-fructose permeabilities were measured with both curved and planar bilayers. The permeability coefficients measured with vesicles at 25°C are (0.3±0.2)×10−10 cm sec−1 for glucose and (4±1)×10−10 cm sec−1 ford-fructose; these are in reasonable agreement with the corresponding values obtained for planar (black) lipid bilayers which are (1.1±0.3)×10−10 cm sec−1 ford-glucose and (9.3±0.3)×10−10 cm sec−1 ford-fructose, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bloom, M., Burnell, E.E., Valic, M.I., Weeks, G. 1975. Nuclear magnetic resonance line shapes in lipid bilayer model membranes.Chem. Phys. Lipids 14:107
Brunner, J., Skrabal, P., Hauser, H. 1976. Single bilayer vesicles prepared without sonication; physico-chemical properties.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 455:322
Brunner, J., Hauser, H., Semenza, G. 1978. Single bilayer lipidprotein vesicles formed from phosphatidylcholine and small intestinal sucrase-isomaltase.J. Biol. Chem. 253:7538
Brunner, J., Hauser, H., Braun, H., Wilson, K.J., Wacker, H., O'Neill, B., Semenza, G. 1979. The mode of association of the enzyme complex sucrase-isomaltase with intestinal brush border membrane.J. Biol. Chem. 254:1821
De Gier, J., Mandersloot, J.G., Van Deenen, L.L.M. 1968. Lipid composition and permeability of liposomes.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 150:666
Feigenson, G.W., Chan, S.I. 1974. Nuclear magnetic relaxation behavior of lecithin multilayers.J. Am. Chem. Soc. 96:1312
Finer, E.G., Flook, A.G., Hauser, H. 1972. Mechanism of sonication of aqueous egg yolk lecithin dispersions and nature of the resultant particles.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 260:49
Finer, E.G., Flook, A.G., Hauser, H. 1972. The nature and origin of the NMR spectrum of unsonicated aqueous egg yolk lecithin dispersions.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 260:59
Graham, D.E., Lea, E.J.A. 1972. The effect of surface charge on the water permeability of phospholipid bilayers.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 274:286
Hauser, H. 1971. The effect of ultrasonic irradiation on the chemical structure of egg lecithin.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 45:1049
Hauser, H., Phillips, M.C., Stubbs, M. 1972. Ion permeability of phospholipid bilayers.Nature (London) 239:342
Hauser, H., Oldani, D., Phillips, M.C. 1973. Mechanism of ion escape from phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylserine single bilayer vesicles.Biochemistry 12:4507
Henson, A.F., Leslie, R.B., Rayner, L., Sanders, N. 1970. A cell design for lipid bilayer studies.Chem. Phys. Lipids 4:345
Horwitz, A.F., Michaelson, D., Klein, M.P. 1973. Magnetic resonance studies on membrane and model membrane systems.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 298:1
Jung, C.Y. 1971. Permeability of bimolecular membranes made from lipid extracts of human red cell ghosts to sugars.J. Membrane Biol. 5:200
Lichtenberg, D., Peterson, N.O., Girardet, J.-L., Kainsho, M., Kroon, P.A., Seiter, C.H., Feigenson, G.W., Chan, S.I. 1975. The interpretation of proton magnetic resonance line widths for lecithin dispersions.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 382:10
Lieb, W.R., Stein, W.D. 1971. The molecular basis of single diffusion within biological membranes.In: Current Topics in Membranes and Transport. F. Bonner and A. Kleinzeller, editors. Vol. 2, pp. 1–39. Academic Press, New York and London
Macek, K. 1963. Sugars.In: Paper Chromatography. I.M. Hais and K. Macek, editors. pp. 289–323. Publishing House of the Czechoslovak Academy of Sciences, Prague
Müller, P., Rudin, D.O. 1969. Translocators in bimolecular lipid membranes: Their role in dissipative and conservative bioenergy transductions.In: Current Topics of Bioenergetics. R.D. Sanadi, editor. Vol. 3, pp. 157–249. Academic Press, New York-San Francisco-London
Papahadjopoulos, D., Nir, S., Ohki, S. 1972. Permeability properties of phospholipid membranes: Effect of cholesterol and temperature.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 266:561
Price, H.D., Thompson, T.E. 1969. Properties of liquid bilayer membranes separating two aqueous phases: Temperature dependence of water permeability.J. Mol. Biol. 41:443
Seiter, C.H.A., Chan, S.I. 1973. Molecular motion in lipid bilayers; a nuclear magnetic resonance line width study.J. Am. Chem. Soc. 95:7541
Stein, W.D. 1967. The Movements of Molecules Across Cell Membranes. pp. 36–124. Academic Press, New York and London
Stockton, G.W., Polnaszek, C.F., Tulloch, A.P., Hasan, F., Smith, I.C.P. 1976. Molecular motion and order in single-bilayer vesicles and multilamellar dispersions of egg lecithin and lecithin-cholesterol mixtures; a deuterium nuclear magnetic reasonance study of specifically labelled lipids.Biochemistry 15:954
Toyoshima, Y., Thompson, T.E. 1975. Chloride flux in bilayer membranes: Chloride permeability in aqueous dispersions of single-walled, bilayer vesicles.Biochemistry 14:1525
Vanderkooi, J.M., Martonosi, A. 1971. Sarcoplasmic reticulum. XVI. The permeability of phosphatidylcholine vesicles for calcium.Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 147:632
Wood, R.E., Wirth, F.P., Jr., Morgan, H.E. 1968. Glucose permeability of lipid bilayer membranes.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 163:171
Zwolinski, B.J., Eyring, H., Reese, C.E. 1949. Diffusion and membrane permeability.J. Phys. Chem. 53:1426
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This paper is dedicated to the memory of Walther Wilbrandt,cuius nomini nullum par elogium.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brunner, J., Graham, D.E., Hauser, H. et al. Ion and sugar permeabilities of lecithin bilayers: Comparison of curved and planar bilayers. J. Membrain Biol. 57, 133–141 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01868999
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01868999