Summary
Metabolic reactions to the increased intake of cholesterol (CH) were studied in ten tupaias (Tupaia belangeri Baf:BIAS, tree shrews), fed a lithogenic diet containing 20% fat and 2% CH. The feeding period was 4 months. Twelve animals on standard diet served as controls.
The CH content was determined in serum, bile, liver, heart, skin, kidney, muscle, jejunum, ileum, and in the total body. In vitro synthesis rates of CH were measured in the liver and in different parts of the gut.
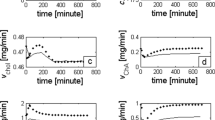
In animals fed the lithogenic diet, serum CH values exceeded those of controls by a factor of 2. However, of all organs examined only the liver showed a rise in the CH content. In hepatic bile, CH values were 14 times higher than in the controls.
Intrahepatic synthesis of CH was suppressed to 7% of the rate in animals on standard diet. In the jejunum, CH synthesis rates were 44%, and in the ileum 15% of those determined in controls.
It is concluded that the administration of a high CH diet induces a feedback mechanism which lowers the production of CH in the liver and small intestine. However, this adaptation does not prevent the rise of CH in serum, liver, and bile which finally results in the formation of gallstones in the gallbladder.
Chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA), added to the lithogenic diet in a daily dose of 20 mg/kg body weight (BW) in five animals, produced an additional significant increase in the hepatic CH content compared to the animals fed the lithogenic diet without CDCA. Other parameters did not differ between the two groups fed the lithogenic diet with and without CDCA.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Besançon F, Marche C, Souchard M, Debray C (1965) Lithiase vesiculaire determinée par le dehydrocholate chez la souris. Seances Soc Biol Ses Fil 159:2333–2337
Den Besten L, Safaie-Shirazi S, Connor WE, Bell S (1974) Early changes in bile composition and gallstone formation induced by a high cholesterol diet in prairie dogs. Gastroenterology 66:1036–1045
Dietschy JM, Siperstein MD (1967) Effect of cholesterol feeding and fasting on sterol synthesis in seventeen tissues of the rat. J Lipid Res 8:97–104
Dietschy JM, Wilson JD (1968) Cholesterol synthesis in the squirrel monkey: Relative rates of synthesis in various tissues and mechanisms of control. J Clin Invest 47:166–174
Dietschy JM, Wilson JD (1970) Medical progress: Regulation of cholesterol metabolism. N Engl J Med 282:1128–1138; 1179–1183; 1241–1249
Gould RG, Taylor CB, Hagermann JS, Warner I, Campbell DJ (1953) Cholesterol metabolism. I. Effect of dietary cholesterol on the synthesis of cholesterol in dog tissue in vitro. J Biol Chem 201:519–528
Ho KJ (1976) Comparative studies on the effect of cholesterol feeding on biliary composition. Am J Clin Nutr 29:698–704
Ho KJ, Taylor CB (1968) Comparative studies on tissue cholesterol. Arch Pathol 86:585–596
Jeske DJ, Dietschy JM (1980) Regulation of rates of cholesterol synthesis in vivo in the liver and cacrass of the rat measured using [3H]water. J Lipid Res 21:364–376
Osuga T, Portman OW (1971) Experimental formation of gallstones in the squirrel monkey. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 136:722–726
Pearlman BJ, Bonorris GG, Phillips MJ, et al. (1979) Cholesterol gallstone formation and prevention by chenodeoxycholic and ursodeoxycholic acids. A new hamster model. Gastroenterology 77:634–641
Pertsemlidis D, Kirchman EH, Ahrens EH (1973) Regulation of cholesterol metabolism in the dog. II. Effects of complete bile diversion and of cholesterol feeding on pool sizes of tissue cholesterol measured at autopsy. J Clin Invest 52:2368
Röschlau P, Bernt E, Gruber W (1974) Enzymatische Bestimmung des Gesamtcholesterins im Serum. Z Klin Chem Klin Biochem 12:403–407
Sabine JR (1977) Cholesterol. Marcel Dekker Inc., New York Basel
Schoenfield LJ, Sjövall J (1966) Bile acids and cholesterol in guinea pigs with induced gallstones. Am J Physiol 211:1069–1074
Schoenfield LJ, Bonorris GG, Ganz P (1973) Induced alterations in the rate limiting enzymes of hepatic cholesterol and bile acid synthesis in the hamster. J Lab Clin Med 32:858–868
Schwaier A (1974) A cage for the successful maintenance of tree shrews (Tupaia belangeri) in captivity. Z Versuchstierk 16:337–340
Schwaier A (1977) Verwendung von Tupaias als Testmodell in der angewandten medizinischen Forschung. 2. Jahresbericht für das Bundesministerium für Forschung und Technologie der BRD
Schwaier A (1979) Tupaias (tree shrews)—a new animal model for gallstone research. First observations of gallstones. Res Exp Med 176:15–24
Schwaier A, Weis HJ, van der Linden J (1979) Tupaias (tree shrews). A new animal model for gallstone research. II. Influence of fat, sugar, and cholesterol on bile composition. Res Exp Med 176:157–172
Tepperman J, Caldwell FT, Tepperman HM (1964) Induction of gallstones in mice by feeding a cholesterol and cholic acid containing diet. Am J Physiol 206:628–634
Tonks DB (1967) The estimation of cholesterol in serum: a classification and critical review of methods. Clin Biochem 1:12–29
Weis HJ, Dietschy JM (1969) Failure of bile acids to control hepatic cholesterogenesis: evidence for endogenous cholesterol feedback. J Clin Invest 48:2398–2408
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van der Linden, J., Schwaier, A. & Weis, H.J. Tupaias (tree shrews) — A new animal model for gallstone research. Res. Exp. Med. 178, 21–28 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01856754
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01856754