Summary
-
1.
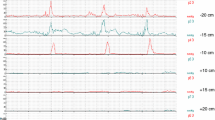
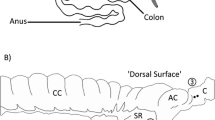
The effects of bethanechol and morphine on electrical and motor activity of the colon were studied by means of needle electrodes and extraluminal strain transducers in 6 unanesthetized cats.
-
2.
Bethanechol and morphine stimulated circular contractions to a similar extent. The contractile pattern after bethanechol injection appeared to be more organized than that after morphine. Bethanechol often caused defecation, morphine induced vomiting.
-
3.
Both drugs lowered slow-wave frequency and increased the occurrence of faster electrical potentials. But bethanechol predominantly activated spiking, whereas the opiate caused long sequences of oscillations besides enhancing spike activity.
-
4.
It is concluded that electromyography of the colon in situ allows differentiation between the effects of the two drugs and indicates different mechanisms of action. The apparent differences observed during previous experimentsin vitro with regard to slow-wave frequency point to the influence of extracolonic factors on the colonic slow wave.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burks, T. F., Long, J. P.: Release of intestinal 5-hydroxytryptamine by morphine and related agents. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther.156, 267 (1967).
Jacoby, H. I., Bass, P., Bennett, D. R.: In vivo extraluminal contractile force transducer for gastrointestinal muscle. J. appl. Physiol.18, 658 (1963).
Rinaldo, J. A., Jr., Orinion, E. A., Simpelo, R. V., Check, F. E., Beauregard, W.: Differential response of longitudinal and circular muscles of intact canine colon to morphine and bethanechol. Gastroenterology60, 438 (1971).
Rinecker, H., Brendel, W.: Kontraktionskraft und -frequenz verschiedener Darmabschnitte des Hundes in vivo. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol.290, 144 (1966).
Türker, R. K., Kaymakçalan, S.: Effect of morphine and nalorphine on the intestinal motility of the cat. Arch. int. Pharmacodyn.193, 397 (1971).
Weisbrodt, N. W., Hug, C. C., Jr., Schmiege, S. K., Bass, P.: Effects of nicotine and tyramine on contractile activity of the colon. Europ. J. Pharmacol.12, 310 (1970).
Wienbeck, M.: The electrical activity of the cat colon in vivo. I. The normal electrical activity and its relationship to contractile activity. Res. exp. Med.158, 286 (1972).
Wienbeck, M., Christensen, J.: Effects of some drugs on electrical activity of the isolated colon of the cat. Gastroenterology61, 470 (1971).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was submitted as part of a thesis in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the habilitation, University of Marburg.
The work was supported in part by “Professor Dr. Adolf Schmidtmann-Stiftung” and by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft Wi 285/2.
I am greatly indebted to Dr. J. Christensen, Department of Internal Medicine, University of Iowa, for his invaluable support and his numerous helpful suggestions and to Dr. N. W. Weisbrodt, University of Texas Medical School in Houston, for his help and his advice.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wienbeck, M. The electrical activity of the cat colonin vivo . Res. Exp. Med. 158, 280–287 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01852211
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01852211