Summary
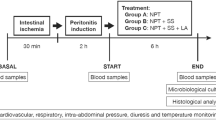
The effects of indomethacin administration on hemodynamics were investigated in canine acute hemorrhagic pancreatitis (AHP). Thirteen mongrel dogs were randomly divided into a fluid treatment group, an indomethacin prophylaxis group (IMP), and an indomethacin therapy (IM) group. Indomethacin (5 mg/kg) was administered as a bolus doage 30min before the induction of AHP in the IMP group. In the IM group, indomethacin was also given as a bolus (5 mg/kg) in 5 min starting 30 min after the induction of AHP. AHP was induced with a mixture of trypsin and sodium taurocholate infused into the pancreatic duct. Hemodynamics were monitored during the 4.5h of surveillance time. Heart rate did not change significantly between the groups. Indomethacin prophylaxis maintained mean arterial pressure at a significantly higher level (P < 0.05) and prevented the initial fall in blood pressure when compared to the fluid treatment or IM group. Indomethacin increased cardiac output (P < 0.05) in the IM group, but did not differ significantly in the IMP group in comparison with the fluid treatment group. In conclusion, the inhibition of the initial fall in blood pressure by indomethacin in AHP suggests prostaglandins to play a role in hemodynamic changes and pancreatic shock to be “septic” as evaluated by hemodynamic changes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson MC, Scoenfeld FB, Iams WB, Suwa M (1967) Circulatory changes in acute pancreatitis. Surg Clin N Am 47:127–140
Carey LC (1970) Low molecular weight dextran in experimental pancreatitis. Am J Surg 119:197–199
Dusting GJ, Moncada S, Vane JR (1979) Prostaglandins, their intermediates and precursors: Cardiovascular actions and regulatory roles in normal and abnormal circulatory system. Prog Cardiovasc Dis 21:405–430
Erdös EG (1968) Effect of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in endotoxic shock. Biochem Pharmacol [Suppl]:283–291
Fletcher JR, Ramwell PW (1977) Modification by aspirin and indomethacin of the haemodynamic and prostaglandin releasing effects ofE. coli endotoxin in the dog. Br J Pharmacol 61:175–181
Glazer G, Bennett A (1976) Prostaglandin release in canine acute haemorrhagic pancreatitis. Gut 17:22–26
Goto T, Fujita T, Otani E, Yamamuro M (1980) The effect of indomethacin and adrenergic receptor blocking agents on rats and canine responses to endotoxin. Circ Shock 7:413–424
Heindrich WL, Hamasaki Y, Said SI, Evering E, Cronin RE (1980) Role of renal nerves and prostaglandins (PG) in endotoxic (E)-induced alterations of systemic and renal haemodynamics. Clin Res 28:844 [Abstr]
Kiviniemi H, Rämö OJ, Ståhlberg M, Laitinen S, Jalovaara P, Viinikka L, Kairaluoma M (1987) Prostacyclin and thromboxane in acute hemorrhagic pancreatitis in dogs. J Surg Res 42:232–236
Lankisch PG, Koop H, Winkler K, Kunze H, Vogt W (1978) Indomethacin treatment of acute experimental pancreatitis in the rat. Scand J Gastroenterol 13:629–633
Macabali GL, Manda AK, Morris JA (1983) An Assessment of the participatory role of prostaglandins and serotonin in the pathophysiology of endotoxic shock. Am J Obstet Gynecol 145:439–445
Olazabal A, Nascimento L (1980) Effect of indomethacin, aspirin and fat-free diet on experimental pancreatitis in the rat. J Lab Clin Med 96:570–576
Sataka K, Rosmanith JS, Appert H, Howard JM (1973) Hemodynamic change and bradykinin levels in plasma and lymph during experimental acute pancreatitis. Ann Surg 178:659–662
Studley JGN, Lee BL, Schenk WG (1982) Pathophysiology of acute pancreatitis: Evaluation of the effect and mode of action of indomethacin in experimental pancreatitis in dogs. J Surg Res 32:563–568
Wallenstein S, Zucker CL, Fleiss JL (1980) Some statistical methods useful in circulation research. Circ Res 47:1–9
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kiviniemi, H., Juhani Rämö, O., Ståhlberg, M. et al. Indomethacin in canine acute hemorrhagic pancreatitis. Res. Exp. Med. 188, 35–40 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01852092
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01852092