Summary
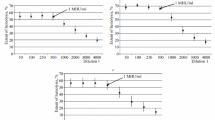
Rabbits immunized against human gammaglobulin (HGG) were fed with either intact HGG or pepsin-digested HGG. Circulating antibodies were determined over an absorption time of 4 h. The oral application of antigenic peptides reduced circulating antibodies from 550 µg/ml to 120 µg/ml. A further parenteral antigen exposure to 50 mg HGG revealed that orally pretreated animals are protected against a marked blood pressure decrease due to antigen antibody reactions. One possible explanation for this phenomenon is that circulating antibodies are fixed in the wall of the gut by enterally applied antigenic peptides and eliminated into the lumen of the gastrointestinal tract. If this phenomenon can be extrapolated to human beings it would be a new therapeutic concept for the treatment of diseases in which circulating antibodies are of importance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andre C, Lambert R, Bazin H, Heremans JF (1974) Interference of oral immunization with the intestinal absorption of heterologous albumin. Eur J Immunol 4:701–704
Andre D, Heremans JF, Vaerman JP, Cambiaso CL (1975) A mechanism for the induction of immunological tolerance by antigen feeding: Antigen antibody complexes. J Exp Med 142:1509–1512
David MF (1979) Desentization of anaphylactically sensitized animals by feeding antigen. J Allergy Clin Immunol 51:138
de Weck A, Girard JF (1972) Specific inhibition of allergic reactions to penicillin in man by a monovalent hapten. II. Clinical studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol 42:798–802
Franks JJ, Takeda V, Reeve EB (1962) Preparation of autologous J-131-albumin for metabolic studies in man. J Lab Clin Med 60:619–631
Hemmings WA (1978) The transmission of high molecular weight breakdown products of protein across the gut of suckling and adult rats. In: Hemmings WA (ed) Antigen absorption by the gut. MTP Press, Lancaster, pp 37–49
Messmer K, Seemann C, Hedin H, Richter W (1980) Anaphylaktoide Reaktionen nach Dextran. Allergologie 3:17–24
Morris JG (1968) Gamma globulin absorption in the newborn. In: Code CF (ed) Handbook of physiology 3. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 1491–1512
Richter W (1973) Built-in hapten inhibition of anaphylaxis by low molecular weight subfractions of a B 512 dextran fraction of MW 3400. Int Arch Allergy 45:930–935
Seifert J (1976) Enterale Resorption großmolekularer Proteine bei Tieren und Menschen. Z Ernährungswiss [Suppl] 18:1–72
Silk DBA (1980) Digestion and absorption of dietary protein in man. Proc Nutr Soc 39:61–70
Stickl H, Kerschner G (1980) Behandlung der Pollinose mit neuen Pollen Kapseln. Fortschr Med 98:341–376
Stokes CR, Swarbrick ET (1977) Induction of tolerance after oral feeding of soluble protein antigen. Biochem Soc Trans 5:1573–1578
Thomas HC, Parrott DMV (1974) Induction of tolerance to a soluble protein by oral administration. Immunology 27:631–637
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by a grant from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seifert, J., Hallfeld, K., Eberle, B. et al. Changes of the immune response due to the absorption of antigenic protein or peptides. Res. Exp. Med. 182, 255–262 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01851715
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01851715