Summary
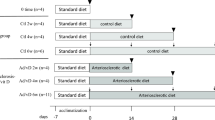
Gross and microscopic morphology of experimental rabbit arteriosclerosis considering some biochemical data are compared with the characteristic arteriosclerotic human lesions. Arterial lesions were induced by three well known methods, repeatedly applied, in the literature: hyperlipidemia, hypoxia, and treatment with catecholamine-thyroxin in 4 groups of each 20 male rabbits. The extent of arterial lesions was expressed in terms of the portion of the aortic surface involved, and was measured planimetrically. Further the intramural cholesterol content of the aortae was determined.
Hyperlipidemic arterial lesions found in 60% of aortic surface consist of intraand extracellular deposition of lipids. These atheroxanthomatous foci were not confined to the arterial wall; lipid loaded macrophages occured also in soft tissue, in spleen and in lymphnodes as well as in myocardium occupying a considerable portion of the organs. The morphological findings are consistent with xanthomateous lesions found in cases of lipid storage diseases and some types of hyperlipoproteinemias and not with typical lesions of human atherosclerosis.
Hypoxic lesions resemble thyroxin-catecholamine induced alterations suggesting a similar pathogenetic causation. 30 to 40% of aortic surface revealed severe changes. The lesions consist of mostly areactive intimal and medial necroses with subsequent calcification giving rise to rarification of the structures of arterial wall. The arterial lesions were comparable with particular human diseases such as calcinosis infantum, medianecrosis (Gsell-Erdheim) and mediacalcinosis (Mönckeberg).
A combination of the mentioned atherogenic agents under additional application of histamine rendered a systemic arterial lesion with particular involvement of coronaries. Not only the gross morphology but also the microscopic features of these lesions revealed a considerable similarity to those of human lesions. The foci presented besides the usual accumulation of lipids, foamcells, and calcifications evident inflammatory reaction and fibrosis with subsequent hyalinosis. The described multifactorial technique counterfies the multietiology of human disease.
Zusammenfassung
Die Morphologie und einige biochemische Daten der experimentellen Arteriosklerose wurden untersucht und mit den charakteristischen pathologisch-anatomischen Läsionen der menschlichen Arteriosklerose verglichen. Die experimentelle Arteriosklerose wurde durch drei besonders häufig angewandte Methoden: Hyperlipidämie, Hypoxie und Katecholamin-Thyroxin-induzierte Hypertonie an jeweils 20 männlichen Kaninchen erzeugt. Die Ausdehnung der Arteriosklerose wurde an Hand des muralen Cholesteringehaltes der Aorten und der befallenen Aortenfläche zum Ausdruck gebracht.
Die hyperlipidämische Arterienläsion zeichnet sich durch starke intra- und extracelluläre Lipideinlagerungen aus. Neben den Arterien kommen lipidbeladene Makrophagen in der Leber, der Milz, den Lymphknoten und dem Myokard vor. Die morphologischen Veränderungen sind nach unseren Befunden am ehesten mit der Xanthomatose im Rahmen einer Lipidspeicherkrankheit vergleichbar.
Die wiederholte Hypoxie erzeugt flächenhafte Verkalkungen der luminalen Intimaabschnitte. In den Aorten nehmen die Läsionen über 30% der Gesamtfläche ein. Dagegen sind Katecholamin-Thyroxin-bedingte Verkalkungen in der Media lokalisiert. Hierbei beträgt die befallene Aortenfläche über 40%. Histologisch findet man in beiden Fällen Verkalkungen ohne jegliche Reaktion. Diese Verkalkungen dürften auf ähnliche pathogenetische Mechanismen zurückgehen. Die Läsionen ähneln menschlichen Erkrankungen wie: Calcinosis infantum, Medianekrose (Gsell-Erdheim) und Mediacalcinose (Mönckeberg).
Eine Kombination der angeführten „sklerogenen“ Faktoren unter gleichzeitiger Histaminbehandlung führte zu einer generalisierten Arterienschädigung mit Beteiligung der Hirnbasis- und Herzkranzarterien. Diese Art der experimentellen Arteriosklerose weist histologisch die größte Ähnlichkeit mit den entsprechenden Veränderungen der menschlichen Arteriosklerose auf. Neben Fetteinlagerungen, Schaumzellbildung und Verkalkung traten deutliche entzündliche Infiltrate auf, die mit Fibrosen und Hyalinosen einhergingen. Die beschriebene multifaktorielle Methode ahmt die Multiätiologie der menschlichen Arteriosklerose nach.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Anitschkow, N.: Über die Veränderungen der Kaninchenaorta bei experimenteller Cholesterinsteatose. Beitr. path. Anat.56, 379–404 (1913).
Astrup, P., Kjeldsen, K., Wanstrup, J.: The effects of exposure to carbon monoxide, hypoxia and hyperoxia on the development of experimental atheromatosis in rabbits. In: Atherosclerosis, Hrsg. von R. J. Jones, S. 108–111. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1970.
Boettcher, C. J. F.: Chemical constituents of human atherosclerotic lesions. Proc. roy. Soc. Med.57, 792–795 (1964).
Buck, R. C., Heagy, F. C.: Uptake of radioactive sulphur by various tissues of normal and cholesterol-fed rabbits. Canad. J. Biochem.36, 63–69 (1958).
Constantinides, P.: Summary of human atherosclerosis. In: Experimental atherosclerosis, Hrsg. von P. Constantinides. Amsterdam-London-New York: Elsevier Publ. Comp. 1965.
Constantinides, P., Booth, J., Carlson, G.: Production of advanced cholesterol atherosclerosis in the rabbits. Arch. Path.70, 712–724 (1960).
Folch, J., Lees, M., Stanley, G. H.: A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J. biol. Chem.226, 497–509 (1957).
Fukuda, T., Kobayashi, T.: On the relation of chemoreceptor stimulation of epinephrine secretion in anoxemia. Jap. J. Physiol.11, 467–472 (1961).
Garbarsch, C., Matthiessen, M. E., Helin, P., Lorenzen, I.: Arteriosclerosis and hypoxia. Part I (Gross and microscopic changes in rabbit aorta induced by systemic hypoxia. Histochemical studies). J. Atheroscler. Res.9, 283–294 (1969).
Geer, J. C., Panganamala, R. v., Newman, H. A. I., Cornwell, D. G.: Mural metabolism. In: Atherosclerosis, Hrsg. von R. J. Jones, S. 6–12. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1970.
Gore, I., Tanaka, K., Larkey, B. J.: Hypercholesteremia and pulmonary arterial lesions produced by thromboplastin. Amer. J. Path.42, 345–356 (1963).
Hartroft, W. S., Ridout, J. H., Sellers, E. A., Best, C. H.: Atheromatous changes in aorta, carotid and coronary arteries of choline-deficient rats. Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. (N.Y.)81, 384–393 (1952).
Hass, G. M.: Observations on vascular structure in relation to human and experimental atherosclerosis. Symposium on Atherosclerosis. Publication 338, National Academy of Sciences, National Research Council, Washington, D. C., pp. 24–32, 1954.
Hass, G. M., Trueheart, R. E., Hemmens, A.: Experimental athero-arterio-sclerosis due to calcific medial degeneration and hypercholesteremia. Amer. J. Path.38, 289–312 (1961).
Haury, H.: Gesamt-Cholesterin im Serum. München: Haury-Katalog 1968.
Haust, M. D., Geer, J. C.: Mechanism of calcification in spontaneous aortic arteriosclerotic lesions of the rabbit. Amer. J. Path.60, 329–337 (1970).
Helin, P., Lorenzen, I.: Arteriosclerosis in rabbit aorta induced by systemic hypoxia. Angiology20, 1–12 (1969).
Helin, P., Lorenzen, I., Garbarsch, C., Matthiessen, M. E.: Relative immunity to arteriosclerosis in rabbits during the hair-shedding period. J. Atheroscler. Res.10, 359–369 (1969).
Kasatkina, L. V.: Effect of histamine on develop of experimental atherosclerosis. Kardiologiya3, 45–48 (1963).
Katz, L. N.: Experimental atherosclerosis. Circulation5, 101–114 (1952).
Katz, L. N., Stamler, J.: Experimental atherosclerosis. Springfield (Ill.): Thomas 1953.
Kaznacheev, J. P., Lozovoi, V. P.: Proceedings of the second plenary meeting of the all-union society of patho-physiologists. Chita153, 1958.
Lindsay, S., Nicholls, C. W., Chaikoff, I. L.: Aortic lesions induced in the bird by diethylstilbestrol injections and cholesterol feeding; a study of their development and regression. Arch. Path.59, 173–184 (1955).
Lopes de Faria, J.: Medianekrose der großen und mittelgroßen Arterien nach orthostatischem Kollaps des Kaninchens. Beitr. path. Anat.115, 373–404 (1955).
Lorenzen, I., Helin, P.: Arteriosclerosis induced by hypoxia. Acta path. microbiol. scand.69, 158–159 (1967).
Matthes, K. J., Junge-Hülsing, G., Schmitt, G., Wagner, H., Oberwittler, W.: Über die Beziehung zwischen gestörtem Mesenchymstoffwechsel und Veränderungen der Lipidkonzentration in der Gefäßwand bei arterieller Hypertension. J. Atheroscler. Res.9, 305–318 (1969).
Meessen, H.: Über die Coronarinsuffizienz nach Histaminkollaps und nach orthostatischem Kollaps. Beitr. path. Anat.99, 329–350 (1937).
Meessen, H.: Veränderungen am Zentralnervensystem des Hundes nach Histaminkollaps. Beitr. path. Anat.109, 352–366 (1944).
Meyer, W. W.: Die Arteriosklerose im Tierexperiment. In: Lehrbuch der speziellen pathologischen Anatomie, Hrsg. von M. Staemmler. Berlin: de Gruyter 1968.
Quintarelli, G., Dellovo, M. C.: The chemical and histochemical properties of alcian blue. IV. Further studies on the methods for the identification of acid glycosaminoglycans. Histochemie5, 196–209 (1965).
Rikhter, A.: Symposium on connetive tissue. Moscow143, 1960.
Rinehart, J. F., Greenberg, L. D.: Vitamin B6 deficiency in the rhesus monkey. With particular reference to the occurence of atherosclerosis, dental caries and hepatic cirrhosis. Amer. J. clin. Nutr.4, 318–328 (1956).
Robertson, A. L.: Oxygen requirements of human arterial intima in atherogenesis. Progr. Biochem. Pharmacol.4, 305–318 (1968).
Ryvkina, D. E.: Effect of histamine on development of experimental atherosclerosis. Usp. sovrem. Biol.44, 389–395 (1957).
Salmon, W. D., Newberne, P. M.: Cardiovascular disease in choline-deficient rats. Effects of choline deficiency, nature and level of dietary lipids and proteins, and duration of feeding on plasma an liver lipid values and cardiovascular lesions. Arch. Path.73, 190–209 (1962).
Schmidtmann, M.: Vigantolversuche. Verh. dtsch. path. Ges.24, 75–82 (1929).
Schwartz, C. J.: The nature of the ground substance changes in experimental lathyrmism and their effect on atherogenesis in cholesterol fed rabbits. Brit. J. exp. Path.40, 44–51 (1959).
Scott, J. E., Dorling, J., Quintarelli, G.: 1964. Zit. in: Differential staining of acid glycosaminoglycans (mucopolysaccharides) by alcian blue in salt solutions. Histochemie5, 221–233 (1965).
Scott, J. E., Quintarelli, G., Dellovo, M. C.: The chemical and histochemical properties of alcian blue. I. The mechanism of alcian blue staining. Histochemie4, 73–85 (1964).
Siggaard-Andersen, J., Bonde-Petersen, F., Hansen, T. I., Mellemgaard, K.: Plasma volume and vascular permeability during hypoxia and carbon monoxide exposure. Scand. J. clin. Lab. Invest.22, Suppl. 103, 39 (1968).
Studer, A.: Experimental platelet thrombus. In: F. Duckert (Hrsg.): Pathogenesis and treatment of thromboembolic diseases. Stuttgart: Schattauer 1966.
Waters, L. L.: In: Symposium on atherosclerosis (Publ. No. 338 of the National Academy of Sciences and the National Research Council, U.S.A.). Washington, p. 91 (1954).
Webster, W. S., Clarkson, T. B., Lofland, H. B.: Carbon monoxide-aggravated atherosclerosis in the squirrel monkey. Exp. molec. Path.13, 36–50 (1968).
Wegelius, O., Asboe-Hansen, G.: Histamine and connective tissue. Acta rheum. scand.3, 18–21 (1957).
Wexler, B. C., Miller, B. F.: Severe arteriosclerosis and other diseases in the rat produced by corticotrophin (ACTH). Science127, 590 (1958).
Zöllner, N. K., Kirsch, K.: Kolorimetrische Bestimmung mit der Sulfophosphovanillin-Reaktion. Z. ges. exp. Med.135, 545–561 (1962).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Mit Unterstützung durch die Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft.
Herrn Prof. Dr. med. Drs. h. c. W. Hallermann zum 72. Geburtstag gewidmet.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Parwaresch, M.R., Mäder, C., Hill, W. et al. Ein kombiniertes Verfahren zur Erzeugung von Arteriosklerose bei Kaninchen in Kurzzeitversuchen. Res. Exp. Med. 160, 269–291 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01851468
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01851468