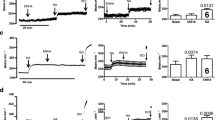
Summary
Isoproterenol-activation of the adenylate cyclase system of human fat cell ghosts was markedly inhibited by dihydroergotamine which had no effect on basal and NaF-stimulated enzyme activity. Our results indicate that the antilipolytic action of this substance in human adipose tissue is probably due to inhibition of catecholamine-sensitive adenylate cyclase activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Braun, T., Hechter, O.: Comparative study of hormonal regulation of adenyl cyclase activity in rat and rabbit fat cell membranes. In: B. Jeanrenaud, D. Hepp (eds.): Adipose tissue, regulation and metabolic functions, pp. 11–19. 1970
Brooker, W. D., Calvert, D. N.: Blockade of catecholamine mediated release of free fatty acids from adipose tissue in vitro. Arch. Int. Pharmacodyn. Ther.169, 117–130 (1967)
Burns, T. W., Langley, P. E.: The effect of alpha and beta adrenergic receptor stimulation on the adenylate cyclase activity of human adipocytes. J. Cyclic Nucleotide Res.1, 321–328 (1975)
Carlson, L. A., Butcher, R. W., Micheli, H.: Fat mobilizing lipolysis and levels of cyclic AMP in human and dog adipose tissue. Acta Med. Scand.187, 525–528 (1970)
Cooper, B., Partilla, J. S., Gregerman, R. I.: Adenylate Cyclase of Human Fat Cells. Expression of epinephrine-sensitive activation revealed by 5-guanylyl-imidodiphosphate. J. Clin. Invest.56, 1350–1353 (1975)
Dale, H. H.: On some physiological actions of ergot. J. Physiol. (Lond.)34, 163–206 (1906)
De Haen, Ch.: Adenylate Cyclase; a new kinetic analysis of the effects of hormones and fluoride ion. J. Biol. Chem.249, 2756–2762 (1974)
Fain, J. N.: Dihydroergotamine, propranolol and the beta adrenergic receptors of fat cells. Fed. Proceed.29, 1402–1407 (1970)
Fain, J. N.: Biochemical aspects of drug and hormone action on adipose tissue. Pharmacological Rev.25, 67–118 (1973)
Gothelf, B., Ellis, S.: Effect of dihydroergotamine (DHE) on liver glycogenolysis and hyperglycemia induced by epinephrine, glucagon and cyclic AMP (cAMP) in the rat. In: 5th Internat. Congr. Pharmacol. (Abstr.), p. 86. 1972
Kather, H., Simon-Crisan, G., Simon, B.: Inhibition of human fat cell adenylate cyclase by clofibrate. Horm. Metab. Res.8, 246–247 (1976)
Kather, H., Simon, B.: Catecholamine-sensitive adenylate cyclase of human fat cell ghosts. Characteristics of the GMP(PNP)-liganded state. Clin. Chim. Acta73, 497–504 (1976)
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., Randall, R. J.: Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem.193, 265–275 (1951)
Murad, F., Chi, Y. M., Rall, T., Sutherland, E. W.: Adenyl Cyclase. III. The effect of catecholamines and choline esters on the formation of adenosine 3,5 monophosphate by preparations from cardiac muscle and liver. J. Biol. Chem.237, 1233–1238 (1962)
Northrop, G., Parks, R. E., Jr.: The effects of adrenergic blocking agents and theophylline on 3,5-AMP-induced hyperglycemia. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther.145, 87–91 (1964)
Northrop, G.: Effects of adrenergic blocking agents on epinephrine and 3,5-AMP-induced responses in the perfused rat liver. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Therap.159, 22–28 (1969)
Poupon, R.: Activity of human adenylate cyclase from human fat cell membranes. Biomedicine23, 438–442 (1975)
Rodbell, M.: Methods of Cyclic Nucleotide Research (ed. M. Chasin), pp. 101–124. New York: Marcel Bekker, Inc. 1972
Salomon, Y., Londos, C., Rodbell, M.: A highly sensitive adenylate cyclase assay. Anal. Biochem.58, 541–548 (1974)
Ward, W. F., Fain, J. N.: The effects of dihydroergotamine upon adenyl cyclase and phosphodiesterase of rat fat cells. Biochem. Biophys. Acta237, 387–390 (1971)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kather, H., Vogt, B. & Simon, B. Catecholamine-sensitive adenylate cyclase of human fat cell ghosts. Res. Exp. Med. 170, 253–257 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01851435
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01851435