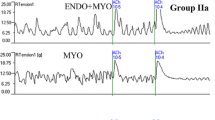
Abstract
Myometrial activity, levels of PGF2α and E2 in uterine flushings were measured in rabbits before and after insertion of four types of IUDs. The results showed that IUDs could increase the uterine contraction during the early stages of insertion. Thereafter, the uterine activity tended to be stable. The sequences of uterine contractility generally were: Cu-IUD > SS-IUD > LNG-Cu-IUD > LNG-IUD. The measurement of prostaglandins, determined by RIA, indicated that the concentrations of PGF2α and E2 in Cu-IUD and SS-IUD groups were higher than those of controls for the early phase of insertion, which was not found after four months of use. Our results suggested that hyperactivity of the uterus in the early stage after insertion of IUDs might be relevant to side-effects like expulsion and pain. Copper released by Cu-IUD stimulates the uterine activity partially through increasing PGF2α and E2 contents. In rabbits wearing LNG-IUD or LNG-Cu-IUD, both PGF2α and E2 levels were low. The relatively low uterine mechanical and electrical activities were also observed in these two groups. Based on these data, it is concluded that development of LNG-Cu-IUD is feasible for reducing expulsion of IUDs.
Resumé
L'activité myométrique, les niveaux de PGF2α et de E2 dans les accès vasomoteurs utérins ont été mesurés sur des lapines avant et après l'insertion de quatre types de dispositifs intra-utérins. Les résultats ont montré que les DIU peuvent augmenter la contraction utérine au début de l'insertion, après quoi l'activité utérine tend à se stabiliser. L'échelle de contractilité de l'utérus était généralement la suivante: DIU-Cu > DIU-SS > DIU-LNG-Cu > DIU-LNG. La mesure des prostaglandines, déterminées par RIA, a indiqué que les concentrations de PGF2α et E2 dans le groupe de lapines munies de DIU SS et Cu étaient, au début de l'insertion, plus fortes que dans le groupe témoin, ce qui n'était plus le cas après quatre mois d'utilisation. Nos résultats laissent penser que l'hyperactivité de l'utérus pendant la période suivant immédiatement l'insertion du DIU peut avoir un rapport avec les effects secondaires tels que l'expulsion et les douleurs. Le cuivre libéré par les DIU au cuivre stimule l'activité utérine, en partie du fait de la teneur accrue en PGF2α et E2. Chez les lapines qui portaient des dispositifs au LNG ou au cuivre, les niveaux aussi bien de PGF2α et de E2 étaient faibles. On a également constaté dans ces deux groupes des activités mécaniques et électriques relativement faibles. Ces résultats ont ammené à conclure qu'une mise au point élaborée des DIU LNG-cu est réalisable en vue d'en réduire l'expulsion.
Resumen
La actividad miométrica, los niveles de PGF2α y E2 en los accesos vasomotores uterinos fueron medidos en conejas antes y después de la colocación de cuatro tipos de dispositivos intrauterinos. Los resultados demostraron que los DIU pueden aumentar la contracción uterina al principio de la colocación, después de lo cual la actividad uterina tiende a estabilizarse. La escala de contractilidad del útero era generalmente la siguiente: DIU-Cu > DIU-SS > DIU-LNG-Cu > DIU-LNG. La medición de las prostaglandinas, determinadas por RIA, indicó que las concentraciones de PGF2α y E2 en el grupo de conejas con DIU SS y Cu eran, en el momento de la colocación, mayores que en el grupo testigo, no siendo más así después de cuatro meses de utilización. Nuestros resultados sugirieron que la hiperactividad del útero durante el período inmediatamente posterior a la colocación del DIU puede estar relacionada con efectos secundarios tales como expulsión y dolores. El cobre descargado por los DIU estimula la actividad uterina, en parte por el hecho de aumentar los niveles de PGF2α y E2. En las conejas con dispositivos de LNG o cobre, los niveles tanto de PGF2α como de E2 eran bajos. Se observaron asimismo en estos dos grupos actividades mecánicas y eléctricas relativamente bajas. Estos resultados llevaron a la conclusión de que el desarrollo de DIU de LNG-Cu es factible para reducir la expulsión.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
TatumH.J. and ConnellE.B. (1986). A decade of intrauterine contraception: 1976 to 1986.Fertil. Steril.,46, 173–192.
MishellD.R.Jr. (1984). Intrauterine device.Clin. Obstet. Gynecol.,11, 679–700.
KurzK.H. (1981). Avoidance of the dimensional incompatibility as the main reason for side effects in intrauterine contraception.Contracept. Deliv. Syst.,2, 21–29
MyattL. (1975). Macrophages on intrauterine contraceptive devices produce prostaglandins.Nature,257, 227–228
HagenfeldtK. (1987). The role of prostaglandins and allied substances in uterine haemostasis.Contraception,36, 23–35
ZipperJ.A., TatumH.J., PasteneL., MedelM. and RiveraM. (1969). Metallic copper as an intrauterine contraceptive adjunct to the ‘T’ device.Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 105, 1274–1278
VerhoeffA., GarfieldR.E., RamondtJ. and WallenburgH.C.S. (1985). Electrical and mechanical uterine activity and gap junctions in peripartal sheep.Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol.,153, 447–456
WildemeerschD., Van DerPasH., ThieryM., VanKetsH., ParewijckW. and DelbargeW. (1988). The Copper-Fix (Cu-Fix): a new concept in IUD technology.Adv. Contracept.,4, 1–9
El-SahwiS., ToppozadaM., KamelM., GaweeshS., RiadW., IbrahimI. and El-SabbaghH. (1987). Prostaglandins and cellular reaction in uterine flushings I. Effect of IUD insertions.Adv. Contracept.,30, 291–302
ChuH.D. (1982).Pharmacology of Steroid, P.H. Print, Beijing, pp. 216–233
Tang, D.C. and Wu, X.R. The effect of cupric ions and levonorgestrel on human myometrium.Acta Univ. Med. Tongji, submitted
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, D.C., Wu, X.R. Dynamic changes of myometrial activity, levels of PGF2α and E2 in rabbits after insertion of four types of IUDs. Adv Contracept 7, 29–38 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01850716
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01850716