Summary
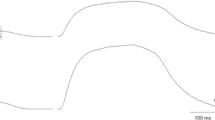
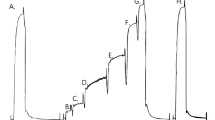
Isometric and isotonic contractions of three muscles in the rat hind leg (soleus, extensor digitorum longus (EDL) and peroneus longus (PL)) were recordedin situ at 35° C and with nerve stimulation. Additionally, the histochemical muscle fibre-type composition of the three muscles was determined by the method of Guth and Samaha (1970). The data obtained from soleus and EDL muscles were similar to those reported in previous studies. On the basis of twitch contraction time, rate of rise of tetanic tension and maximum shortening velocity, the contraction speed of EDL was 2–3 times higher than in soleus. In the PL muscle, the twitch contraction time, rate of tension rise and shortening velocity were 17 ms, 30Po/s and 12 muscle fibre lengths/s, respectively; the data showed that the contraction speed of PL muscle was intermediate between that of the soleus and EDL muscles. In the case of soleus, more than 75% of the cross-sectional area was occupied by type 1 (slow) fibres; in both EDL and PL muscles more than 90% of the area was occupied by type 2 (fast fibres). However, the two fast muscles (EDL and PL) had different proportions of type 2B fibres; the area occupied by the type 2B fibre complement was less than 5% in PL, whereas it was around 70% in EDL muscle. The differences in shortening velocity and force—velocity relation among the three muscles could be explained on the basis of their respective muscle fibre-type compositions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armstrong, R. B. &Phelps, R. O. (1984) Muscle fiber type composition of the rat hind limb.Amer. J. Anat. 171, 259–72.
Bárány, M. (1967) ATPase activity correlated with speed of muscle shortening.J. Gen. Physiol. 50, 197–218.
Brooke, M. H. &Kaiser, K. K. (1970) Three myosin adenosine triphosphate systems: the nature of their pH lability and sulfhydryl dependence.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 18, 670–2.
Brooke, M. H. &Kaiser, K. K. (1974) The use and abuse of muscle histochemistry.Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 228, 121–44.
Brooke, M. H., Williamson, E. &Kaiser, K. K. (1971) The behaviours of four fiber types in developing and reinnervated muscle.Arch. Neurol. 25, 360–6.
Buller, A. J., Kean, C. J. C. &Ranatunga, K. W. (1987) Transformation of contraction speed in muscle following cross-reinnvervation; dependence on muscle size.J. Musc. Res. Cell Motil. 8, 504–16.
Buller, A. J. &Lewis, D. M. (1965) The rate of tension development in isometric tetanic contractions of mammalian fast and slow skeletal muscles.J. Physiol. 176, 337–54.
Buller, A. J. &Pope, R. (1977) Plasticity in mammalian skeletal muscle.Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc. B,278, 295–305.
Burke, R. E., Levine, D. N., Tsairis, P. &Zajac, F. E. (1973) Physiological types and histochemical profiles in motor units of cat gastrocnemius.J. Physiol. 234, 723–48.
Cecchi, G., Colomo, F. &Lombardi, V. (1978). Force—velocity relation in normal and nitrate treated frog single muscle fibres during rise of tension in an isometric tetanus.J. Physiol. 285, 257–73.
Claflin, D. R. &Faulkner, J. A. (1985) Shortening velocity extrapolated to zero load and unloaded shortening velocity of whole rat skeletal muscle.J. Physiol. 359, 357–63.
Claflin, D. R. &Faulkner, J. A. (1989) The force—velocity relationship at high shortening velocities in the soleus muscle of the rat.J. Physiol. 411, 627–37.
Close, R. (1964) Dynamic properties of fast and slow skeletal muscles of the rat during development.J. Physiol. 173, 75–95.
Close, R. (1967) Properties of mortor units in fast and slow skeletal muscles of the rat.J. Physiol. 193, 45–55.
Close, R. (1969) Dynamic properties of fast and slow skeletal muscles of the rat after nerve cross-union.J. Physiol. 204, 331–46.
Close, R. (1972). Dynamic properties of mammalian skeletal muscles.Physiol. Rev. 52, 129–97.
Dalla Libera, L., Sartore, S., Pierobon-Bormioli, S. &Schiaffino, S. (1980). Fast-white and fast-red isomyosins in guinea pig muscles.Biochem Biophys. Res. Comm. 96, 1662–70.
Donselaar, Y., Eerbeek, O., Kernell, D. &Verhey, B. A. (1987) Fibre sizes and histochemical staining characteristics in normal and chronically stimulated fast muscle of cat.J. Physiol. 382, 237–54.
Eddinger, T. J., Moss, R. L. &Cassens, R. G. (1985) Fiber number and type composition in EDL, soleus and diaphragm muscle with ageing in Fisher 344 rats.J. Histochem Cytochem. 33, 1033–41.
Elmubarak, M. H. &Ranatunga, K. W. (1984) Temperature sensitivity of tension development in a fast twitch muscle of the rat.Muscle Nerve,7, 298–303.
Elmubarak, M. H. &Ranatunga, K. W. (1988) Differentiation of fast and slow muscles in the rat after neonatal denervation: a physiological study.J. Musc. Res. Cell Motil. 9, 219–32.
Greaser, M. L., Moss, R. L. &Reiser, P. J. (1988) Variations in contractile properties of rabbit single muscle fibres in relation to troponin T isoforms and myosin light chains.J. Physiol. 406, 85–98.
Guth, L. &Samaha, F. J. (1970) Research note. Procedure for the histochemical demonstration of actomyosin ATPase.Exp. Neurol. 28, 365–7.
Hill, A. V. (1938) The heat of shortening and the dynamic constants of muscle.Proc. Roy. Soc. B 126, 136–95.
Hill, A. V. (1949) The abrupt transition from rest to activity in muscle.Proc. Roy. Soc. B 136, 399–420.
Jewell, B. R. &Wilkie, D. R. (1958) An analysis of mechanical components in frog's striated muscle.J. Physiol. 143, 515–40.
Josephson, R. K. &Edman, K. A. P. (1988) The consequences of fibre heterogeneity on the force-velocity relation of skeletal muscle.Acta. Physiol. Scand. 132, 341–52.
Julian, F. J., Rome, L. C., Stephenson, D. G. &Stritz, S. (1986) The maximum speed of shortening in living and skinned frog muscle fibres.J. Physiol. 370, 181–99.
Lucas, S. M., Ruff, R. L. &Binder, M. D. (1987) Specific tension measurements in single soleus and medial gastrocnemius muscle fibers of the cat.Exp. Neurol. 95, 142–54.
Ranatunga, K. W. (1977) Changes produced by chronic denervation in the temperature dependent isometric contractile characteristics of rat fast and slow twitch skeletal muscles.J. Physiol. 273, 255–262.
Ranatunga, K. W. (1982) Temperature dependence of shortening velocity and rate of isometric tension development in rat skeletal muscle.J. Physiol. 329, 465–83.
Ranatunga, K. W. (1984) The force—velocity relation of rat fast- and slow-twitch muscles examined at different temperatures.J. Physiol. 351, 517–29.
Ranatunga, K. W. &Thomas, P. E. (1988) A lever system for recording shortening and tension development in rat muscle.J. Physiol. 401, 9P.
Ranatunga, K. W. &Thomas, P. E. (1989) Contraction characteristics of peroneus longus muscle in the anaesthetized rat.J. Physiol. 412, 48P.
Sacks, R. D. &Roy, R. R. (1982) Architecture of the hind limb muscles of cats: functional significance.J. Morphol. 173, 185–95.
Schiaffino, S., Ausoni, S., Gorza, L., Saggin, L., Gundersen, K. &Lomo, T. (1988) Myosin heavy chain isoforms and velocity of shortening of type 2 skeletal muscle fibres.Acta. Physiol. Scand. 134, 575–6.
Schiaffino, S., Saggin, L., Viel, A., Ausoni, S., Sartore, S. &Gorza, L. (1986) Muscle fiber types identified by monoclonal antibodies to myosin heavy chains. InBiochemical Aspects of Physical Exercise (edited byBenzi, G., Packer, L. &Siliprandi, N.), pp. 27–34. Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Sweeney, H. L., Kushmerick, M. J., Mabuchi, K., Gergely, J. &Sréter, F. A. (1986) Velocity of shortening and myosin isoenzymes in two types of rabbit fast-twitch muscle fibers.Amer. J. Physiol. 251, C431–4.
Sweeney, H. L., Kushmerick, M. J., Mabuchi, K., Sréter, F. A. &Gergely, J. (1988) Myosin alkali light chain and heavy chain variations correlate with altered shortening velocity of isolated skeletal muscle fibers.J. Biol. Chem. 263, 9034–9.
Wells, J. B. (1965) Comparison of mechanical properties between slow and fast mammalian muscles.J. Physiol. 178, 252–69.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ranatunga, K.W., Thomas, P.E. Correlation between shortening velocity, force—velocity relation and histochemical fibre-type composition in rat muscles. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 11, 240–250 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01843577
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01843577